Summary
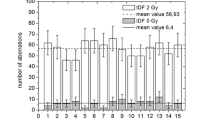
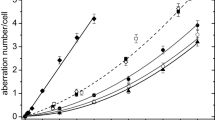
Changes in the chromatin conformational state (CCS) of human leukocytes were detected by the anomalous viscosity time dependence (AVTD) method. The dose dependence was studied for seven donors with doses of up to 10 cGy. X-rays caused no statistically significant changes in the leukocytes of two of the donors. The dose dependences registered on leukocytes of the other donors showed some distinctions which may be due to individual traits of the donors. Extrapolation of all the results produced a nonlinear dose dependence which consisted of two sections. The first one was characterized by a fast growth of the effect, the second section was extrapolated to a slightly sloping linear dependence which was close to a plateau. It was shown that the AVTD method was highly sensitive to X-rays and can register changes in the CCS of leukocytes exposed to doses of about 0.5 cGy. The possible role of DNA breaks and processes of ionization and excitation are analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alipov YD, Belyaev IY, Yedneral DI, Izmaylov DM, Lukashevsky KV, Obukhova LK, Okladnova OV, Shcheglov VS (1989) Specific effect of millimeter waves on genome and some genetic processes in normal state and after X-ray exposure. (in Russian) In: Proceedings of Workshop on Genetic Effects of Charged Particles. JINR, Dubna, pp 150–160
Arinichev AD, Belyaev IY, Samedov VV, Sitko SP (1992) Physical model of direct electromagnetic field effect on genome conformational state. In: Transactions of First Congress of The European Bioelectromagnetics Association. Brussels, Belgium, p 1
Baverstock KF, Cundal RB (1988) Solitons and energy transfer in DNA. Nature 332:312–313
Bednar J (1985) Electronic excitations in condensed biological matter. Int J Radiat Biol 48:147–166
Belyaev IY, Alipov YD, Shcheglov VS, Yedneral DI, Lystsov VN (1990) Effect of millimeter waves on radiation-induced repair of genome conformational state. (in Russian) In: Proceedings of Workshops on DNA, Repair and Mutagenesis Induced by Radiation. JINR, Dubna, pp 242–261
Belyaev IY (1992) Some biophysical aspects of the genetic effect of low-intensity millimeter waves. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 27:11–18
Belyaev IY, Alipov YD, Shcheglov VS, Lystsov VN (1992a) Resonance effect of microwaves on the genome conformational state ofE. coli cells. Z Naturforsch 47c:621–627
Belyaev IY, Shcheglov VS, Alipov YD (1992b) Selection rules on helicity during discrete transitions of the genome conformational state in intact and X-rayed cells ofE. coli in millimeter range of electromagnetic field. In: Allen MJ, Cleary SF, Sowers AE, Shillady DD (eds) Charge and field effects in biosystems 3. Birkhäuser, Boston, pp 115–126
Belyaev IY, Alipov YD, Shcheglov VS (1992c) Chromosome DNA as a target of resonant interaction betweenE. coli cells and low intensity millimeter waves. Electro Magnetobiol 11:97–108
Belyaev IY, Shcheglov VS, Alipov YD, Radko SP (1992d) Regularities of spearate and combined effects of circularly polarized millimeter waves onE. coli cells at different phases of culture growth. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg (in press)
Bolshakov VY, Drobchenko YA, Landa SB, Peimer SI (1990) Activation of neuron generator of glow-worms under influence of pulse X-rays. (in Russian) Radiobiologiya 30:133–135
Bosi A, Olivieri G (1989) Variability of the adaptive response to ionizing radiation in humans. Mutat Res 211:13–17
Fabry L, Leonard A, Wambersie A (1985) Induction of chromosome aberrations in G0 human lymphocytes by low doses of ionizing radiations of different quality. Radiat Res 103:122–134
Fedorov NA, Yaneva IS (1982) Excretion of DNA by human lymphocytes. (in Russian) Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biol 93:171–183
Feinendegen LE, Mühlensiepen H, Porschen W, Booz J (1982) Acute non-stochastic effect of very low-dose whole-body exposure, a thymidine equivalent serum factor. Int J Radiat Biol 41:139–150
