Abstract
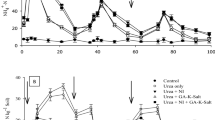
Some of the measures suggested for amelioration of drought effects include application of N fertilizer and plant growth regulators (PGRs). Since N2-fixing bacteria produce plant growth substances (PGRs), the effect of foliar application of an active strain of Klebsiella sp. (KUPOS) on IR-50 rice was examined using three foliar sprays applied at 10-day intervals. Irrigation once every 3 days was essential for plant growth. Application of KUPOS and 40 kg N ha-1 improved grain yield of acutely water stressed plants from 330 kg ha-1 to more than 1300 kg ha-1 along with an improvement in several growth variables and yield determinants. Indole acetic acid, kinetin and GA3, in a mixture of 10-4 M of each, were less effective than KUPOS in alleviating stress effects. The adverse effects of water stress on respiration and photosynthesis as indicated by CO2 exchange were also alleviated by these treatments. While uptake of K, Mg, Ca, Fe and Mo was increased, Na content decreased, accompanied by an increase in proline content. The order of effectiveness of the treatments was 40 kg N ha-1 >KUPOS>PGRs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal GS, Sidhu AS, Singh NT (1987) Effect of periodic moisture stress at different fertilizer levels on rice. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 35:280–281
Amon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bashan Y (1990) Current status of Azospirillum inoculation technology: Azospirillum inoculation technology: Azospirillum as a challenge for agriculture. Can J Microbiol 36:591–608
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress. Plant and Soil 39:205–207
Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (1975) Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Fiske CH, Subba Row Y (1925) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem 66:375–400
Garg BK, Vyas SP, Kathju S, Lahiri AN (1984) Influence of repeated water stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum cultivar Kalyansona). Proc Indian Acad Sci B Plant Sci 93:477–484
Humphries EC (1956) Mineral components and ash analysis. In: Paech K, Tracy MV (eds) Modern methods of plant analysis, vol 1. Springer, Heidelberg Berlin New York, pp 487–450
Karmokar JL (1984) Hormonal regulation of ion transport in plants. In: Purohit SS (ed) Hormonal regulation of plant growth and development. Agro Botanical Publishers Bikaner India, pp 219–264
Kathju S, Vyas SP, Grag BK, Lahiri AN (1990) Fertility induced improvements in performance and metabolism of wheat under different intensities of water stress. In: Sinha SK, Sane PV, Bhargva SC, Agarwal PK (eds) Proc Intern Cong Plant Physiol, vol 2. Society of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, New Dehli, pp 854–858
Kramer PJ (1969) Plant and soil water relationships: a modern synthesis. McGraw-Hill, New York
Lahiri AN, Singh S (1970) Studies on plant water relationship V: Influence of soil moisture on plant performance and nitrogen status of the shoot tissue. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad B Plant Sci 36:112–125
Leopold AC, Kriedemann PE (1975) Plant growth and development, Tata, McGraw-Hill, New Dehli
Luna M, Maurizio B, Marcella F, Franca A, Giovanni GS (1985) Selective enzymes inactivation under water stress in maize (Zea mays) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 25:153–156
Maidebura EV, Chernyadey II, Kosakoskaya IV (1989) Change in the level of abscisic acid and activity of RuPBCase in different varieties of Triticum aestivum L. under water stress (in Russian). Dokl Akad Nauk Ukr SSRB Geol Khim Biol Nauki O:65–68
Maitra N, Sen SP (1987) Variations in photosynthetic activities of tissues and chloroplasts of leaves and non-leaf green organs of grasses. Photosynthetica 21:515–524
Nilokskaya NT, Morozova EV, Moiseeva TV, Moiseeva AD (1988) The effect of kinetin and nitrogen levels on the productivity and photosynthetic activity of spring wheat in soil drought (in Russian). Dokl Vses Ordena Lenina trud Krasno GO Znamenl Akad-S-Kh Nauk im Vilenima 0:7–10
Postgate JR (1982) The fundamentals of nitrogen fixation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Quarrie SA (1989) Abscisic acid as a factor in modifying drought resistance. In: Cherry JH (ed) Environmental stress in plants: biological and physiological mechanisms. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 27–37
Sharma DP, Swarup A (1989) Effect of short-term waterlogging on growth, yield and nutrient composition of wheat in alkaline soil. J Agric Sci 112:191–198
Sen SP, Maity TK, Pal D, Samanta RK, Sen M, Somchoudhury M (1986) Dinitrogen fixation in the phyllosplane and its agricultural and its agricultural and ecological implication. In: Mukerji KG, Pathak NC, SinghVP (eds) Frontiers in applied microbiology. Print House, Lucknow, pp 293–314
Sen SP (1990) Physiology of ectosymbiotic N2 fixation on the leaf surface. In: Sinha SK, Sane PV, Bhargava SC, Agarwal PK (eds) Proc Intern Congr Plant Physiol, vol 2. Society of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry New Dehli, pp 1034–1037
Veéranjaneyulu K, Ranjitakumari BD (1989) Proline metabolism during water stress in mulberry. J Exp Bot 40:581–584
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razi, S.S., Sen, S.P. Amelioration of water stress effects on wetland rice by urea-N, plant growth regulators, and foliar spray of a diazotrophic bacterium Klebsiella sp.. Biol Fertil Soils 23, 454–458 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335922
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335922