Summary
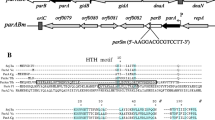
We report here the existence and initial characterization of a genetic locus (imp) that inhibits maintenance of SLP1-derived plasmids as extrachromosomal replicons in a manner distinct from normal incompatibility between autonomous SLP1 replicons. Thetrans-actingimp function has been localized to a 1.8 kbEco47III restriction fragment present on integrated SLP1 elements. At least part of this DNA segment is absent from SLP1-derived plasmids. DNA sequence analysis of theimp region indicates that it contains three overlapping open reading frames (ORFs) that may constitute a polycistronic operon. The effects of insertions within theimp region indicate that uninterrupted transcription through all three ORFs is necessary forimp activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bibb MJ, Cohen SN (1982) Gene expression inStreptomyces: construction and application of promoter-probe plasmid vectors inStreptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet 187:265–272
Bibb MJ, Freeman RF, Hopwood DA (1977) Physical and genetic characterization of a second sex factor SCP2 forStreptomyces coelicolor A32. Mol Gen Genet 154:155–166
Bibb MJ, Ward JM, Kieser T, Cohen SN, Hopwood DA (1981) Excision of chromosomal DNA sequences fromStreptomyces coelicolor forms a novel family of plasmids detectable inStreptomyces lividans. Mol Gen Genet 184:230–240
Bibb MJ, Findlay PR, Johnson MW (1985) The relationship between base composition and codon usage in bacterial genes and its use for the simple and reliable identification of protein-coding sequences. Gene 30:157–166
Chang ACY, Cohen SN (1978) Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol 134:1141–1156
Das A, Yanofsky C (1984) A ribosome binding site sequence is necessary for efficient expression of the distal gene of a translationally-coupled gene pair. Nucleic Acids Res 12:4757–4768
Enquist LW, Bradley SG (1970) Characterization of deoxyribonucleic acid fromStreptomyces venezueleae. Dev Ind Microbiol 12:225–236
Froehlich BJ, Tatti K, Scott JR (1983) Evidence for positive regulation of plasmid prophage P1 replication: integrative suppression by copy mutants. J Bacteriol 156:205–211
Grant SR (1986) Characterization of a gene encoded by the SLP1 integrated element ofStreptomyces coelicolor that inhibits maintenance of SLP1 plasmids. Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University
Hopwood DA, Kieser T, Wright HM, Bibb MJ (1983) Plasmids recombination and chromosome mapping in Streptomyces lividans 66. J Gen Microbiol 129:2257–2269
Hopwood DA, Bibb MJ, Chater KF, Kieser T, Bruton CJ, Kieser HM, Lydiate DJ, Smith CP, Ward JM, Schrempf H (1985) Genetic manipulation ofStreptomyces. A laboratory manual. John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK
Hsiang MW, Cole RD, Takeda Y, Echols TH (1977) Amino acid sequence of the Cro regulatory protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature 270:275–277
Jaurin B, Cohen SN (1984)Steptomyces lividans RNA polymerase recognizes and usesEscherichia coli transcription signals. Gene 28:83–91
Kendall KJ, Cohen SN (1988) Complete nucleotide sequence of theSteptomyces lividans plasmid pIJ101 and correlation of the sequence with genetic properties. J Bateriol 170:4634–4651
Kieser T, Hopwood DA, Wright HM, Thompson C (1982) pIJ101, a multi-copy broad host-rangeStreptomyces plasmid: functional analysis and development of DNA cloning vectors. Mol Gen Genet 185:223–238
Lee SC, Grant SR, Cohen SN (1988) SLP1 genes and sites involved in the integration of the element into the genome ofStreptomyces lividans. In: Okami Y, Beppu T, Ogawara H (eds) Biology of Actinomycetes ’88. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 123–126
Lydiate DJ, Malpartida F, Hopwood DA (1985) TheStreptomyces plasmid SCP2*: its functional analysis and development into useful cloning vectors. Gene 35:223–235
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Matthews BW, Ohlendohrf DH, Anderson WF, Takeda Y (1982) Structure of the DNA-binding region oflac repressor inferred from its homology withcro repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:1428–1432
Ogawa TO, Tomizawa J-I (1967) Abortive lysogenization of bacteriophage lambda b2 and residual immunity of non-lysogenic segregants. J Mol Biol 23:225–245
Omer CA, Cohen SN (1984) Excision and integration of the SLP1 replicon at a specific chromosomal site. Mol Gen Genet 196:429–438
Omer CA, Cohen SN (1985) SLP1: A transmissibleStreptomyces chromosomal element capable of site-specific integration, excision and autonomous replication. In: Schlessinger D (ed) Microbiology 1985. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 449–453
Omer CA, Cohen SN (1986) Structural analysis of plasmid and chromosomal loci involved in site-specific excision and integration of the SLP1 element ofStreptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 166:999–1006
Omer CA, Stein D, Cohen SN (1988) Site-specific insertion of biologically functional adventitious genes into theStreptomyces lividans chromosome. J Bacteriol 170:2174–2184
Oppenheim DS, Yanofsky C (1980) Translational coupling during expression of the tryptophan operon ofEscherichia coli. Genetics 95:785–795
Pabo CO, Sauer RT (1984) Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem 53:293–321
Sanger F, Micklin S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Sauer RT (1978) DNA sequence of the bacteriophage lambdacI gene. Nature 270:301–302
Sinclair RB, Bibb MJ (1988) The repressor gene (c) of theStreptomyces temperate phage ϕ C31: nucleotide sequence, analysis and functional cloning. Mol Gen Genet 213:269–272
Thomas R, Bertani LE (1964) On the control of the replication of temperate bacteriophages superinfecting immune hosts. