Summary
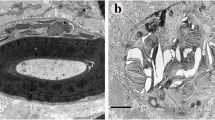
In this study we evaluated the relationship between polyglucosan bodies and peripheral nerve lesions. The biopsied sural nerve from a patient with late-onset chronic sensori-motor neuropathy showed many intra-axonal polyglucosan bodies and segmental demyelination/remyelination. The formation of Schwann cell hyperplasia around the demyelinated axons was found at the sites of polyglucosan bodies. These findings suggest that demyelinating neuropathy is a part of the spectrum of the diseases characterized by the accumulation of polyglucosan bodies within cellular compartments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asbury AK, Johnson PC (1978) Pathology of peripheral nerve. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp256–257
Atsumi T (1981) The ultrastructure of intramuscular nerves in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 55:193–198
Averback P, Langevin H (1978) Corpora amylacea of the lumbar spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. Arch Neurol 35:95–96
Bernsen RAJAM, Busard HLSM, Ter Laak HJ, Gabreëls FJM, Renier WO, Joosten EMG, Theeuwes AGM (1989) Polyglucosan bodies in intramuscular motor nerves. Acta Neuropathol 77:629–633
Busard HLSM, Gabreëls-Festen AAWM, van't Hof MA, Renier WO, Gabreëls FJM (1990) Polyglucosan bodies in sural nerve biopsies. Acta Neuropathol 80:554–557
Cafferty MS, Lovelace RE, Hays AP, Servidei S, DiMauro S, Rowland LP (1991) Polyglucosan body disease. Muscle Nerve 14:102–107
Goebel HH, Shin YS, Gullotta F, Yokota T, Alroy J, Voit T, Haller P, Schulz A (1992) Adult polyglucosan body myopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51:24–35
Gray F, Gherardi R, Marshall A, Janota I, Poirier J (1988) Adult polyglucosan body disease (APBD). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:459–474
Lossos A, Barash V, Soffer D, Argov Z, Gomori M, Ben-Nariah Z, Abramsky O, Steiner I (1991) Hereditary branching enzyme dysfunction in adult polyglucosan body disease: a possible metabolic cause in two patients. Ann Neurol 30:655–662
Mancardi GL, Schenone A, Tabaton M, Tassinari T, Mainardi P (1985) Polyglucosan bodies in the sural nerve of a diabetic patient with polyneuropathy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 66:83–86
Okamoto K, Llena JF, Hirano A (1982) A type of adult polyglucosan body disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 58:73–77
Robitaille Y, Carpenter S, Karpati G, DiMauro S (1980) A distinct form of adult polyglucosan body disease with massive involvement of central and peripheral neuronal processes and astrocytes. A report of four cases and a review of the occurrence of polyglucosan bodies in other conditions such as Lafora's disease and normal ageing. Brain 103:315–336
Vos AJM, Joosten EMG, Gabreëls-Festen AAWM (1983) Adult polyglucosan body disease: clinical and nerve biopsy findings in two cases. Ann Neurol 13:440–444
Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Nakano T (1977) Corpora amylacea in the peripheral nerve axons. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 37:73–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumuro, K., Izumo, S., Minauchi, Y. et al. Chronic demyelinating neuropathy and intra-axonal polyglucosan bodies. Acta Neuropathol 86, 95–99 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00454906
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00454906