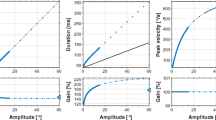
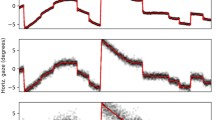
Abstract
New computation methods for removing saccades in analysis of smooth pursuit eye movement characteristics were developed. They have removed saccades more completely than previous methods, and were very effective especially for noisy data recorded by the EOG method. The fully developed method was applicable to eye movement data in tracking of pseudo-random target movement as well as deterministic target movement. Furthermore, the methods were also useful for extracting the number and magnitudes of saccades more precisely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahill AT, McDonald JD (1983a) Frequency limitation and optimal step size for the two-point central difference derivative algorithm with applications to human eye movement data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng BME-30:191–194
Bahill AT, McDonald JD (1983b) Model emulates human smooth pursuit system producing zero-latency target tracking. Biol Cybern 48:213–222
Bahill AT, Clark MR, Stark L (1975) Dynamic overshoot in saccadic eye movements is caused by neurological control signal reversals. Exp Neurol 48:107–122
Bahill AT, Iandolo MJ, Troost BT (1980) Smooth pursuit eye movement in response to unpredictable target waveforms. Vision Res 20:923–931
Bahill AT, Brockenbrough AE, Troost BT (1981) Variability and development of a normative data base for saccadic eye movements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 21:116–125
Bahill AT, Kallman JS, Lieberman JE (1982) Frequency limitations of the two-point central difference differentiation algorithm. Biol Cybern 45:1–4
Ebisawa Y, Minamitani H, Mori Y, Takase M (1987) Characteristic of saccade depend upon attention during tracking eye movement. Proceedings of the 9th IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp 1403–1406
Robinson DA (1963) A method of measuring eye movement using a scierai search coil in a magnetic field. IEEE Trans Biomed Electron BME-10:137–145
Robinson DA, Gordon JL, Gordon SE (1986) A model of the smooth pursuit eye movement system. Biol Cybern 55:43–57
Savitzky A, Golay MJE (1964) Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem 36:1627–1639
Schalén L (1980) Quantification of tracking eye movements in normal subjects. Acta Otolaryngol 90:404–413
Schalén L, Henriksson NG, Pyykkö I (1982) Quantification of tracking eye movements in patients with neurological disorders. Acta Otolaryngol 93:387–395
Troost BT, Daroff RB, Weber RB, Dell'Osso LF (1972) Hemispheric control of eye movements. II. Quantitative analysis of smooth pursuit in a hemispherectomy patient. Arch Neurol 27:449–452
Wolfe JW, Olson JW, Engelken EJ, Allen JP (1978) Cross-power spectral density analysis of pursuit tracking — evaluation of central and peripheral pathology. Ann Otol 87:837–844
Wyatt HJ, Pola J (1983) Smooth pursuit eye movements under open-loop and closed-loop conditions. Vision Res 23:1121–1131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebisawa, Y., Minamitani, H., Mori, Y. et al. New methods for removing saccades in analysis of smooth pursuit eye movement. Biol. Cybern. 60, 111–119 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202898
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00202898