Abstract
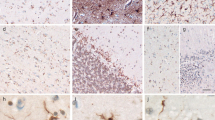
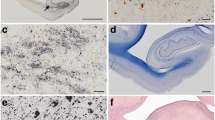
This report concerns an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study of cerebral astrocytes in a patient with Pick's disease of 20 years' duration. The autopsied brain was prominently small (710 g) with marked fronto-temporal lobar atrophy. Histological examination demonstrated profound neuronal loss and spongy changes with tau-positive Pick bodies in the frontal and temporal cortex. In addition, many glial cells in the temporal lobe white matter contained round to oval, argentophilic and slightly hematoxinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions that were also immunolabeled with the anti-tau antibody. On electron microscopy, the glial inclusions were observed in the perikarya of astrocytes that were recognized as such from intracytoplasmic glial filaments and the presence of gap junctions. The inclusions were free in the cytoplasm, without a limiting membrane, and mainly comprised irregular aggregations of bundles of about 15-nm straight tubules, which were indistinguishable from those of intraneuronal Pick bodies. Furthermore, various patterns of accumulation of the same straight tubules were frequently noted in perivascular astrocytic processes carrying a basal lamina. These findings indicate that in Pick's disease astrocytes are also affected by a similar insult to that which affects neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brion JP, Passareiro H, Nunez J, Flament-Durand J (1985) Mise en evidence de la proteine Tau au niveau des lesions de degenerescence neurofibrillaire de la maladie d'Alzheimer. Arch Biol 95: 229–235
Delacourte A, Defossez A (1986) Alzheimer's disease: tau proteins, the promoting factors of microtubule assembly, are major components of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci 76: 173–786
Ghadially FN (1988) Ultrastructural pathology of the cell and matrix, 3rd edn. Butterworths, London
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung YC, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM (1986) Microtubule-associated protein tau: a component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem 261: 6084–6089
Houropian DS, Dickson DW (1991) Striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and “atypical” Pick disease. Acta Neuropathol 81: 287–295
Ihara Y, Abraham C, Selkoe DJ (1983) Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature 304: 727–730
Ikeda K, Haga C, Akiyama H, Kase K, Iritani S (1992) Coexistence of paired helical filaments and glial filaments in astrocytic processes within ghost tangles. Neurosci Lett 148: 126–128
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Haga C, Haga S (1992) Evidence that neurofibrillary tangles undergo glial modification. Acta Neuropathol 85: 101–104
Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Kondo H, Ikeda K (1993) Anti-tau-positive glial fibrillary tangles in the brain of postencephalitic parkinsonism of Economo type. Neurosci Lett 162: 176–178
Izumiyama Y, Ikeda K, Oyanagi S (1994) Extracellular or ghost Pick bodies and their lack of tau immunoreactivity: a histological, immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol 87: 277–283
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1986) Microtubule-associated protein tau is a major component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 4044–4048
Mori H, Kondo J, Ihara Y (1987) Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science 235: 1641–1644
Murayama S, Mori H, Ihara Y, Tomonaga M (1990) Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural studies of Pick's disease. Ann Neurol 27: 394–405
Nakano I, Iwatsubo T, Otsuka N, Kamei M, Matsumura K, Mannen T (1992) Paired helical filaments in astrocytes: electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry in a case of atypical Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 83: 228–232
Nakano I, Kato S, Yazawa I, Hirano A (1992) Anchorage densities associated with hemidesmosome-like structures in perivascular reactive astrocytes. Acta Neuropathol 84: 85–88
Nakazato Y, Yamazaki H, Hirato J, Ishida Y, Yamaguchi H (1990) Oligodendroglial microtubular tangles in olivopontocerebellar atrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 49: 521–530
Nishimura M, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Oda M (1992) Glial fibrillary tangles with straight tubules in the brains of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 143: 35–38
Nukina N, Ihara Y (1986) One of the antigenic determinants of paired helical filaments is related to tau protein. J Biochem 99: 1541–4544
Nukina N, Quan Y, Nakano I, Otomo E (1992) Widespread tau abnormality in a case of corticobasal degeneration. Clin Neurol 32: 1093–1101
Papasozomenos SC (1989) Tau protein immunoreactivity in dementia of the Alzheimer type. I. Morphology, evolution, distribution, and pathogenetic implications. Lab Invest 60:123–137
Papasozomenos SC (1989) Tau protein immunoreactivity in dementia of the Alzheimer type. II. Electron microscopy and pathogenetic implications. Effects of fixation of the morphology of the Alzheimer's abnormal filaments. Lab Invest 60: 375–389
Papp MI, Kahn JE, Lantos PL (1989) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome). J Neurol Sci 94: 79–100
Pollock N, Mirra SS, Binder LI, Hansen LA, Wood JG (1986) Filamentous aggregates in Pick's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Alzheimer's disease share antigenic determinants with microtubule-associated protein, tau. Lancet II: 1211
Yamada T, McGeer PL (1990) Oligodendroglial microtubular masses: an abnormality observed in some human neurodegenerative diseases. Neurosci Lett 120:163–166
Yamada T, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1992) Appearance of paired nucleated, tau-positive glia in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy brain tissue. Neurosci Lett 135: 99–102
Yamada T, Calne DB, Akiyama H, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1993) Further observations on tau-positive glia in the brains with progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 85:308–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamazaki, M., Nakano, I., Imazu, O. et al. Astrocytic straight tubules in the brain of a patient with Pick's disease. Acta Neuropathol 88, 587–591 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296498
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296498