Summary
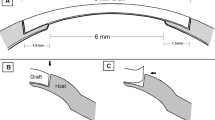
Introduction: The correction of low to moderate astigmatism is possible today by means of photoablation (PRK), while the treatment of moderate and higher astigmatism still involves refractive keratotomy. Experience has shown that cataract surgery, using modern tunnel techniques with self-healing incisions, results in earlier stability in both the refractive outcome and wound healing. In this study, we attempted to combine the advantages of lamellar keratotomy with those of a pair-wise T-incision as arcuate lamellar keratotomy (ALK).
Patients and methods: The clinical outcome of 41 patients who underwent ALK was investigate in a prospective study over a period of 3 years. The pre- and postoperative investigations undertaken included the measurement of astigmatism using a Zeiss keratometer, uncorrected visual acuity, and corrected glare vision using a Humphrey autorefractor. All patients had astigmatism between 2.0 and 7.0 D. Together with a uniform arcuate incision, we used 7 mm (n = 26) and 8 mm (n = 15) mm zones for correction.
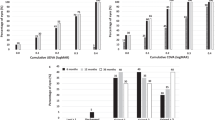
Results: The average preoperative astigmatism was 4.01 ± 1.90 (median, 3.50) D. After a 3-year follow-up the average postoperative astigmatism was 1.59 ± 1.29 (median, 1.38) D. The astigmatic change induced (Jaffé) after 3 years was about 3.23 ± 2.23 (median, 3.16) D. The average uncorrected visual acuity (log MAR) before ALK was 0.20 ± 0.12 (median, 0.22) and after follow-up, 0.41 ± 0.14 (median, 0.39). Corrected glare vision before surgery was 0.23 ± 0.19 (median, 0.10) and afterwards, 0.25 ± 0.22 (median, 0.14).
Conclusions: Arcuate lamellar keratomy (ALK) stood the test as a routine clinical procedure for correction of moderate astigmatism with stable postoperative functional outcomes. We did not find impairment of glare vision following this procedure.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund: Während geringe bis mäßige Astigmatismuskorrekturen heute bereits photoablativ mit gutem Erfolg durchgeführt werden können, erfordert die Korrektur mittlerer und höherer Astigmatismen nach wie vor den Einsatz refraktiver Keratotomien. Bei Verwendung heute üblicher Tunneltechniken mit selbstschließenden Inzisionen kann durch die lamellierende Präparation sowohl eine frühere postoperative Stabilisierung der Refraktion, als auch eine hohe mechanische Stabilität erreicht werden. Wir versuchten, die Vorteile dieser lamellierenden Technik mit der refraktiven Wirkung einer paarigen T-Inzision in der bogenförmigen lamellierenden Keratotomie (BLK) zu kombinieren.
Patienten und Methode: Wir untersuchten prospektiv die klinischen Langzeitergebnisse (prä- und postoperativ: mit Zeiss-Ophthalmometer gemessener Astigmatismus, sc-Visus sowie cc-Blendungsvisus ‚Humphrey’-Autorefraktor) nach BLK von 41 Patienten bei durchschnittlich 3-jähriger Nachbeobachtungszeit. Alle Patienten wiesen vor BLK einen Astigmatismus von mind. 2,0 bis max. 7,0 dpt auf. Wir verwendeten bei der Korrektur 7- (n = 26) und 8- (n = 15) mm-Zonen, sowie eine einheitliche Bogenlänge von 3 mm. Alle Inzisionen wurden paarweise durchgeführt.
Ergebnisse: Der durchschnittliche, präoperative mit dem Zeiss-Ophthalmometer gemessene Astigmatismus betrug 4,01 ± 1,90 (Median 3,50) dpt. Nach einer Nachbeobachtungszeit von durchschnittlich 3 Jahren betrug der postoperative Astigmatismus im Mittel 1,59 ± 1,29 (Median 1,38) dpt. Die induzierte vektoranalytische Astigmatismusänderung betrug nach 3 Jahren 3,23 ± 2,23 (Median 3,16) dpt. Der ohne Korrektur erzielte Visus (log MAR) betrug präoperativ 0,20 ± 0,12 (Median 0,22) und nach durchschnittlich 3 Jahren 0,41 ± 0,14 (Median 0,39) dpt. Der Blendvisus betrug präoperativ mit Korrektur 0,23 ± 0,19 (Median 0,10) dpt und postoperativ 0,25 ± 0,22 (Median 0,14) dpt.
Schlußfolgerungen: Die bogenförmige lamellierende Keratotomie (BLK) hat sich bei mäßiggradigen Astigmatismen auch in den Langzeitergebnissen als refraktives Verfahren mit stabilen postoperativen Refraktionsergebnissen bewährt. Eine Reduktion des Blendvisus konnte nicht festgestellt werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nordwald, K., Anders, N., Walkow, T. et al. A prospective study investigating the long-term stability of changes in astigmatism following arcuate lamellar keratotomy (ALK): 3-year results. Ophthalmologe 96, 453–458 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003470050436
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003470050436