Abstract
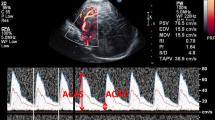
In a controlled study serial determinations of cerebral blood flow velocity using Doppler ultrasound and repeated real-time ultrasonographic- or computerized axial tomographic studies of the brain were performed in 17 (nearly) full-term newborns who experienced perinatal asphyxia and in 17 healthy matched controls during the first week of life. A higher cerebral blood flow velocity was found during the first 4 days of life, indicating a lower cerebrovascular resistance in the asphyxiated infants compared to the control infants. These haemodynamic changes coincided with cerebral oedema and neurological abnormalities. It is speculated that the changes in the cerebral circulation in asphyxiated infants are at least partly caused by cerebral oedema-induced increase of intracranial pressure due to severe perinatal asphyxia. Serial Doppler ultrasound investigations of the brain may be a useful non-invasive method for early detection and follow-up of the consequences of severe perinatal asphyxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACA:
-
anterior cerebral artery
- AUVC:
-
area under the velocity curve
- CT:
-
computerized axial tomography
- EDFV:
-
end diastolic flow velocity
- HIE:
-
hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy
- PI:
-
pulsatility index
- PSFV:
-
peak systolic flow velocity
References
Ahmann PA, Dykes FD, Lazzara A, Holt PHJ, Giddens DP, Carrigan TA (1983) Relationship between pressure passivity and subependymal/intraventricular hemorrhage as assessed by Doppler ultrasound. Pediatrics 72:665–669
Allan WC, Philip AGS (1985) Neonatal cerebral pathology diagnosed by ultrasound. Clin Perinatol 12:195–218
Allan WC, Holt PHJ, Sawyer LR, Tito AM, Kellogmeade S (1982) Ventricular dilation after neonatal periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage. Am J Dis Child 136:589–593
Alvisi C, Cerisoli M, Giulioni M, Monari P, Salvioli GP, Sandri F, Lippi C, Bovicelli L, Pilu G (1985) Evaluation of cerebral blood flow changes by transfontanelle Doppler ultrasound in infantile hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 1:244–247
Archer LNJ, Evans DH, Levene MI (1985) Doppler ultrasound examination of the anterior cerebral arteries of normal infants: the effect of postnatal age. Early Hum Dev 10:255–260
Archer LNJ, Evans DH, Paton JY, Levene MI (1986) Controlled hypercapnia and neonatal cerebral artery Doppler ultrasound waveforms. Pediatr Res 20:218–221
Bada HS, Sumner DS (1984) Transcutaneous Doppler ultrasound: pulsatility index, mean flow velocity, end diastolic flow velocity, and cerebral blood flow. J Pediatr 104:395–397
Bada HS, Hajjar W, Chua C, Sumner DS (1979) Non-invasive diagnosis of neonatal asphyxia and intraventricular hemorrhage by Doppler ultrasound. J Pediatr 95:775–779
Ballard JL, Kazmaier-Novak K, Driver M (1979) A simplified score for assessment of fetal maturation of newly born infants. J Pediatr 95:769–774
Barks J, Hellmann J, Daneman A (1985) The spectrum of sonographic findings in full-term asphyxia. Pediatr Res 19:387A
Batton DG, Hellmann J, Hernandez MJ, Mabels MJ (1983) Regional cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood velocity, and pulsatility index in newborn dogs. Pediatr Res 17:908–912
Bel F van, Bor M van de (1985) Cerebral edema caused by perinatal asphyxia, detection and follow-up. Helv Paediatr Acta 40:361–369
Bel F van, Hirasing RA, Grimberg MTT (1984) Can perinatal asphyxia cause cerebral edema and effect cerebral blood flow velocity? Eur J Pediatr 149:29–32
Bel F van, Bor M van de, Buis-Liem TN, Stijnen TH, Baan J, Ruys JH (1987) The relation between left to right shunt due to patent ductus arteriosus and cerebral blood flow velocity in preterm infants. J Cardiovasc Ultr Son 6:19–25
Brann AW, Dykes FD (1977) The effects of intrauterine asphyxia on the full-term neonate. Clin Perinatol 4:149–161
Clifford SH (1941) The effects of asphyxia on the newborn infant. J Pediatr 18:567–578
Cooper R, Winchester P, Brill P (1984) Head ultrasound: unsuspected ventricular configurations in healthy newborn infants. Pediatr Res 18:317A
Fishman RA (1975) Brain edema. N Engl J Med 2:706–711
Fitzhardinge PM, Flodmark O, (1981) The prognostic value of computed tomography as an adjunct to assessment of the term infant with postasphyxial encephalopathy. J Pediatr 99:777–781
Flodmark O, Becker LE, Harwood-Nash DC, Fitzhardinge PM, Fitz CR, Chuang SH (1980) Correlation between CT and autopsy in premature and full-term neonates that have suffered perinatal asphyxia. Radiology 137:93–103
