Abstract
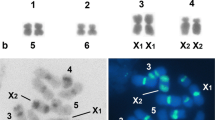
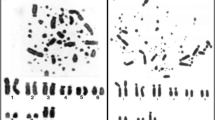
Chromosome measurements were performed in four species of snakes related at the level of suborder (Boa constrictor amarali, Xenodon merremii, Philodryas patagoniensis, Bothrops jararaca). The data obtained point out that pairs 1–3 were common to the four snakes and probably inherited from the ancestor of the suborder Serpentes. Pairs 5–8-W were characteristic of each snake; hence, it is possible to assume that they followed evolving after the appearing of the suborder Serpentes. Z-chromosomes were metacentric in B. constrictor amarali, X. merremii and B. jararaca and slightly submetacentric in P. patagoniensis. Area of these chromosomes varied from 8.6–10.6% of the haploid set in the four species studied.-The study of chromosome replication at the end of the S period points out that “shared chromosomes” have similar patterns of labeling. Therefore, it is proposed that the distribution of late replicating regions and heterochromatin in the genome is phylogenetically transmitted and probably genetically determined.—The analysis of the ending-sequence of chromosome replication shows that sex chromosomes finish earlier than macroautosomes. It is concluded that snakes probably have no mechanism of sex chromosome heterochromatinization in either sex. The absence of late replicating Z-chromosome in the males, favours the hypothesis that no mechanism of sex dosage compensation is acting in the suborder Serpentes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beçak, W.: Constituição cromossômica e mecanismo de determinação do sexo em ofídios sul-americanos. I. Aspectos cariotípicos. Mem. Inst. Butantan 32, 37–78 (1965).
—: Constituiçoã sex cromossômica e mecanismo de determinação doo em ofídios sul-americanos. II. Cromossomos sexuais e evolução do cariotípo. Mem. Inst. Butantan, Simp. Intern. 33, 775–798 (1966).
—, M. L. Beçak, and H. R. S. Nazareth: Karyotype studies of two species of South American snakes (Boa constrictor amarali and Bothrops jararaca). Cytogenetics 1, 305–313 (1962).
—: Chromosomes of snakes in short term cultures of blood leucocytes. Amer. Naturalist 97, 253–256 (1963).
Beçak, W., M. L. Beçak, H. R. S. Nazareth, and S. Ohno: Close karyological kinship between the reptilian suborder Serpentes and the class Aves. Chromosoma (Berl.) 15, 606–617 (1964).
—, and O. Peccinini: Chromosomes of cold-blood animals from whole blood short-term cultures. Microtechnique Mamm. Chrom. Newsl. 14, 55–56 (1964).
Bianchi, N. O., and O. J. Molina: Chronology and pattern of replication in the bone marrow chromosomes of Gallus domesticus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 21, 387–397 (1967a).
—: DNA replication patterns in somatic chromosomes of Leptodactylus ocellatus (Amphibia, Anura). Chromosoma (Berl.) 22, 391–400 (1967b).
—, A. Lima-de-faria, and H. Jaworska: A technique for removing silver grains and gelatin from tritium autoradiograms of human chromosomes. Hereditas (Lund) 31, 207–211 (1964).
Cattanach, B. M.: A chemically induced variegated-type position effect in the mouse. Z. Vererbungsl. 92, 165–182 (1961).
—, and J. H. Isaacson: Genetic control over the inactivation of autosomal attached to the X-chromosome. Z. Vererbungsl. 96, 313–323 (1965).
Evans, H. J., C. E. Ford, M. F. Lyon, and J. Gray: DNA replication and genetic expression in female mice with morphologically distinguishable X-chromosomes. Nature (Lond.) 206, 900–903 (1965).
Ford, C. F., and E. P. Evans: A reciprocal translocation in the mouse between the X-chromosome and a short autosome. Cytogenetics 3, 295–305 (1964).
Gustavsson, I., M. Fraccaro, L. Tiepolo, and J. Lindsten: Presumptive X-autosome translocation in a cow: preferential inactivation of the normal X chromosome. Nature (Lond.) 218 183–184 (1968).
Lima-de-faria, A., and H. Jaworska: Late DNA synthesis in heterochromatin. Nature (Lond.) 217, 138–142 (1968).
Martin, P. G., and D. L. Hayman: Quantitative comparison between the karyotypes of australian marsupials from three different superfamilies. Chromosoma (Berl.) 20, 290–310 (1967).
Ohno, S., W. Beçak, and M. L. Beçak: X-autosome ratio and the behavior pattern of individual X-chromosomes in placental mammals. Chromosoma (Berl.) 15, 14–30 (1964).
Schmid, W.: DNA replication patterns of the heterochromosomes in Gallus domesticus. Cytogenetics 1, 344–352 (1962).
Searle, A. G.: Is sex linked tabby really recesive in the mouse? Heredity 17, 297 (1962).
White, M. S. D.: Animal cytology and evolution, 2nd ed., 454 p. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1954.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was partially supported by Public Health Service Research grant No. GM-14577-03 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and by the Fundo de Pesquisas do Instituto Butantan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianchi, N.O., Beçak, W., de Bianchi, M.S.A. et al. Chromosome replication in four species of snakes. Chromosoma 26, 188–200 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326454
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326454