Summary
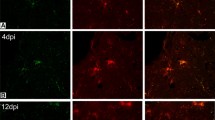
Monoclonal antibodies (MRC OX-6 and OX-17) recognized three types of cells expressing Ia antigen during the course of acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in rats. In earlier stages of the disease, in animals with or without paralysis, Ia antigens were mostly localized to subarachnoidal and perivascular lymphocytic and histiocytic cell infiltrates, possibly serving as antigen-presenting cells. On the other hand, in convalescent rats, Ia antigens were expressed in a large number of cells with dendritic processes heavily populating the spinal gray matter. The appearance of these Ia-expressing cells in the convalescent stage coincided with the development of degenerating axon terminals in the spinal gray matter. These Ia-expressing cells possessed morphological features characteristic of microglia and were positive for ML-1 lectin but did not express glial fibrillary acidic protein. Immune electron microscopy disclosed the presence of Ia reaction products in the Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane of these cells with dendritic processes, indicating active synthesis of Ia molecules in microglia. In addition, Ia antigens were localized to the cells with ultrastructural features of macrophages. Thus, Ia-expressing cells in EAE seems to play dual roles: the induction of immunological reactions during earlier stages and the participation in reparative processes during convalescence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahata K, Engel AG (1986) Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. III. Immunoelectron microscopy aspects of cell-mediated muscle fiber injury. Ann Neurol 19:112–125
Bayer J, Reske K (1983) Biochemical analysis of class II antigens. Identification of a two- and a three-polypeptide chain complex of I-A locus equivalent molecules in the rat. Eur J Immunol 13:18–24
Barclay AN, Mayrhofer G (1981) Bone marrow origin of Ia-positive cells in the medulla of rat thymus. J Exp Med 153:1666–1671
Craggs RI, Webster HF (1985) Ia antigens in the normal rat nervous system and in lesions of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:263–272
Fujita S, Kitamura T (1975) Origin of brain macrophages and the nature of the so-called microglia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) [Suppl] 6:291–296
Hauser SL, Bhan AK, Gilles F, Kemp M, Kerr C, Weiner HL (1986) Immunohistochemical analysis of the cellular infiltrate in multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol 19:578–587
Hickey WF, Gonatas NK, Kimura H, Wilson DB (1983) Identification and quantitation of T lymphocyte subsets found in the spinal cord of the Lewis rat during acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 131:2805–2809
Hickey WF, Osborn JP, Kirby WM (1985) Expression of Ia molecules by astrocytes during acute experimental allergic encephalomyclitis in the Lewis rat. Cell Immunol 91:528–535
Kitamura T, Tsuchihashi Y, Fujita S (1978) Initial response of silver-impregnated “resting microglia” to stab wounding in rabbit hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 44:31–39
Kitamura T (1980) Dynamic aspects of glial reactions in altered brains. Pathol Res Pract 168:301–343
Lassmann H, Vass K, Brunner CH, Seitelberger F (1986) Characterization of inflammatory infiltrates in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Progr Neuropathol 6:33–62
Matsumoto Y, Hara N, Tanaka R, Fujiwara M (1980) Immunohistochemical analysis of the rat central nervous system during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with special reference to Ia-positive cells with dendritic morphology. J Immunol 136:3668–3676
Matsumoto Y, Fujiwara M (1987) The immunopathology of adoptively transferred experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in Lewis rat. Part 1. Immunohistochemical examination of developing lesions of EAE. J Neurol Sci 77:35–47
Murabe Y, Sano Y (1982) Morphological studies on neuroglia. VI. Postnatal development of microglial cells. Cell Tissue Res 225:469–485
Polak M, D'Amelio F, Johnson JE, Haymaker W, Hager H (1982) Microglial cells: origins and reactions. In: Haymaker W, Adams RD (eds) Histology and histopathology of the nervous system. Charles C Thomas, Springfield, pp 481–559
Reske K, Weitzel R (1985) Immunologically discrete conformation isomers of I-A locus-equivalent class II molecules detected in Lewis rats. Eur J Immunol 15:1229–1239
Rowden G (1977) Immuno-electron microscopic studies of surface receptors and antigens of human Langerhans cells. Br J Dermatol 97:593–608
Sakai K, Namikawa T, Kunishita T, Yoshimura T, Tabira T (1985) Ia restriction of murine encephalitogenic T cell lines in vitro and in vivo. J Neuroimmunol 9:281–291
Sakai K, Tabira T, Endoh M, Steinman L (1986) Ia expression in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced by long-term cultured T cell lines in mice. Lab Invest 54:345–352
Sobel RA, Blanchette BW, Bhan AK, Colvin RB (1984) The immunopathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. II. Endothelial cell Ia increases prior to inflammatory cell infiltration. J Immunol 132:2402–2407
Sobel RA, Natale JM, Schneeberger EE (1987) The immunopathology of acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, IV. An ultrastructural immunocytochemical study of class II major histocompatibility complex molecule(Ia) expression. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46:239–249
Sriram S, Steinman L (1983) Anti-Ia-antibody suppresses active encephalomyelitis. Treatment model for disease linked to IR genes. J Exp Med 158:1362–1367
Suzuki H, Franz H, Yamamoto T, Iwasaki Y, Konno H (1988) Identification of the normal microglial population in human and rodent nervous tissue by lectin-histochemistry. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 14:221–227
Ting JPY, Shigekawa BL, Linthicum DS, Weiner LP, Frelinger JA (1981) Expression and synthesis of murine immune response-associated(Ia) antigens by brain cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 78:3170–3174
Traugott U, Raine CS, McFarlin DE (1985) Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse: immunopathology of the developing lesion. Cell Immunol 91:240–254
Vass K, Lassmann KV, Wekerle H, Wisniewski HM (1986) The distribution of Ia antigen in the lesions of rat acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70:149–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Health and Welfare for “Intractable Neuroimmunological Diseases” and from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture (Project 61570380 to HK)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konno, H., Yamamoto, T., Iwasaki, Y. et al. Ia-expressing microglial cells in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Acta Neuropathol 77, 472–479 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687248
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687248