Summary
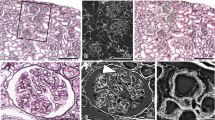
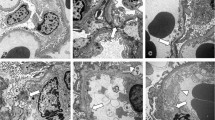
The ultrastructure of anionic sites in the lamina rara externa (LRE) of rat glomerular basement membrane (GBM) was studied in three dimensions by a quick-freezing and deep-etching method using polyethyleneimine (PEI) as a cationic tracer. Results were compared with those obtained with conventional ultrathin sections examined by transmission electron microscopy. Examination with the quick-freezing and deep-etching method was done without (group 1) or with (group 2) contrasting/fixation with a phosphotungstic acid and glutaraldehyde mixture and post-fixation with osmium tetroxide, which were necessary for visualization of PEI particles by conventional ultrathin sections. Using the quick-freezing and deep-etching method without following contrasting/fixation and post-fixation (group 1), many PEI particles were observed to decorate around fibrils, which radiated perpendicularly from the lamina densa to connect with the podocyte cell membrane. The arrangement of PEI particles was not as regular as that previously reported using conventional ultrathin sections. In contrast, the tissue that was studied with quick-freezing and deep-etching followed by contrasting/fixation and post-fixation (group 2) showed a shrunken appearance. The arrangement of PEI particles was regular (about 20 particles/1000 nm of LRE) as that previously observed using conventional ultrathin sections. However, the number of PEI particles on the LRE was markedly decreased and interruption of decorated fibrils was prominent, as compared with group 1. Ultrastructural examination using conventional ultrathin sections with contrasting/fixation and post-fixation (group 3) demonstrated PEI particles on the LRE in reasonable amounts (18–21 particles/1000 nm of LRE) with fairly regular interspacing (45–65 nm) as reported previously.
This is the first report to identify the three-dimensional ultrastructure of anionic sites of GBM, and provides new information on the location and distribution of anionic sites in the glomerular capillary wall. In addition, these studies suggest that several chemical procedures used in conventional transmission electron microscopy to visualize PEI tracers, may produce structural changes and disarrangement of PEI particles that can be avoided with the quick-freezing and deep-etching method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes JL, Venkatachalam MA (1985) The role of platelets and polycationic mediators in glomerular vascular injury. Semin Nephrol 5:57–68
Bastford SR, Rohrbach R, Vogt A (1987) Size restriction in the glomerular capillary wall: importance of lamina densa. Kidney Int 31:710–717
Caulfield JP, Farquhar MG (1974) The permeability of glomerular capillaries to graded dextran. J Cell Biol 63:883–903
Caulfield JP, Farquhar MG (1976) Distribution of anionic sites in glomerular basement membrane: their possible role in filtration and attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:1646–1650
Caulfield JP, Farquhar MG (1978) Loss of anionic sites from the glomerular basement membrane in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest 39:505–512
Heuser JE, Kirschner MW (1980) Filament organization revealed in platinum replicas of freeze-dried cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol 86:212–234
Hirokawa N, Heuser JE (1981) Quick-freeze, deep-etch visualization of the cytoskeleton beneath surface differentiations of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 9:399–409
Hirokawa N, Heuser JE (1982) The inside and outside of gap-junction membranes visualized by deep etching. Cell 30:395–406
Hora K, Ohno S, Oguchi H, Furuta T (1990) Three-dimensional study of glomerular slit diaphragm by the quick-freezing and deep-etching replica method. Eur J Cell Biol 53:402–406
Kanwar YS, Farquhar MG (1979a) Presence of heparan sulfate in the glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1303–1307
Kanwar YS, Farquhar MG (1979b) Isolation of glycosaminoglycans (heparan sulfate) from glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4493–4497
Kanwar YS, Farquhar MG (1979c) Anionic sites in the glomerular basement membrane. In vivo and in vitro localization to the laminae rarae by cationic probes. J Cell Biol 81:137–153
Kaysen GA, Myers BD, Couser WG, Rabkin R, Felts JM (1986) Biology of diseases. Mechanism and consequences of proteinuria. Lab Invest 54:479–498
Kubosawa H, Kondo Y (1985) Ultrastructural organization of the glomerular basement membrane as revealed by a deep-etch replica method. Cell Tissue Res 242:33–39
Naramoto A, Ohno S, Itoh N, Takami H, Nakazawa K, Shigematsu H (1990) Three-dimensional identification of actin filaments in phalloidin-treated rat livers by quick-freezing and deep-etching method. Virchows Archiv [A] 417:15–20
Ohno S (1985) Immunocytochemial study on the cytoplasmic side of cell membranes infected with vesicular stomatitis virus by quick-freezing and deep-etching replica method. Histochemistry 82:565–575
Ohno S, Takasu N (1989) Three-dimensional studies of cytoskeletal organization in cultured thyroid cells by quick-freezing and deep-etching method. J Electron Microsc 38:352–362
Ohno S, Fujii Y (1990) Three-dimensional and histochemical studies of peroxisomes in cultured hepatocytes by quick-freezing and deep-etching method. Histochem J 22:143–154
Reale E, Luciano L, Kuhn K-W (1983) Ultrastructural architecture of proteoglycans in the glomerular basement membrane. J Histochem Cytochem 31:662–668
Rennke HG, Cotran RS, Venkatachalam MA (1975) Role of molecular charge in glomerular permeability. Tracer studies with cationic ferritins. J Cell Biol 67:638–646
Schurer JW, Hoedemaeker PHJ, Molenaar I (1977) Polyethyleneimine as tracer particle for (immuno) electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 25:384–387
Schurer JW, Kalicharan D, Hoedemaeker PHJ, Molenaar I (1978) The use of polyethyleneimine for demonstration of anionic sites in basement membrane and collagen fibrils. J Histochem Cytochem 26:688–689
Schiller A, Taugner R (1980) Freeze-fracture and deep-etching with the volatile cryoprotectant ethanol reveals true membrane surfaces of kidney structures. Cell Tissue Res 210:57–69
Takami H, Naramoto A, Nakazawa K, Shigematsu H, Ohno S (1990) Ultrastructure of glomerular mesangial matrix by quick-freeze and deep-etch method. Kidney Int 38:1211–1215
Takami H, Naramoto A, Shigematsu H, Ohno S (1991) Ultrastructure of glomerular basement membrane by quick-freeze and deep-etch method. Kidney Int 39:659–664
Venkatachalam MA, Cotran RS, Karnovsky MJ (1970) An ultrastructural study of glomerular permeability in aminonucleoside nephrosis using catalase as a tracer protein. J Exp Med 132:1168–1180
Yoshimura A, Ideura T, Iwasaki S, Taira T, Koshikawa S, Nakano K, Oniki H (1989) Electron microscopic studies of the glomerulus in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. — An experimental model for investigating renal deposits in human IgA nephropathy. J Clin Electron Microsc 22:940–941
Yoshimura A, Ideura T, Nakano K, Oniki H, Sugisaki Y, Koshikawa S (1991) Recovery of anionic sites of the glomerular basement membrane after their disappearance by the cationic probe molecule. Nephron (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshimura, A., Ohno, S., Nakano, K. et al. Three-dimensional ultrastructure of anionic sites of the glomerular basement membrane by a quick-freezing and deep-etching method using a cationic tracer. Histochemistry 96, 107–113 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315980
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315980