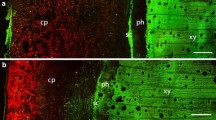
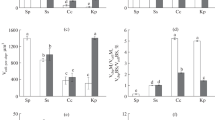
Abstract
Photosynthetic mechanisms have been compared in leaves and, separately, in stems of Egeria densa Planch. In order to correlate the structural and functional characteristics of the two organs (1) the ultrastructural features of leaves and stems have been studied and (2) their photosynthetic activity has been evaluated by measuring in vivo both oxygen evolution and the kinetics of chlorophyll fluorescence. The results confirm the aquatic behaviour of the leaf which is able to utilize inorganic C supplied both as CO2 and HCO −3 . In this respect, the different wall organization found in the two cell layers of the leaf is particularly interesting, since it could be related to the known polar mechanism of inorganic-C uptake. The stem, by contrast, behaves rather as an aerial organ, needing very high CO2 concentrations in the aquatic environment in order to carry out photosynthesis. In the stem, the aerenchyma plays a role in supplying the green cells with gaseous respiratory CO2, thus facilitating the photosynthetic activity of the submerged stems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1975) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. Am. Public Health Assoc., New York
Badger, M.R.I. (1987) The CO2-concentrating mechanism in aquatic phototrophs. In: The biochemistry of plants, vol. 10; Photosynthesis, pp. 219–274, Hatch, M.D., Boardman, N.K., eds. Academic Press, San Diego New York London
Beer, S., Israel, A. (1990) Photosynthesis of Ulva fasciata IV. pH, carbonic anhydrase and inorganic carbon conversions in the unstirred layer. Plant Cell Environ. 13, 555–560
Beer, S., Eshel, A., Waisel, Y. (1977) Carbon metabolism in seagrasses. I The utilization of exogenous inorganic carbon species in photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 28, 1180–1189
Björkman, O., Demmig, B. (1987) Photon yield of O2 evolution and Chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics at 77 K among vascular plants of diverse origin. Planta 170, 489–504
Bowes, G., Salvucci M.E. (1989) Plasticity in the photosynthetic carbon metabolism of submerged aquatic macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 34, 233–266
Elzenga, J.T.M., Prins, H.B.A. (1988) Adaptation of Elodea and Potamogeton to different inorganic carbon levels and the mechanism for photosynthetic bicarbonate utilization. Austr. J. Plant Physiol. 15, 727–735
Elzenga, J.T.M., Prins, H.B.A. (1989a) Light induced polar pH changes in leaves of Elodea canadensis. I Effects of carbon concentration and light intensity. Plant Physiol. 91, 62–67
Elzenga, J.T.M., Prins, H.B.A. (1989b) Light induced polar pH changes in leaves of Elodea canadensis. II Effects of ferricyanide: evidence for modulation by the redox state of the cytoplasm. Plant Physiol. 91, 68–72
Falk, H., Sitte, P. (1963) Zellfeinbau bei Plasmolyse. I Der Feinbau der Elodea Blattzellen. Protoplasma 57, 290–303
Franceschi, V.R., Lucas, W.J. (1980) Structure and possible function(s) of charasomes: Complex plasmalemma cell wall elaborations present in some characean species. Protoplasma 104, 253–271
Harche, R., Chandly, R., Catesson, M.A. (1990) Diversity of cellulose microfibril arrangement in the cell wall of Lygeum spartumleaves. Ann. Bot. 65, 79–86
Helder, R.J., Berma, J., Zanstra, P.E. (1980) Uptake pattern of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate by leaves of Potamogeton lucens L. Proc. K. Ned. Acad. Van Wet. Ser. C 83, 151–166
Inskeep, W.P., Bloom, P.R. (1985) Extinction coefficients of chlorophyll a and b in N,N-dimethylformamide and 80% acetone. Plant Physiol. 77, 483–485
Ishii, R., Yamagishi, T.Y., Murata, Y. (1977) On a method for measuring photosynthesis and respiration of leaf slices with an oxygen electrode. Jap. J. Crop. Sci. 46, 53–57
Kadono, Y. (1980) Photosynthetic carbon sources in some Potamogeton species. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 93, 185–194
Kitajima, M., Butler, W.L. (1975) Quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence and primary photochemistry in chloroplasts by dibromothymoquinone. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 376, 105–115
Lucas, W.J. (1983) Photosynthetic assimilation of exogenous HCO −3 by aquatic plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 34, 71–104
