Summary
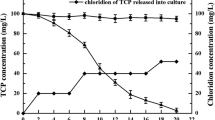
Degradation of a fungicide, 2,4,5,6-tetrachloroisophthalonitrile (TPN) in soil was studied under laboratory conditions. TPN degraded more rapidly under 60% WHC conditions than at 20%, 40% and 100% WHC, while its degradation was rapid at temperatures of 25°C-30°C, evidently due to the microbial degradation. TPN degraded mainly through dechlorination and partly a substitution reaction. The degradation products identified by gas chromatographic analyses were: 2,4,5-trichloroisophthalonitrile (abbreviated as 2,4,5-Cl3-IPN), 2,4,6-Cl3-IPN, 2,4-Cl2-lPN, 2,5-Cl2-IPN, 4-Cl-IPN, 5-Cl-IPN, IPN, 2,5,6-Cl34-(OH)-IPN and 2,5,6-Cl3-4-(OCH3)-IPN. Peaks with longer retention times than that of TPN were not identified. Tentative degradation pathways were proposed on the basis of the identified degradation products. About 90% of the bacterial strains isolated from the soil to which TPN had been added degraded TPN, suggesting enrichment of the soil with TPN-degrading bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audus LJ (1950) Biological detoxication of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in soil: isolation of an effective organism. Nature 166:365
Chu JP, Kirsch EJ (1972) Metabolism of pentachlorephenol by an axenic bacterial culture. Appl Microbiol 23:1033–1035
Ferris IG, Lichtenstein EP (1980) Interactions between agricultural chemicals and soil microflora and their effects on the degradation of [14C] parathion in a cranberry soil. A Agr Food Chem 28:1011–1019
Harrigan WF, McCance ME (1966) Laboratory methods in microbiology. Academic Press, London, pp 1–68
Hill IR, Wright SJL (1978) The behavior and fate of pesticides in microbial environments. In: Hill IR, Wright SJL (eds) Pesticide microbiology. Academic Press, London, pp 79–136
Hiltbold AE (1974) Persistence of pesticides in soil. In: Guenzi WD (ed) Pesticide in soil and water. Soil Sci Soc Am Inc, Madison, Wisconsin, pp 203–222
Kunc F, Rybăřovă J (1983) Mineralization of carbon atoms of14C-2,4-D side chain and degradation ability of bacteria in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 15:141–144
Kuwatsuka S (1977) Studies on the fate and behavior of herbicides in soil and plant. J Pest Sci 2:201–213
MacRae IC, Raghu K, Bautista EM (1969) Anaerobic degradation of insecticide lindane byClostridium sp. Nature 221:859–860
Naik MN, Jackson RA, Stokes J, Swaby RJ (1972) Microbial degradation and phytotoxicity of picloram and other substituted pyridines. Soil Biol Biochem 4:313–323
Ottow, JCG (1985) Pesticides — contamination, self-purification, and fertility of soils. Plant Res Dev 21:7–26
Ozaki M, Hayase Y, Kobayashi S, Kuwatsuka S (1984) Degradation pathways of Isouron by soil perfusion and isolated yeast. J Pest Sci 9:285–291
Patil K, Matsumura F, Boush GM (1970) Degradation of endrin, dieldrin and DDT by soil microoganisms. Appl Microbiol 19:879–881
Rosenberg A, Alexander M (1980) Microbial metabolism of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid in soil, soil suspensions, and axenic culture. J Agric Food Chem 28:297–302
Rott B, Nitz S, Korte F (1979) Microbial decomposition of sodium pentachlorophenol. J Agric Food Chem 27:306–310
Sethunathan N, Bautista EM, Yoshida T (1969) Degradation of benzene hexachloride by a soil bacterium. Can J Microbiol 15:1349–1354
Sethunathan N, Yoshida T (1973) AFlavobacterium sp. that degrades diazinon and parathion. Can J Microbiol 19:873–875
Sethunathan N (1973) Microbial degradation of insecticides in flooded soil and anaerobic cultures. Res Rev 47:143–165
Stanlake GJ, Finn RK (1982) Isolation and characterization of a pentachlorophenol degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1421–1427
Stenerson JHB (1965) DDT metabolism in resistant and susceptible stable flies and bacteria. Nature 207:660–661
Torstensson L (1980) Role of microorganisms in decomposition. In: Hance RJ (ed) Interaction between herbicides and the soil. Academic Press, London, pp 158–178
Weiss UM, Scheunert I, Klein W, Korte F (1982) Fate of pentachlorophenol-14C in soil under controlled conditions. J Agric Food Chem 30:1191–1194
Young HM, Kuwatsuka S (1985) Factors influencing microbial dechlorination of benthiocarb (Thiobencarb) in the soil suspension. J Pest Sci 10:523–528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Japanese International Cooperation Agency
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, K., Tanaka, H. Degradation and metabolism of a fungicide, 2,4,5,6-tetra-chloroisophthalonitrile (TPN) in soil. Biol Fert Soils 3, 205–209 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00640631
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00640631