Abstract
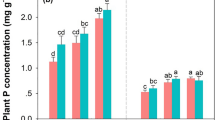
This paper describes a field study to assess the effect of increasing the frequency of split applications of N fertiliser on the pattern of plant uptake, soil N availability, and microbial biomass C and N. Measurements were taken during the growing season in different positions relative to young trees (Prunus avium L.) in an upland silvopastoral system in its first year after establishment. At fertiliser rates of 72 and 144 kg ha-1 N applied as NH4NO3, increasing the number of split applications increased N uptake by the pasture. Mineral forms of soil N measured 2 weeks after application indicated that residual NH sup+inf4 -N and total mineral N were also greater in this treatment on certain dates. Soil NO sup-inf3 -N was positively correlated with the soil moisture content, and nitrification reached a maximum in early May and declined rapidly thereafter except within the herbicide-treated areas around the trees where soil moisture had been conserved. Results of the study suggest that high NO sup-inf3 -N in herbicide-treated areas was probably caused by mineralisation of grass residues and low uptake by the tree rather than by preferential urine excretion by sheep sheltering beside the trees. Mean microbial biomass C and N values of 894 and 213 kg ha-1, respectively, were obtained. Microbial C was slightly increased by the higher frequency of split applications at 144 kg ha-1 N and was probably related to the greater herbage production with this treatment. Microbial N was not significantly affected by the N treatments. Both microbial biomass C and N increased during the growing season, resulting in the net immobilisation of at least 45 kg ha-1 N which was later released during the autumn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams TMcM, Adams SN (1983) The effects of liming on soil pH and carbon contained in the soil biomass. J Agric Sci 101:553–558
Arnold GW, Dudzinski ML (1978) Ethology of free-range domestic animals. Developments in Animal Veterinary Science 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Aronsson A, Elowsson S (1980) Effects of irrigation and fertilisation on mineral nutrients in Scots pine needles. Ecol Bull (Stockholm) 32:219–228
Bristow AW, Jarvis SC (1991) Effects of grazing and nitrogen fertiliser on the soil microbial biomass under permanent pasture. J Sci Food Agric 54:9–21
Bristow AW, Ryden JC, Whitehead DC (1987) The fate at several time intervals of 15N-labelled ammonium nitrate applied to an established grass sward. J Soil Sci 38:245–254
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Campbell CD (1989) The importance of root interactions for grass and trees in a sivopastoral system. Aspects Appl Biol 22:255–261
Campbell CD, Atkinson D, Jarvis PG, Newbould P (1994) Effects of nitrogen fertiliser on tree/pasture competition during the establishment phase of a silvopastoral system. Ann Appl Biol 124:83–96
Chapman SJ (1987) Inoculum in the fumigation method for soil biomass determination. Soil Biol Biochem 19:83–87
Cuttle SP, Gill EK (1991) Concentrations of nitrate in soil water following herbicide treatment of tree planting positions in an upland agroforestry system. Agrofor Syst 13:225–234
Frame J (1981) Herbage mass. In: Hodgson J, Baker RD, Davies A, Laidlaw AS, Leaver JD (eds) Sward measurement handbook. Br Grassland Soc, pp 39–70
Hodgson J, Mackie CK, Parker JWG (1986) Sward surface heights for efficient grazing. Grass Farmer 24:5–10
Houot S, Chaussod R, Hounemenou C, Barriuso E, Bourgeois S (1991) Differences induced in the soil organic matter characteristics and microbial activity by various management practices in long term field experiments. In: Berthelin J (ed) Diversity of environmental biogeochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 435–442
Ingestad T (1987) New concepts on soil fertility and plant nutrition as illustrated by research on forest trees and stands. Geoderma 40:237–252
Ingestad T (1988) A fertilisation model based on the concepts of nutrient flux density and nutrient productivity. Scand J For Res 3:157–173
Jarvis SC, Barraclough D (1991) Variation in mineral nitrogen under grazed grassland swards. Plant and Soil 138:177–188
Jenkinson DS, Powlson DS (1976) The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil V. A method for measuring soil biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 8:209–213
Miller MG (1981) Forest fertilisation: Some guiding concepts. Forestry 54:157–167
Miller RD, Johnson DD (1964) The effect of soil moisture tension on carbon dioxide evolution, nitrification and nitrogen mineralisation. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 28:644–647
Patra DD, Brookes PC, Coleman K, Jenkinson DS (1990) Seasonal changes of soil biomass in an arable and a grassland soil which have been under uniform management for many years. Soil Biol Biochem 22:739–742
Prins WH (1980) Changes in quantity of mineral nitrogen in three grassland soils as affected by intensity of nitrogen fertilisation. Fert Res 1:51–63
Ross DJ (1987) Soil microbial biomass estimated by the fumigationincubation procedure: Seasonal fluctuations and influence of soil moisture content. Soil Biol Biochem 19:397–404
Ross DJ (1988) Modifications to the fumigation procedure to measure microbial biomass C in wet soils under pasture: Influence on estimates of seasonal fluctuations in the soil biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 20:377–383
Sarathchandra SU, Perrot KW, Boase MR, Waller JE (1988) Seasonal changes and the effects of fertilizer on some chemical, biochemical and microbiological characteristics of high-producing pastoral soil. Biol Fertil Soils 6:328–335
Sparling GP, West AW (1988a) A direct extraction method to estimate soil microbial C: Calibration in situ using microbial respiration and 14C-labelled cells. Soil Biol Biochem 20:337–343
Sparling GP, West AW (1988b) Modifications to the fumigation-extraction technique to permit simultaneous extraction and estimation of soil microbial C and N. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19:327–344
Tamm CO (1968) An attempt to assess the optimum nitrogen level in Norway spruce under field conditions. Stud For Suec 61:1–67
Thomas RJ, Logan KAB, Ironside AD, Milne JA (1986) Fate of sheep urine-N applied to an upland grass sward. Plant and Soil 91:425–427
Thomas RJ, Logan KAB, Ironside AD (1988) Transformations and fate of sheep urine-N applied to an upland UK pasture at different times during the growing season. Plant and Soil 107:173–181
Van Veen JA, Merckx R, Van de Geijn SC (1989) Plant and soil related controls on the flow of carbon from roots through the soil microbial biomass. Plant and Soil 115:179–188
Wardle DA (1992) A comparative assessment of the factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil Biol Rev 67:321–358
Watson CA, Bodeux C, Birley MA, Newbould P, Hooker JE, Atkinson D, Nixon CJ (1991) The effect of ground vegetation management in agri-forestry systems on tree growth and environmental impact. In: Brighton Crop Protection Conference. Weeds, 1991. British Crop Protection Council, Farnham, 2:631–638
White RE, Haigh RA, Macduff JH (1987) Frequency distributions and spatially dependent variability of ammmonium and nitrate concentrations in soil under grazed and ungrazed grassland. Fert Res 11:193–208
Whitehead DC, Briston AW, Lockyer DR (1990) Organic matter and nitrogen in the unharvested fractions of a grass sward in relation to the potential for nitrate leaching after ploughing. Plant and Soil 123:39–49
Williams BL, Wheatley RE (1992) Mineral nitrogen dynamics in poorly drained blanket peat. Biol Fertil Soils 3:96–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell, C.D., Chapman, S.J. & Urquhart, F. Effect of nitrogen fertiliser on temporal and spatial variation of mineral nitrogen and microbial biomass in a silvopastoral system. Biol Fertil Soils 19, 177–185 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336156
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336156