Summary
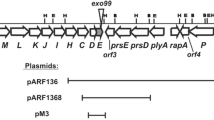
A Tn5-induced mutant strain of R. phaseoli which failed to synthesize exopolysaccharide (EPS) was isolated and was shown to induce normal nitrogen-fixing nodules on Phaseolus beans, the host of this Rhizobium species. The corresponding wild-type Rhizobium DNA was cloned in a wide host-range vector and by isolating Tn5 insertions in this cloned DNA, mutations in a gene termed pss (polysaccharide synthesis) were isolated. These were introduced by marker exchange into near-isogenic strains of R. leguminosarum and R. phaseoli which differed only in the identity of their symbiotic plasmids. Whereas the EPS-deficient mutant strain of R. phaseoli induced normal nitrogen-fixing nodules on Phaseolus beans, the same mutation prevented nodulation of peas by a strain of R. leguminosarum which normally nodulates this host. Further, it was found that DNA cloned from the plant pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pathover campestris could correct the defect in EPS synthesis in R. leguminosarum and R. phaseoli and also restored the ability to nodulate peas to the pss::Tn5 mutant strain of R. leguminosarum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Chakravorty AK, Zurkowski W, Shine J, Rolfe BG (1982) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation: molecular cloning of Rhizobium genes involved in exopolysaccharide synthesis and effective nodulation. J Mol Appl Genet 1:585–596
Daniels MJ, Barber CE, Turner PC, Sawzyc MK, Byrde RJW, Fielding AH (1984) Cloning of genes involved in pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris using the broad host range cosmid pLAFR1. EMBO J 3:3323–3328
Downie JA, Hombrecher G, Ma Q-S, Knight CD, Wells B, Johnston AWB (1983a) Cloned nodulation genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum determine host range specificity. Mol Gen genet 190:359–365
Downie JA, Ma Q-S, Knight CD, Hombrecher G, Johnston AWB (1983b) Cloning of the symbiotic region of Rhizobium leguminosarum: the nodulation genes are between the nitrogenase genes and a nifA-like gene. EMBO J 2:947–952
Figurski DH, Helinski DR (1979) Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1648–1652
Friedman AM, Long SR, Brown SE, Buikema WJ, Ausubel FM (1982) Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene 18:289–296
Hewitt EJ, Smith TA (1975) Plant mineral nutrition. English Universities Press London, pp 31–36
Hombrecher G, Brewin NJ, Johnston AWB (1981) Linkage of genes for nitrogenase and nodulation ability on plasmids in Rhizobium leguminosarum and R. phaseoli. Mol Gen Genet 182:133–136
Jorgensen RA, Rothstein SJ, Reznikoff WS (1979) A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet 177:65–72
Leigh JA, Singer ER, Waker GC (1985) Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6231–6235
Merrick M, Filser M, Kennedy C, Dixon R (1978) Polarity of mutations induced by insertion of transposons Tn5, Tn7 and Tn10 into the nif gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet 165:103–111
Lamb JW, Hombrecher G, Johnston AWB (1982) Plasmid-determined nodulation and nitrogen fixation abilities in Rhizobium phaseoli. Mol Gen Genet 186:449–452
Lamb JW, Downie JA, Johnston AWB (1985) Cloning of the nodulation (nod) genes of Rhizobium phaseoli and their homology to R. leguminosarum nod genes. Gene 34:235–241
Ruvkun GB, Ausubel FM (1981) A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in procaryotes. Nature 289:85–88
Sanders R, Raleigh E, Signer E (1981) Lack of correlation between extracellular polysaccharide and nodulation ability in Rhizobium. Nature 292:148–149
Sandford PA, Baird J (1983) In: Aspinall GO (Ed) The polysaccharides. Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 411–490
Sutherland IW (1985) Biosynthesis and composition of Gram negative bacterial extracellular and wall polysaccharides. Ann Rev Microbiol 39:243–270
Wood WB (1966) Host specificity of DNA produced by E. coli bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol 16:118–133
Young JPW (1985) Rhizobium population genetics: enzyme polymophism in isolates from peas, clover, beans and lucerne grown at the same site. J Gen Microbiol 131:2399–2408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. Auerbach
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borthakur, D., Barber, C.E., Lamb, J.W. et al. A mutation that blocks exopolysaccharide synthesis prevents nodulation of peas by Rhizobium leguminosarum but not of beans by R. phaseoli and is corrected by cloned DNA from Rhizobium or the phytopathogen Xanthomonas . Molec Gen Genet 203, 320–323 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333974
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333974