Summary
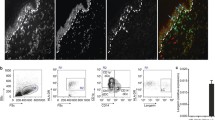
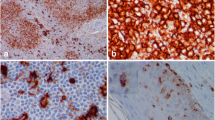
The effect of orally administered aromatic retinoid (Ro 10-9359) on murine epidermal Langerhans cells (LC) was studied in vivo and in vitro. Daily administration of retinoid caused a transient increase in LC density, as determined by staining for Ia antigens, during the first few days of treatment and thereafter a continuing decrease that reached a maximum at 2 weeks. In addition, the morphology and location in the epidermis had been altered. When the treatment was continued to 4 weeks, the density of LC returned to normal. The Ia-antigen-presenting function of epidermal cells to an allo-Ia-reactive cloned T cell line was elevated at all stages of retinoid treatment examined. This elevation did not correlate with the density of histochemically stainable Ia+ LC. These findings suggest that orally administered retinoid profoundly alters the functional capacity of Ia+ LC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberer W, Schuler G, Stingl G, Honigsmann H, Wolff K (1981) Ultraviolet light depletes surface markers of Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol 76:202–210
Bauer R, Orfanos CE (1981) Trimethylmethoxyphenyl-retinoic acid (Ro 10-1670) inhibits mitogen-induced DNA synthesis in peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro. Br J Dermatol 105:19–24
Bollag W (1974) Therapeutic effect of an aromatic retinoic acid analog on chemically induced skin papillomas and carcinomas of mice. Eur J Cancer 10:731–737
Breathnach SM, Katz SI (1983) Keratinocytes synthesize Ia antigen in acute cutaneous graft-vs.-host disease. J Immunol 131:2741–2745
Crocker TT, Sauders LL (1970) Influence of vitamin A and 3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienal (citral) on the effect of benzo-(a)pyrene on hamster trachea in organ culture. Cancer Res 30:1312–1318
Dennert G, Lotan R (1978) Effects of retinoic acid on the immune system: stimulation of T killer cell induction. Eur J Immunol 8:23–29
Elias PM, Williams ML (1981) Retinoids, cancer and the skin. Arch Dermatol 117:160–180
Hercend T, Bruley-Rosset M, Florentin I, Mathé G (1981) In vivo immunostimulating properties of two retinoids: Ro 10-9359 and Ro 13-6398. In: Orfanos CE, Braun-Falco O, Farber EM, Grupper C, Polano MK, Schuppli R (eds) Retinoid. Springer, Heidelberg New York, Berlin pp 21–30
Janeway CA, Bottomly K, Babich J, Conrad P, Conzen S, Jones B, Kaye J, Katz M, McVay L, Murphy DB, Tite J (1984) Quantitative variation in Ia antigen expression plays a central role in immune regulation. Immunol Today 5:99–105
Lasnitzki I (1976) Reversal of methylcholanthrene-induced changes in mouse prostates in vitro by retinoic acid and its analogues. Br J Cancer 34:239–248
Levine L, Ohuchi K (1978) Retinoids as well as tumor promoters enhance deacylation of cellular lipids and prostaglandin production in MDCK cells. Nature 276:274–275
Lotan R, Dennert G (1979) Stimulatory effects of vitamin A analogs on induction of cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vivo. Cancer Res 39:55–58
Nordlund JJ, Ackles AE, Lerner AB (1981) The effects of ultraviolet light and certain drugs on Ia-bearing Langerhans cells in murine epidermis. Cell Immunol 60:50–63
Rowden G (1980) Expression of Ia antigens on Langerhans cells in mice, guinea pigs, and man. J Invest Dermatol 75:22–31
Schultz-Ehrenburg U, Orfanos CE (1981) Light and electron microscopic changes of human epidermis under oral retinoid treatment. In: Orfanos CE, Braun-Falco O, Farber EM, Grupper C, Polano MK, Schuppli R (eds) Retinoids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 85–92
Schweizer J (1981) Langerhans cells, epidermal growth control mechanisms and type keratinization. In: Marks R, Christophers E (eds) The epidermis in disease. MTP Press, Lancaster, pp 481–499
Shiohara T, Moriva N, Tsuchiya K, Nagashima M, Narimatsu H (1986) Lichenoid tissue reaction induced by local transfer of Ia-reactive T cell clones. J Invest Dermatol 87:33–38
Sontheimer RD, Bergstresser PR (1982) Epidermal Langerhans cell involvement in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol 79:237–243
Teelmann K (1981) Experimental toxicology of the aromatic retinoid Ro 10-9359 (etretinate). In: Orfanos CE, Braun-Falco O, Farber EM, Grupper C, Polano MK, Schuppli R (eds) Retinoids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 41–47
Tsambaos D, Mahrle G, Orfanos CE (1980) Epidermal changes induced by oral excess of aromatic retinoid in guinea pigs. Arch Dermatol Res 267:141–152
Tsambaos D, Orfanos Ce (1981) Ultrastructural evidence suggesting an immunomodulatory activity of oral retinoid. Br J Dermatol 104:37–45
Walsh LJ, Seymour GJ, Powell RN (1985) The in vitro effect of retinol on human gingival epithelium. II. Modulation of Langerhans cell markers and interleukin-1 production. J Invest Dermatol 85:501–506
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiohara, T., Kobayashi, M., Narimatsu, H. et al. Effect of orally administered aromatic retinoid on murine Langerhans cells. Arch Dermatol Res 279, 198–203 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413258
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413258