Summary
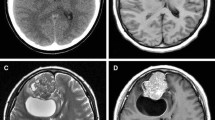
Bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis (neurofibromatosis 2, NF2) accounts for less than 10% of all cases of neurofibromatosis and manifests itself with bilateral acoustic schwannomas, multiple schwannomas of spinal nerve roots, meningiomas, glial tumors and hamartomatous CNS lesions. We have observed dysplastic foci of immature neuroectodermal cells in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia of six patients afflicted with neurofibromatosis 2, ranging from occasional clusters of immature, dysplastic cells to numerous, confluent lesions. These cells, although often polymorphic and multinuclear did not show mitotic acitivity or a tendency for neoplastic transformation. To determine the histogenesis of these foci, extensive immunocytochemical reactions were carried out with antibodies to a variety of glial, neuronal and nonneural cell lineages. With the exception of S-100 protein, no immunoreactivity was detectable. S-100 was consistently expressed in these foci, irrespective of their size, location, and degree of polymorphism. On the basis of cytological appearance, distribution and immunoreactivity we tentatively designate these foci as glial micro-hamartomas. Although we did not systematically analyze the CNS of patients with von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis (neurofibromatosis 1, NF1), the present study strongly suggests that these micro-hamartomas constitute a morphological hallmark of bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis (NF2).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey P, Hermann JD (1938) The role of the cells of Schwann in the formation of tumors of the peripheral nerves. Am J Pathol 14:1–37
Barker D, Wright E, Nguyen K, Cannon L, Fain P, Goldgar D, Bishop DT, Carey J, Baty B, Kivlin J, Willard H, Waye JS, Greig G, Leinwand L, Nakamura Y, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lalouel J-M, White R, Skolnick M (1987) Gene for von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis is in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17. Science 236:1100–1102
Donato R (1986) S-100 proteins. Cell Calcium 7:123–145
Farber E (1984) Cellular biochemistry of the stepwise development of cancer with chemicals: G. H. A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res 44:5463–5474
Gardner WJ, Frazier CH (1930) Bilateral acoustic neurofibromas: a clinical study and field survey of a family of five generations with bilateral deafness in thirty eight members. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 23:266–302
Huson SM (1987) The different forms of neurofibromatosis. Br Med J 294:1113–1114
Kahn HJ, Marks A, Thom H, Baumal R (1982) Role of antibody to S-100 protein in diagnositic pathology. Am J Clin Pathol 79:341–347
Kanter WR, Eldridge R, Fabricant R, Allen JC, Koerber T (1980) Central neurofibromatosis with bilateral acoustic neuroma: genetic, clinical and biochemical distinctions from peripheral neurofibromatosis. Neurology 30:851–859
Kleihues P, Kiessling M, Janzer RC (1987) Morphological markers in neuro-oncology. Curr Top Pathol 77:307–338
Martuza RL, Eldridge R (1988) Neurofibromatosis 2 (bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis). N Engl J Med 318:684–688
National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference (1987) Neurofibromatosis 6:1–7
Neurofibromatosis (1987) Lancet I:663–664
Orzechowski K, Nowicki W (1912) Zur Pathogenese und pathologischen Anatomie der multiplen Neurofibromatose und der Sclerosis tuberosa (Neurofibromatosis universalis). Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr 11:16–307
Riccardi VM, Eichner JE (eds) (1986) Neurofibromatosis. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore
Rosman NP, Pearce J (1967) The brain in multiple neurofibromatosis (von Recklinghausen's disease): a suggested neuropathological basis for the associated mental defect. Brain 90:829–837
Rubinstein AE (1986) Neurofibromatosis: a review of the clinical problem. Ann NY Acad Sci 486:1–13
Rubinstein LJ (1963) Tumeurs et hamartomes dans la neurofibromatose central. In: Miehaux L, Feld M (eds) Les Phakomatoses cérébrales. SPEI Editeurs, Paris, pp 427–451
Rubinstein LJ (1986) The malformative central nervous system lesions in the central and peripheral forms of neurofibromatosis. A neuropathological study of 22 cases. Ann NY Acad Sci 486:14–29
Russell DS, Rubinstein LJ (1989) Pathology of tumours of the nervous system, 5th ed. Edward Arnold, London, pp 766–808
Schwechheimer K (1986) Nervale Tumormarker (neural tumor markers). Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 70:82–103
Seizinger BR, Martuza RL, Gusella JF (1986) Loss of genes on chromosome 22 in tumorigenesis of human acoustic neuroma. Nature 322:644–647
Seizinger BR, Rouleau G, Ozelius LJ, Lane AH, ST George-Hyslop P, Huson S, Gusella JF, Martuza RL (1987) Common pathogenetic mechanism of three tumor types in bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis. Science 236:317–319
Seizinger BR, Rouleau GA, Ozelius LJ, Lane AH, Faryniarz AG, Chao MV, Huson S, Korf BR, Parry BG, Pericak-Vance MA, Collins FS, Hobbs WJ, Falcone BG, Iannazi JA, Roy JC, St George-Hyslop PH, Tanzi RE, Bothwell MA, Upadhyaya M, Harper P, Goldstein AE, Hoover DL, Bader JL, Spence MA, Mulvihill JJ, Aylsworth AS, Vance JM, Rossenwasser GOD, Gaskell PC, Roses AD, Martuza RL, Breakefield XO, Gusella JF (1987) Genetic linkage of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis to the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Cell 49:589–594
Takahashi K, Isobe T, Ohtsuki Y, Akagi T, Sonobe H, Okuyama T (1984) Immunohistochemical study on the distribution of a and b subunits of S-100 protein in human neoplasm and normal tissues. Virchows Arch [B] 45:385–396
Wertelecki W, Rouleau GA, Superneau DW, Forehand LW, Williams JP, Haines JL, Gusella JF (1988) Neurofibromatosis 2: clinical and linkage studies of a large kindred. N Engl J Med 319:278–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiestler, O.D., von Siebenthal, K., Schmitt, H.P. et al. Distribution and immunoreactivity of cerebral micro-hamartomas in bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis (neurofibromatosis 2). Acta Neuropathol 79, 137–143 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294370
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294370