Summary
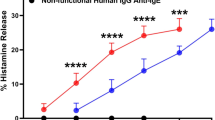
The influence of arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism upon histamine release (HR) from human basophils after stimulation with anti-IgE was studied in 23 atopic and 11 normal individuals. HR occurred significantly faster in atopics than in normals; the total amount of HR after a 40 min incubation period was not significantly different between the two groups. Indomethacin and acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) increased the quantity of HR significantly both in atopics and normals without influencing the time course. Addition of exogenous PGE2 decreased HR; here atopics were more affected than normals 5 and 10 min after challenge with anti-IgE. Production of PGE2 after stimulation with anti-IgE was very low in both groups (in the range of 30–50 pg/106 cells) and often below detection limit (10–20 pg/ml). Addition of glutathione (GSH), a coenzyme of PGE2-isomerase, increased PGE2 production 2 to 5-fold during stimulation with anti-IgE. These data support the idea that arachidonic acid metabolites play an important role in modulating the “releasability” of human basophils. It is suggested that the basophils of atopic individuals may release their histamine faster than normals — perhaps on the basis of a more slowly acting endogenous feedback mechanism by PGE2. Both phenomena support the idea of an altered “releasability” of basophils from atopics compared to normals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conroy MC (1981) Releasability — a new dimension in basophil and mast cell reactivity. In: Ring J, Burg G (eds) New trends in allergy. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 40–45
Coulson CJ, Ford RE, Marshall S, Walker KL, Wooldrige KRH, Bowden K, Coombs RJ (1977) Interrelationships of cyclic nucleotides and anaphylactic reactions. Nature 265:545–547
Dorsch W, Frey L (1981) Allergen tachyphylaxis of guinea pig in vivo: a prostaglandin E mediated phenomenon? Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 317:351–356
Dorsch W, Frey L, Müller W (1984) In vivo allergen tachyphylaxis in guinea pig lung is mediated by endogenous protaglandin E biosynthesis. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 953:1–8
Dorsch W, Ring J, Riepel H (1984) Effect of 15-hydroxytetraenoic acid (15-HETE) on anti-immunglobulin E- and calcium ionophore-induced histamine release from human leukocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 73, 274–279
Engineer DM, Niederhauser U, Piper PJ, Sirois P (1978) Release of mediators of anaphylaxis: inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and the modification of release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis and histamine. Br J Pharmacol 62:61–66
Gillespie E (1979) Effects of S-lactoylglutathione and inhibitors of glyoxylase I on histamine release from human leukocytes. Nature 277:135–137
Kantor HS, Hampton M (1978) Indomethacin in submicromolar concentrations inhibits cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature 267:841–842
Kennerly DA, Sullivan TJ, Parker CW (1979) Activation of phospholipid metabolism during mediator release from stimulated rat mast cells. J Immunol 122:152–159
Lewis GP, Whittle BJR (1977) The inhibition of histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells by non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs and its reversal by calcium, Br J Pharmacol 61:229–235
Lichtenstein LM, Margolis G (1968) Histamine release in vitro: inhibition by catecholamines and methylxanthines. Science 161:902–903
Marone G, Kagey-Sobotka A, Lichtenstein LM (1981) Control mechanisms of histamine release from human basophils in vitro: the role of phospholipase A2 and of lipoxygenase metabolites. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 66 [Suppl 1]: 144–148
Marone G, Kagey-Sobotka A, Lichtenstein LM (1981) IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophils: differences between antigen E and anti-IgE-induced secretion. Inter Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 65:339–348
Marone G, Poto S, Petracca R, De Lucio del Castelgiudone E, Condorelli M (1984) Bedeutung der 5-Lipoxagenase Metaboliten undder Phospholipase A2 bei der Histamin-freisetzung aus menschlichen Basophilen. Allergologie 1:23–26
Mathe AA (1976) Studies on action of prostaglandines in the lung. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 441:1–55
Morley J, Page CP, Sanjar S (1985) Pharmacology of the late response to allergen and its relevance to asthma prophylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 77:73–78
Okazaki T, Ilea VS, Rosario NA, Reisman RE, Arbesman CE, Lee JB, Middleton E Jr (1977) Regulatory role of pro-staglandin E in allergic histamine relase with observations on the responsiveness of basophil leukocytes and the effect of acetylic acid. J Allergy Clin Immunol 60:360–366
Okazaki T, Johnson TF, Reisman RE, Arbesman LE, Middleton E Jr (1979) Plasma prostaglandin concentrations in allergic bronchial asthma. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 57:279–281
Peters SP, Kagey-Sobotka A, McGlashan DW Jr, Siegel MJ, Lichtenstein LM (1982) The modulation of human basophil histamine release by products of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. J Immunol 129:797–803
Piper PJ, Walker JL (1973) The release of spasmogenic substances from human chopped lung tissue and its inhibition. Br J Pharmacol 47:291–304
Ring J (1979) Atopic dermatitis: a disease of general vasoactive mediator dysregulation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 59:233–239
Ring J, Mathison DA, O'Connor R (1981) In vitro cyclic nucleotide responsiveness of leukocytes and platelets in patients suffering from atopic dermatitis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 65:1–7
Ruzicka T, Ring J (1987) Enhanced releasability of prostaglandin E2 and leukotrienes B4 and C4 from leukocytes of patients with atopic eczema. Acta Derm Venereol (in press)
Shore, PA, Burkhalter A, Cohn VH (1959) A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 127:182–191
Siraganian RP, Brodsky MJ (1975) Automated histamine analysis for in vitro allergy testing. I. A method utilizing allergen-induced histamine release from whole blood. Immunochemistry 12:149–157
Stevenson DD, Mathison DA (1975) Aeroallergen inhalation challenge in aspirin-intolerant asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 55:127–128
Strandberg K, Mathe AA, Yen SS (1977) Release of histamine and formation of prostaglandins in human lung tissue and rat mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 53:520–529
Sullivan TJ, Parker TW (1979) Possible role of arachidonic acid and its metabolites in mediator release from mast cells. J Immunol 122:431–436
Szentivanyi A (1969) The beta-adrenergic theory of the atopic abnormality in asthma. J Allergy 42:203–211
Tanizaki Y, Komagoe H, Morinaga H, Kitani H, Goda J, Kimura I (1984) Allergen and anti-IgE-induced histamine release from whole blood. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 73:141–145
Tauber AJ, Kaliner M, Stechschulte DJ, Austen KF (1973) Immunologic release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human lung. J Immunol 111:27–32
Thomas RU, Whittle BJR (1976) Prostaglandins and the release of histamine from rat peritoneal mast cells. Br J Pharmacol 57:474–478
Vane JR (1971) Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nature 231:232–235
Walker JL (1972) The regulatory function of prostaglandins in the release of histamine and SRS-A from passively sensitized human lung tissue. In: Bergstroem S, Bernhard S (eds) Advances in the biosciences, vol 9. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 235–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von der Helm, D., Ring, J. & Dorsch, W. Comparison of histamine release and prostaglandin E2 production of human basophils in atopic and normal individuals. Arch Dermatol Res 279, 536–542 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413286
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00413286