Summary
The Trembler mouse is a neurological mutant showing dominant inheritance. The peripheral nerves show a delay in myelination, segmental demyelination and the development of an onion bulb neuropathy.
Using electron microscopy a comparative morphometric study of nerve fibres in the sciatic nerve in normal and Trembler mice was made. The animals ranged in age from 3 days to adult.
The following features were noted:
-
1.
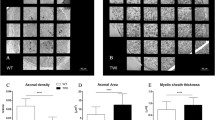
Mean axon diameters of the Trembler mice were smaller than normal at all ages.
-
2.
Myelination was delayed and myelin was thinner than normal in the Trembler mice.
-
3.
The ratio of myelin thickness to axon diameter was reduced in Trembler mice.
-
4.
There were no significant quantitative or qualitative differences observed between middle and distal levels of Trembler nerves.
The balance of evidence from these findings and the previous morphological studies is in keeping with the suggestion that the primary lesion resides in the Schwann cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers, M. M., Anderson, R. McD.: Onion bulb neuropathy in the Trembler mouse: A model of hypertrophic interstitial neuropathy (Dejerine-Sottas) in man. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)25, 54–70 (1973)
Ayers, M. M., Anderson, R. McD.: Development of onion bulb neuropathy in the Trembler mouse. Comparison with normal nerve maturation. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)32, 43–59 (1975)
Dyck, P. J., Johnson, W. J., Lambert, E. H., O'Brien, P. C.: Segmental demyelination secondary to axonal degeneration in uremic neuropathy. Proc. Mayo Clin.46, 400–430 (1971)
Dyck, P. J., Lais, A. C., Offord, K. P.: The nature of myelinated nerve fibre degeneration in dominantly inherited hypertrophic neuropathy. Proc. Mayo Clin.49, 34–39 (1974)
Fraher, J. P.: A quantitative study of anterior root fibres during early myelination. J. Anat. (Lond.)112, 99–124 (1972)
Friede, R. L.: Control of myelin formation by axon calibre (with a model of the control mechanism). J. comp. Neurol.144, 233–252 (1972)
Friede, R. L., Samorajski, T.: Myelin formation in the sciatic nerve of the rat. A quantitative, electronmicroscopic, histochemical and radioautographic study. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.27, 546–570 (1968)
Geren, B. B.: The formation from the Schwann cell surface of myelin in the peripheral nerves of chick embryos. Exp. Cell Res.7, 558–562 (1954)
Low, P. A., Mcleod, J. G.: Hereditary demyelinating neuropathy in the Trembler mouse. J. neurol. Sci.26, 565–574 (1975)
Peters, A., Muir, A. R.: The relationship between axons and Schwann cells during development of peripheral nerves in the rat. Quart. J. exp. Physiol.44, 117–130 (1959)
Webster, H. de F.: The geometry of peripheral myelin sheaths during their formation and growth in rat sciatic nerves. J. Cell Biol.48, 348–367 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by a Research Grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayers, M.M., Anderson, R.D. Development of onion bulb neuropathy in the Trembler mouse. Acta Neuropathol 36, 137–152 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685276
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685276