Abstract
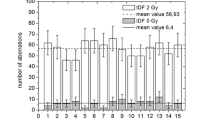
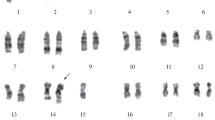
The variation in yield and the dose-response for chromatid aberration types following x-irradiation of Schistocerca gregaria embryo cells is described. Marked variations in yield are found for all aberration types during the G2 and latter part of S stages of interphase. Only gaps appear to follow similar curves, other aberration types having unique patterns of response. The dose exponents for the various chromatid aberration types are similar to, but lower than, those reported for other organisms. Chromatid “breaks” appear to have a dose exponent greater than 1.0 — a fact which is in conformation with the exchange hypothesis. The chromosome radiosensitivity of this organism is similar to that reported for other organisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brewen, J. G.: Kinetics of X-ray-induced chromatid aberrations in Vicia faba and studies relating aberration frequencies to the cell cycle. Mutation Res. 1, 400–408 (1964).
Carlson, J. G.: Immediate effects on division morphology and viability of the cell. In: Radiation biology (ed. A. Hollaender), vol. 1 (2), p. 763–824. New York: McGraw Hill Book Co. 1954.
Davies, D. R.: Radiation-induced chromosome aberrations and loss of reproductive integrity in Tradescantia. Radiation Res. 20, 726–740 (1963).
Dewey, W. C., R. M. Humphrey, and B. A. Jones: Comparisons of tritiated thymidine, tritiated water, and cobalt — 60 gamma rays in inducing chromosomal aberrations. Radiation Res. 24, 214–238 (1965).
Evans, H. J.: Chromatid aberrations induced by gamma-radiation. I. The structure and frequency of chromatid interchanges in diploid and tetraoplid cells of Vicia faba. Genetics 46, 257–275 (1961); - Chromosome aberrations induced by ionizing radiations. Int. Rev. Cytol. 13, 221–321 (1962); - Possible reasons for variation in chromosome radiosensitivity during mitotic and meiotic cycles. In: Repair from genetic radiation damage (ed. F. H. Sobels), p. 31–49. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1963a; - Chromosome aberrations and the target theory. In: Radiation-induced chromosome aberrations, (ed. S. Wolff), p. 8–40. New York: Columbia University Press 1963b; - Effects of radiations on meristematic cells. Radiat. Bot. 5, 171–182 (1965).
—, and D. Scott: Influence of DNA synthesis on the production of chromatid aberrations by X-rays and maleic hydrazide in Vicia faba. Genetics 49, 17–38 (1964).
Fox, D. P.: The effects of X-rays on the chromosomes of locust embryos. I. The early responses. Chromosoma (Berl.) 19, 300–316 (1966a); - The effects of X-rays on the chromosomes of locust embryos. II. Chromatid interchanges and the organisation of the interphase nucleus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 20, 173–194 (1966b); - The effects of X-rays on the chromosomes of locust embryos. III. The chromatid aberration types. Chromosoma (Berl.) 20, 396–412 (1967).
Grant, C. J.: Chromosome aberrations and the mitotic cycle in Trillium root tips after X-irradiation. Mutation Res. 2, 247–262 (1965).
McGrath, R. A.: X-ray-induced incorporation of tritiated thymidine into deoxyribonucleic acid of grasshopper neuroblast chromosomes. Radiat. Res. 19, 526–537 (1963).
Neary, G. J.: The relation between the exponent of dose response for chromosome aberrations and the relative contribution of “two-track” and “one-track” processes. Mutation Res. 2, 242–246 (1965).
Revell, S. H.: A new hypothesis for ‘chromatid’ changes. In: Proceedings of the radiobiology symposium, 1954 Liège (eds. Z. M. Bacq and P. Alexander). p. 243–253. London: Butterworth 1955; - The accurate estimation of chromatid breakage and its relevance to a new interpretation of chromatid aberrations induced by ionizing radiations. Proc. roy. Soc. B 150, 563–589 (1959); - An attempt at the continuous metaphase estimation of chromatid and chromosome aberration frequencies in broad bean root meristem cells in the period 2–23 h. after 50r of X-rays. Proc. Symp. on the effects of ionizing radiations on seeds, p. 229–242. Vienna: I.A.E.A. 1961; - Evidence for a dose-squared term in the dose-response curve for real chromatid discontinuities induced by X-rays, and some theoretical considerations thereof. Mutation Res. 3, 34–53 (1966).
Sax, K.: Types and frequencies of chromosomal aberrations induced by X-rays. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 9, 93–103 (1941).
Sisken, J. E., and L. Morasca: Intrapopulation kinetics of the mitotic cycle. J. Cell Biol. 25, 179–189 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fox, D.P. The effects of X-rays on the chromosomes of locust embryos. Chromosoma 20, 413–441 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394263
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394263