Abstract
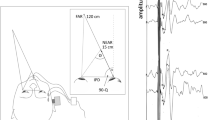
Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) occurring after click stimulation in cervical muscles are thought to be a polysynaptic response of otolith-vestibular nerve origin. In optokinetic after-nystagmus (OKAN) the direction of after-nystagmus changes and slow-phase velocity decreases with head tilt. This phenomenon may be an otolith response to the direction of gravity. We assumed that intense clicks might have some influence on OKAN via the otolith-vestibular nerve. Twelve normal subjects who showed VEMP at 75 dB normal hearing level (nHL) clicks were examined. The OKAN was recorded under four conditions: right monaural, left monaural and binaural stimulation by 75 dB nHL clicks, and absence of click stimulation. Horizontal optokinetic stimulation was applied using stepwise increasing speeds from 30 deg/s to 90 deg/s. Two seconds before the stimulus ended, clicks were sounded. The slow-phase velocity of the recorded electro-nystagmography was manually measured. There was no effect on OKAN with unilateral stimulation but binaural stimulation suppressed it. These results suggest that a velocity storage integrator is influenced by intense clicks via the otolithic area.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 November 1999 / Accepted: 30 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, O., Asawa, S., Katsuno, S. et al. The effects of intense click sounds on velocity storage in optokinetic after-nystagmus. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 257, 490–492 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050000266
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004050000266