Friis-Hansen B (1985) Perinatal brain injury and cerebral blood flow in newborn infants. Acta Pediatr Scand 74:323–331
Gelmers HJ (1980) Regulatie van de cerebrale circulatie. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 26:1065–1069
Goitein KJ, Amit Y, Mussaffi H (1983) Intracranial pressure in central nervous system. Infarctions and cerebral ischaemia of infancy. Arch Dis Child 58:184–186
Gray PH, Griffin EA, Drumm JE, Fitzgerald DE, Duignan NM (1983) Continuous wave Doppler ultrasound in evaluation of cerebral blood flow in neonates. Arch Dis Child 58:677–681
Greisen G, Johansen K, Ellison PH, Fredriksen PS, Mali J, Friis-Hansen B (1984) Cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant: comparison of Doppler ultrasound and Xenon/clearance. J Pediatr 104:411–418
Hill A, Martin DJ, Daneman A, Fitz CR (1983) Focal ischemic cerebral injury in the newborn: diagnosis by ultrasound and correlation with computed tomographic scan. Pediatrics 71:790–793
Huber P, Handa JH (1967) Effect of contrast material, hypercapnia, hyperventilation, hypertonic glucose and papaverine on the diameter of the cerebral arteries. Invest Radiol 2:17–32
Ignelzi RJ (1979) Cerebral edema: present perspectives. Neurosurgery 4:338–342
Levene MI, Evans DH (1983) Continuous measurement of subarachnoid pressure in the severely asphyxiated newborn. Arch Dis Child 58:1013–1015
Levene MI, Williams JL, Fawer CL (1985) Ultrasound of the infant brain. Clin Develop Med 92:62–75
Lipp-Zwahlen AE, Deonna T, Chrzanowski R, Micheli JL, Calame A (1985) Temporal evolution of hypoxic-ischaemic brain lesions in asphyxiated full-term newborns as assessed by computerized tomography. Neuroradiology 27:138–144
Martin DJ, Hill A, Fitz CR, Daneman DA, Havill DA, Becker LE (1983) Hypoxic/ischemic cerebral injury in the neonatal brain. Pediatr Radiol 13:307–312
Matakas F (1978) The interrelationship between cerebral micro circulation and intracranial pressure. In: Baan J, Noordergraaf A, Raines J (eds) Cardiovascular system dynamics. The MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, pp 224–229
McHedlishvili GI (1980) Physiological mechanisms controlling cerebral blood flow. Stroke 11:240–248
Perlman JM, Herscovitch P, Corriveau S, Raichle M, Volpe JJ (1985) The relation of cerebral blood flow velocity determined by Doppler, to regional cerebral blood flow, determined by positron emission tomography. Annual Meeting of the Society for Pediatric Research, Washington, May 9
Pourcelot L (1974) Applications cliniques de l'examen Doppler transcutane. In: Peronneau P (ed) Vélocimètre ultrasonore Doppler. INSERM, Paris, p 213
Raju THK, Vidyasagar D, Papazafiratou C (1981) Cerebral perfusion pressure and abnormal intracranial pressure wave form: their relation to outcome in birth asphyxia. Crit Care Med 9:449–453
Rudolph AM (1983) Circulatory changes during the perinatal period. Pediatr Cardiol 4:17–20
Shankaran K, Peters K, Finer NN (1981) Estimated cerebral blood flow in term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res 15:1415–1418
Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS (1976) Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress. Arch Neurol 33:696–705
Sauerbrei EE, Digney M, Harrison PB, Cooperberg PL (1981) Ultrasonic evaluation of neonatal intracranial hemorrhage and its complications. Radiology 139:677–685
Sheehy-Skeffington F, Pearse RG (1983) The “bright brain”. Arch Dis Child 58:509–511
Siegel MJ, Patel J, Gado MH, Shackel-Ford GD (1983) Cranial computed tomography and real-time sonography in full-term neonates and infants. Radiology 149:111–116
Slovis TL, Shankaran S (1984) Ultrasound in the evaluation of hypoxic-ischemic injury and intracranial hemorrhage in neonates: the state of the art. Pediatr Radiol 14:67–75
Smith SJ, Vogelzang RL, Marzand MI, Cerullo JJ, Gore RM, Neiman HL (1985) Brain edema: ultrasound examination. Radiology 155:379–382
Walther FJ, Siassi B, Ramadan NA, Wu PYK (1985) Cardiac output in newborn infants with transient myocardial dysfunction. J Pediatr 107:781–785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Bel, F., van de Bor, M., Stijnen, T. et al. Cerebral blood flow velocity pattern in healthy and asphyxiated newborns: a controlled study. Eur J Pediatr 146, 461–467 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441595
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441595