Feinendegen LE, Bond VP, Booz J, Mühlensiepen H (1988) Biochemical and cellular mechanisms of low-dose effects. Int J Radiat Biol 53:23–37
Graubmann S, Dikomey E (1983) Induction and repair of DNA strand breaks in CHO cells irradiated in various phases of the cycle. Int J Radiat Biol 43:475–483
Greer WL, Kaplan JG (1983) DNA strand breaks in murine lymphocytes: induction by purine and pyrimidine analogues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 115:834–840
shii K, Murakami K, Muto N, Yamamoto I (1990) The effect of low-dose X-ray irradiation on the mitogen responses of rat splenocytes. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 31:66
Kuzin AM (1977) Stimulation effect of ionizing radiation on biological processes. (in Russian) Atomizdat, Moscow
Lloyd DC, Edwards AA, Leonard A, Deknudt GP, Natarajan AT, Obe G, Palitti F, Tanzarella C, Tawn EJ (1988) Frequencies of chromosomal aberrations induced in human blood lymphocytes by low doses of X-rays. Int J Radiat Biol 53:49–55
Luchnik NV, Sevankaev AV (1976) Radiation-induced chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocytes. 1. Dependence on the dose of gamma-rays and an anomaly at low doses. Mutat Res 36:363–369
McWilliams RS, Gross WG, Kaplan JG, Birnboim HC (1983) Rapid rejoining of DNA strand breaks in resting human lymphocytes after irradiation by low-doses of60Co γ-rays or 14.6-MeV neutrons. Radiat Res 94:499–507
Muto V, Halding J, Christiansen PL, Scott AC (1988) Solitons in DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn 5:873–894
Peimer SI, Dudkin AO, Sverdlov AG (1986) Response of hippocampal pacemarker-like neurons to low doses of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 49:597–600
Pohl-Rüling J, Fisher P, Haas O, Obe G, Natarajan AT, van Buul PPW, Buckton KE, Bianchi NO, Larramendy H, Kucerova M, Polivkova Z, Leonard A, Fabry L, Palitti F, Sharma T, Binder W, Mukherjee RN, Mukherjee U (1983) Effect of low-dose acute X-irradiation on the frequencies of chromosomal aberrations in human peripheral lymphocytes in vitro. Mutat Res 110:71–82
Pohl-Rüling J (1990) Chromosome aberrations of blood lymphocytes induced by low-level doses of ionizing radiation. In: Obe G (ed) Advances in mutagenesis research 2. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, 155–190
Polozov RV, Yakushevich LV (1988) Nonlinear waves in DNA and regulation of transcription. J Theor Biol 130:423–430
Shafer RH, Laiken N, Zimm BH (1974) Radial migration of DNA molecules in cylindrical flow. I Theory of the free-draining model. Biophys Chem 2:180–188
Sitko SP, Andreev EA, Dobronravova IS (1988) The whole as a result of selforganization. J Biol Phys 16:71–73
Swenberg CE (1989) Response to: Are solitons responsible for energy transfer in oriented DNA? Int J Radiat Biol 56:383–386
Uhlenhopp EL, Zimm BH (1973) Rotating cylinder viscosimeters. In: Hirs CHW, Timasheff SN (eds) Methods in enzymology 21. Academic Press, New York, pp 483–491
Webb SJ (1986) Newly developing approaches to disease: the crystal properties of living cells, their control over normal cell activities and role in oncogenic and virally induced malfunctions. IRCS Med Sci 14:98–103
Wolff S, Afzal V, Wiencke JK, Olivieri G, Michaeli A (1988) Human lymphocytes exposed to low doses of ionizing radiations become refractory to high doses of radiation as well as to chemical mutagents that induced double-strand breaks in DNA. Int J Radiat Biol 53:39–48
Yonezawa M, Takeda A, Misonoh J (1990) Acquired radioresistance after low-dose X-irradiation in mice. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 31:256–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belyaev, I.Y., Alipov, Y.D. & Yedneral, D.I. High sensitivity of chromatin conformational state of human leukocytes to low-dose X-rays. Radiat Environ Biophys 32, 99–107 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01212796
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01212796