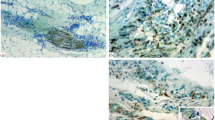
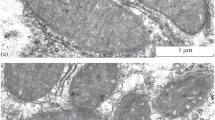
Summary
Light and electron-microscopic studies were performed on the muscles taken from 4 cases with hypokalemic periodic paralysis. The authors conclude that the earliest changes concern the sarcoplasmic reticulum: vacuolisation of the longitudinal system and probably, multiplication of the transverse system. It is suggested, that vacuoles are formed as a result of fusion of the vesicles of the transverse system. Destruction of myofibrilles and enlargement of the interfibrillar spaces appear at a later period of the disease process. Extensive and intensive changes of that kind present a typical appearance of myogenic changes in histological study observed in the cases with clinically fixed symptomes of myopathy.
Zusammenfassung
Licht- und elektronenoptische Untersuchungen wurden an Muskelbiopsien von 4 Fällen hypokaliämischer periodischer Paralyse durchgeführt. Die frühesten Veränderungen betreffen nach Meinung der Verfasser das sarkoplasmatische Reticulum: Vacuolisierung des Längssystems und vermutlich Multiplikation des Quersystems. Es wird vermutet, daß die Vacuolenbildung die Folge einer Fusion der Vesikeln des Quersystems darstellt. Destruktion von Myofibrillen und Vergrößerung der, interfibrillären Räume treten erst in späteren Phasen des Krankheitsprozesses auf. Ausdehnung und Intensität dieser Veränderungen bedingen das typische histologische Bild myogener Läsionen bei Fällen m klinisch fixierten Symptomen der Myopathie.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleu, F. P., andA. K. Afifi: Ultrastructure of muscle in dystrophia myotonica. Amer. J. Path.45, 221–232 (1964).
Van Breemen, V. L.: Ultractructure of human muscle. Observation on dystrophic striated muscle fibres. Amer. J. Path.37, 333–341 (1960).
Engel, A. G.: Electron microscopic observations in primary hypokaliemic and thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Proc. Mayo Clin.41, 797–808 (1966).
Fisher, E. E., R. E. Cohn, andT. S. Danowski: Ultrastructural observation of skeletal muscle in myopathy and neuropathy with special reference to muscular dystrophys. Lab. Invest.15, 778–793 (1966).
Goldflam, S.: Weitere Mittheilung über paroxysmale, familiäre Lähmung. Dtsch. Z. Ner-venheilk.7:1–31 (1895).
—: Dritte Mittheilung über die paroxysmale, familiäre Lähmung. Dtsch. Z. Nervenheilk.11, 242–260 (1897)
Gruner, J. E.: Anomalies du reticulum sarcoplasmique et prolifération de tubules dans le muscle d'une paralysie periodique familial. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris)160, 193–195 (1966).
Howes, E. L., H. M. Price, C. M. Pearson, andJ. M. Blumberg: Hypokaliemic periodic paralysis. Electromicroscopic changes in the sarcoplasm. Neurology (Minneap).16, 242–256 (1966).
Klinkerfuss, G. H.: An electron microscopic study of myotonic dystrophy. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.)16, 181–193 (1967)
Mölbert, E. u.H. Marx: Elektronenmikroskopische Befunde bei Myopathien, pp. 89–103. Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1965.
Odor, D. L., A. N. Patel, andL. A. Pearce: Familial hypokaliemic periodic paralysis with permanent myopathy. J. Neuropath. exp Neurol.26, 98–114 (1967).
Oppenheim (1891): cit. afterPearson (1964).
Pearson, C. M.: The periodic paralysis: differential features and pathological observations in permanent myopathic weakness. Brain87, 341–354 (1964).
Seitelberger, F., u.L. Stockinger: Bioptische Befunde bei paroxysmaler Lähmung. 8. Internat. Kongr. Neurol., Wien, Sept. 1965, Proc. Neuromuskuläre Erkrankungen (Tom. II), pp. 607–610.
Shy, C. M., T. Wanko, P. T. Rowley, andA. G. Engel: Studies in familial periodic paralysis. Exp. Neurol.3, 53–121 (1961).
Stenger, R. J., D. Spiro, R. E. Scully, andJ. M. Shannon: Ultrastructural and physiologic alterations in ischemic skeletal muscle. Amer. J. Path.40, 1–20 (1962).
Wechsler, W. u.H. Hager: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen bei myotonischer Muskeldystrophie. Arch. Psychiat. Nervenkr.201 668–690 (1960/61).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by a Special Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biczyskowa, W., Fidziańska, A. & Jedrzejowska, H. Light and electron microscopic study of the muscles in hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Acta Neuropathol 12, 329–338 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00809129
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00809129