Abstract
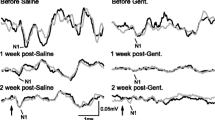
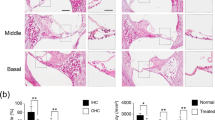
The effects of intravenous furosemide on the perilymphatic oxygen tension of the scala tympani (OT) in the guinea pig and the relationship between changes in OT and changes in auditory cortical-evoked reponses were studied, as well as changes in cochlear morphology. Furosemide in dosages of 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg caused a sharp decline in OT in addition to elevation of the threshold of auditory cortical-evoked responses. Ischemia of the cochlear stria vascularis was also found but without any damage of hair cells at the light microscopic level. Changes in OT were associated with transient threshold elevations and ischemia of the stria vascularis. Improvements in hearing were directly proportional to the recovery of OT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anniko M, Sobin A (1987) Ethacrynic acid effects in the isolated inner ear: evaluation of the ototoxic potential in an organ culture system. Am J Otolaryngol 8:48–62
Federspil P, Mausen H (1973) Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Ototoxicität des Furosemids. Res Exp Med 161:175–184
Liang Z, Feng J (1984) Method and technique of physiology. Science Publishing House, Beijing, 97
Marcus DC, Rokugo M, Ge XX, et al (1983) Response of cochlear potentials to presumed alteration of ionic conductance: endolymphatic perfusion of barium, valinomycin and nystatin. Hear Res 12:17–30
Mathog RH, Matz GJ (1972) Ototoxic effects of ethacrynic acid. Ann Otol 81:871–876
Pike D, Bosher SK (1980) The time course of the strial changes produced by intravenous furosemide. Hear Res 3:79–89
Prazma J (1972) Ototoxicity of the ethacrynic acid. Arch Otolaryngol 95:448–456
Rarey KE, Ross MD (1982) A survey of the effects of loop diuretics on the zonulae occludents of the perilymph-endolymph barrier by freeze fracture. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 94:307–316
Ruggero MA, Rich NC (1991) Furosemide alters organ of Corti mechanics: evidence for feedback of outer hair cells upon the basilar membrane. J Neurosci 11:1057–1067
Rybak LP (1982) Pathophysiology of furosemide ototoxicity. J Otolaryngol 11:127–133
Rybak LP (1985) Furosemide ototoxicity: clinical and experimental aspects. Laryngoscope [Suppl] 95:1–9
Rybak LP, Morizono T (1982) Effect of furosemide upon endolymph potassium concentration. Hear Res 7:223–231
Rybak LP, Whitworth C (1986) Comparative ototoxicity of furosemide and piretanide. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 101:59–65
Tasaki I, Spyropolous CS (1959) Stria vascularis as a source of the endocochlear potential. J Neurophysiol 22:149–155
Tuzel IH (1981) Comparison of adverse reactions to bumetanide and furosemide. J Clin Pharmacol 21:615–619
Yin J, Yuan Y (1993) Effects of low frequency noise exposure and co-effects combined with carbon monoxide on hearing. Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis 11:328–329
Yuan Y, Yin J (1993) Detection of cochlear perilymphatic oxygen tension with polarographic technique in guinea pigs. Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis 11:211–213
Yuan Y, Yin J (1993) Relationship between intracochlear oxygen tension and acoustic trauma following explosion. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol 28:222–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J.X., Zhou, X.N. & Yuan, Y.G. Effects of furosemide on intracochlear oxygen tension in the guinea pig. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 253, 367–370 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178294
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178294