Summary
It is presently debated how much cellular acidosis contributes to brain cell damage during ischemia and hypoxia. To study the influence of acidosis occurring in the absence of energy failure, extreme hypercapnia was produced in anesthetized, artificially ventilated, and well oxygenated rats by increasing the inspired CO2 concentration until arterialPCO2 reached 150 or 300 mm Hg. At these CO2 tensions intracellular pH falls from a control value of about 7.05 to about 6.85 and 6.65, respectively. After 45 min the brains were fixed in perfusion and processed for light and electron microscopy.
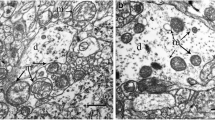
AtPaCO2 150 mm Hg no clear neuronal abnormality was detected, but atPaCO2 300 mm Hg some neuronal changes were observed. Notably, the nuclei showed slightly coarser chromatin than normally. In a few nerve cells mild swelling of mitochondria and dispersion of polysomes as well as detachment of ribosomes from the endoplasmic reticulum appeared. In both groups, slight to moderate astrocytic edema developed.
Thus, even extreme hypercapnia, with its acompanying marked tissue acidosis, alters ultrastructure in the brain only to such a moderate extent that irreversible cell damage is unlikely. We conclude, therefore, that acidosis occurring during ischemia or hypoxia is detrimental only if pH is further lowered and/or if it occurs in conjunction with cerebral energy failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agardh C-D, Kalimo H, Olsson Y, siesjö BK (1980) Hypoglycemic brain injury. I. Metabolic and light microscopic findings in rat cerebral cortex during profound insulin-induced hypoglycemia and in the recovery period following glucose administration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 50:31–41
Bakay L (1976) Blood-brain barrier and its alterations in pathological states. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Metabolic and deficiency diseases of the nervous system. Part II. (Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 28). Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 365–399
Bakay L, Lee JC (1968) The effect of acute hypoxia and hypercapnia on the ultrastructure of the central nervous system. Brain 41:697–710
Berntman L, Dahlgren N, Siesjö BK (1979) Cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in the rat brain during extreme hypercarbia. Anesthesiology 50:299–305
Betz E (1972) Effects of high CO2 concentration on EEG, cerebral cortical energy rich substrates and the morphology of cortical cells. Ann Anesthesiol Fr 13, Spécial 2:32–36
Bourke RS, Kimelberg H, West CR, Bremer AM (1975) The effect of HCO3 on the swelling and ion uptake of monkey cerebral cortex under conditions of raised extracellular potassium. J Neurochem 29:323–328
Bourke RS, Nelson KM (1972) further studies on the K+-dependent swelling of primate cerebral cortex in vivo: the enzymatic basis of the K+-dependent transport of chloride. J Neurochem 19:663–685
Dahmen HG, Müller W (1978) Luxol-fast-blue staining of nerve cell nucleoli as indication for acidotic lesions in case of intracranial hypertension. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 42:243–246
Folbergrová J, MacMillan V, Siesjö BK (1972) The effect of moderate and marked hypercapnia upon the energy state and upon the cytoplasmic NADH/NAD+ ratio of the rat brain. J Neurochem 19:2507–2517
Folbergrová J, Pontén U, Siesjö BK (1974) Patterns of changes in brain carbohydrate metabolites, amino acids and organic phosphates at increased carbon dioxide tensions. J Neurochem 22:1115–1125
Hansen AJ (1981) Extracellular ion concentrations in cerebral ischemia. In: Zeuthen T (ed) The application of ion-selective microelectrodes. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 239–254
Hertz L (1981) Features of astrocytic function apparently involved in the response of central nervous tissue to ischemia-hypoxia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1:143–153
Jennings RB, Reimer KS (1981) Lethal myocardial ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 102:241–255
Johansson B, Nilssson B (1977) The pathophysiology of blood-brain barrier dysfunction induced by severe hypercapnia and by epileptic brain activity. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 38:153–158
Kalimo H, Rehncrona S, Söderfeldt B, Olsson Y, Siesjö BK (1981) Brain lactic acidosis and ischemic cell damage: 2. Histopathology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1:313–327
Ljunggren B, Schutz H, Siesjö BK (1974) Changes in energy state and acid-base parameters of the rat brain during complete compression ischemia. Brain Res 73:277–289
Myers RE (1979) Lactic acid accumulation as a cause of brain edema and cerebral necrosis resulting from oxygen deprivation. In: Korobkin R, Guilleminault G (eds) Advances in perinatal neurology. Spectrum Publishers, New York, pp 85–114
Myers RE, Yamaguchi M (1976) Effects of serum glucose concentration on brain response to circulatory arres. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 305:301
Myers RE, Yamaguchi S (1977) Nervous system effects of cardiac arrest in monkeys. Preservation of vision. Arch Neurol 34:65–74
Ortiz Vazquez J (1979) neurological manifestations of chronic respiratory diseases. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Neurological manifestations of systemic diseases. Part I. (Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 38). Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 285–307
Peters A, Palay SL, Webster H (1976) The fine structure of the nervous system. Neurons and supporting cells. Saunders, Philadelphia
Rehncrona S, Rosén I, Siesjö BK (1981) Brain lactic acidosis and ischemic cell damage: 1. Biochemistry and neurophysiology. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1:297–311
Roos A, Boron WF (1981) Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev 61:296–434
Salford LG, Siesjö BK (1974) The influence of arterial hypoxia and unilateral carotid artery occlusion upon regional blood flow and metabolism in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand 92:130–141
Schlote W, Betz E, Nguyen-Duong H (1975) Reversible apical swelling of dendrites in the cerebral cortex of cats during respiratory acidosis. Adv Neurol 12:483–495
Siemkowicz E, Hansen AJ (1978) Clinical restitution following cerebral ischemia in hypo-, normo- and hyperglycemic rats. Acta Neurol Scand 58:1–8
Siesjö BK (1978) Brain energy metabolism. John Wiley, New York
Siesjö BK (1981) Cell damage in the brain: A speculative synthesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1:234–238
Siesjö BK, Folbergrová J, MacMillan V (1972) The effect of hypercapnia upon intracellular pH in the brain evaluated by bicarbonate-carbonic acid method and from the creatine phosphokinase equilibrium. J Neurochem 19:2483–2495
Söderfeld B, Kalimo H, Olsson Y, Siesjö BK (1981) Pathogenesis of brain lesions caused by experimental epilepsy. Light and electron microscopic changes in the rat cerebral cortex following bicuculline-induced status epilepticus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 54:219–231
Trump BF, Berzesky IK, Collan Y, Kahng MW, Mergner WJ (1976) Recent studies on the pathophysiology of ischemic cell injury. Beitr Pathol 158:363–388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paljärvi, L., Söderfeldt, B., Kalimo, H. et al. The brain in extreme respiratory acidosis. Acta Neuropathol 58, 87–94 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691646
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691646