Lucas, W.J., Berry, J.A. (1985) Inorganic carbon transport in aquatic photosynthetic organisms. Physiol. Plant. 65, 539–543
Lucas, W.J., Brechignac, F., Mimura, T., Oross, J.W. (1989) Charasomes are not essential for photosynthetic utilization of exogenous HCO −3 in Chara corallina. Protoplasma 151, 106–114
Maberly, S.C., Spence, D.H.N. (1983) Photosynthetic inorganic carbon use by freshwater plants. J. Ecol. 71, 705–734
Marrè, M.T., Albergoni, F.G., Moroni, A., Marrè, E. (1989a) Light-induced activation of electrogenic H+ extrusion and K+ uptake in Elodea densa depends on photosynthesis and is mediated by the plasma membrane H+ ATPase. J. Exp. Bot. 40, 343–352
Marrè, M.T., Albergoni, F.G., Moroni, A., Pugliarello, M.C. (1989b) Evidence that H+ extrusion in Elodea densa leaves is mediated by an ATP-driven H+ pump. Plant Sci. 62, 21–28
Moran, R., Porath, D. (1980) Chlorophyll determination in intact tissues using N,N-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol. 65, 478–479
Neville, A.C. (1985) Molecular and mechanical aspects of helicoid development in plant cell walls. BioEssays 3, 4–8
Pate, J.S., Gunning, B.E.S. (1977) Transfer cells. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 23, 173–196
Pokorny, J., Ondok, J.P., Koncalová, H. (1985) Photosynthetic response to inorganic carbon in Elodea densa (Planchon) Caspary. Photosynthetica 19, 366–372
Price, G.D., Whitecross, M.I. (1983) Cytochemical localization of ATPase activity on the plasmalemma of Chara corallina. Protoplasma 116, 65–74
Prins, H.B.A., Elzenga, J.T.M. (1989) Bicarbonate utilization: Function and mechanism. Aquat. Bot. 34, 59–83
Prins, H.B.A., Snel, J.F.H., Zanstra, P.E., Helder, R.J. (1982) The mechanism of bicarbonate assimilation by the polar leaves of Potamogeton and Elodea. CO2 concentration at the leaf surface. Plant Cell Environ. 5, 207–214
Prins, H.B.A., Zanstra, P.E. (1985) Bicarbonate assimilation in aquatic angiosperms. Significance of the apoplast and unstirred layer. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 22, 2962–2967
Robert, D., Roland, J.C. (1989) Biologie Vegetale. I Organization cellulaire, Dom Editeurs, Paris
Roland, J.C., Vian, B., Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B., Mosiniak, M. (1987) Morphogenesis of plant cell walls at the supramolecular level: Internal geometry and versatility of helicoidal expression. Protoplasma 140, 75–91
Sand-Jensen, K. (1983) Photosynthetic carbon sources of stream macrophytes. J. Exp. Bot. 139, 198–210
Schreiber, U., Schliwa, U., Bilger, W. (1986) Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer. Photosynth. Res. 10, 51–62
Sorrell, K.B., Dromgoole, F.I. (1987) Oxygen transport in the submerged freshwater macrophyte Egeria densa Planch. I Oxygen production, storage and release. Aquat. Bot. 28, 63–80
Sorrell, K.B., Dromgoole, F.I. (1988) Oxygen transport in the submerged freshwater macrophyte Egeria densa Planch. II Role of lacunar gas pressure. Aquat. Bot. 31, 93–106
Staal, M., Prins, H.B.A., Van Harmelen, M., Helder, R.J. (1988) The isolation of leaf protoplasm from the submerged aquatic angiosperm Potamogeton lucens L. Plant Cell Environ. 11, 715–719
Titus, J.E., Stone, W.H. (1982) Photosynthetic response of two submerged macrophytes to dissolved inorganic carbon concentration and pH. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27, 151–160
Walker, N.A. (1983) The uptake of inorganic carbon by freshwater plants. Plant Cell Environ. 6, 323–328
Williams, W.T., Barber, D.A. (1961) The functional significance of aerenchyma in plants. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 15, 132–144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are grateful to C.U.G.A.S. (University of Padua) for the use of the scanning electron microscope. They also wish to thank Mr. Claudio Furlan and Mr. Giorgio Varotto for helpful technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from C.N.R. and M.P.I, and was developed within the cooperation agreement between the Universities of Padova (Italy) and Innsbruck (Austria).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rascio, N., Mariani, P., Tommasini, E. et al. Photosynthetic strategies in leaves and stems of Egeria densa . Planta 185, 297–303 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201047
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201047