Abstract
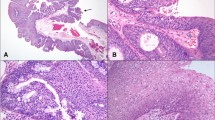
The presence of human papillomavirus DNA in cholesteatoma may have some role in the development of middle ear cholesteatoma as well as in papilloma. In the present study, polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization with human papillomavirus (HPV)-6 and ¶-11 DNA probes were used to detect the presence of HPV DNA in 32 human middle ear cholesteatomas. Only one specimen contained HPV-6 DNA. Although its occurrence may have been coincidental, it is also possible that the hyperproliferative epithelium of cholesteatomas might have some relationship with HPV infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 February 1999 / Accepted: 3 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, WY., Chang, SJ. & Jin, YT. Detection of human papillomavirus in cholesteatomas. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 257, 120–123 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050050206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050050206