Summary
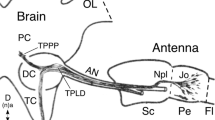
The peripheral nerves of the suboesophageal ganglion of the locust,Locusta migratoria have been investigated with respect to their innervation by dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurons. The DUM neuron supply of the suboesophageal periphery was found to be strikingly sparse: No segmental DUM neurons could be found in all three mouthpart segments. While in the mandibular segment DUM neuron innervation appears to be missing entirely, both the maxillary and the labial peripheral nerves are supplied by a single, intersegmentally projecting prothoracic DUM neuron.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DUM :
-
dorsal unpaired median
References
Altman JS, Kien J (1979) Suboesophageal neurons involved in head movements and feeding in locusts. Proc R Soc Lond B 205:209–227
Bacon JP, Altman JS (1977) A silver intensification method for cobalt-filled neurons in wholemount preparations. Brain Res 138:359–363
Bate M, Goodman CS, Spitzer NC (1981) Embryonic development of identified neurons: segment-specific differences in the H cell homologues. J Neurosci 1:103–106
Boyan GS, Altman JS (1985) The suboesophageal ganglion: a ‘missing link’ in the auditory pathway of the locust. J Comp Physiol A 156:413–428
Bräunig P (1982) The peripheral and central nervous organization of the locust coxo-trochanteral joint. J Neurobiol 13:413–433
Bräunig P (1987a) The satellite nervous system — an extensive neurohemal network in the locust head. J Comp Physiol A 160:69–77
Bräunig P (1987b) Serotonin-immunoreactive neurosecretory cells of the locust suboesophageal ganglion. In: Elsner N, Creutzfeldt O (eds) New frontiers in brain research. Thieme, Stuttgart, p 254
Brogan RT, Pitman RM (1981) Axonal regeneration in an identified insect motoneurone. J Physiol 319:34P-35P
Christensen TA, Carlson AD (1982) The neurophysiology of larval firefly luminescence: Direct activation through four bifurcating (DUM) neurons. J Comp Physiol 148:503–514
Clements AN, May TE (1974) Studies on locust neuromuscular physiology in relation to glutamic acid. J Exp Biol 60:673–705
Crossman AR, Kerkut GA, Pitman RM, Walker RJ (1971) Electrically excitable nerve cell bodies in the central ganglia of two insect speciesPeriplaneta americana andSchistocerca gregaria. Investigation of cell geometry and morphology by intracellular dye injection. Comp Biochem Physiol 40A:579–594
Davis NT (1987) Neurosecretory neurons and their projections to the serotonin neurohemal system of the cockroachPeriplaneta americana (L.), and identification of mandibular and maxillary motor neurons associated with this system. J Comp Neurol 259:604–621
Davis NT, Alanis J (1979) Morphological and electrophysiological characteristics of a dorsal unpaired median neuron of the cricket,Acheta domesticus. Comp Biochem Physiol 62A:777–788
Doe CQ, Goodman CS (1985) Early events in insect neurogenesis. I. Development and segmental differences in the pattern of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol 111:193–205
Elepfandt A (1980) Morphology and output coupling of wing muscle motoneurons in the field cricket. Zool Jb Physiol 84:26–45
Evans PD, O'Shea M (1977) An octopaminergic neurone modulates neuromuscular transmission in the locust. Nature 270:257–259
Evans PD, O'Shea M (1978) The identification of an octopaminergic neurone and the modulation of a myogenic rhythm in the locust. J Exp Biol 73:235–260
Goodman CS, Spitzer NC (1979) Embryonic development of identified neurons: differentiation from neuroblast to neurone. Nature 280:208–214
Goodman CS, Spitzer NC (1981a) The mature electrical properties of identified neurones in grasshopper embryos. J Physiol 313:369–384
Goodman CS, Spitzer NC (1981b) The development of electrical properties of identified neurones in grasshopper embryos. J Physiol 313:385–403
Goodman CS, Bate M, Spitzer NC (1981) Embryonic development of identified neurons: origin and transformation of the H cell. J Neurosci 1:94–102
Heitler WJ, Goodman CS (1978) Multiple sites of spike initiation in a bifurcating locust neurone. J Exp Biol 76:63–84
Honegger HW, Altman JS, Kien J, Müller-Tautz R, Pollerberg E (1984) A comparative study of neck muscle motor neurons in a cricket and a locust. J Comp Neurol 230:517–535
Hoyle G (1978) The dorsal, unpaired, median neurones of the locust metathoracic ganglion. J Neurobiol 9:43–57
Hoyle G, Dagan D (1978) Physiological characteristics and reflex activation of DUM (octopaminergic) neurons of locust metathoracic ganglion. J Neurobiol 9:59–79
Kutsch W, Schneider H (1987) Histological characterization of neurones innervating functionally different muscles ofLocusta. J Comp Neurol 261:515–528
Lange AB, Orchard I (1984) Dorsal unpaired median neurons, and ventral bilaterally paired neurons, project to a visceral muscle in an insect. J Neurobiol 15:441–453
Pflüger HJ, Watson AHD (1988) The structure and distribution of dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurones in the abdominal nerve cord of male and female locusts. J Comp Neurol 268:329–345
Tyrer NM, Gregory GE (1982) A guide to the neuroanatomy of locust suboesophageal and thoracic ganglia. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 297:91–123
Watson AHD (1984) The dorsal unpaired median neurons of the locust metathoracic ganglion: neuronal structure and diversity, and synapse distribution. J Neurocytol 13:303–327
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bräunig, P. Identification of a single prothoracic ‘dorsal unpaired median’ (DUM) neuron supplying locust mouthpart nerves. J. Comp. Physiol. 163, 835–840 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00604060
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00604060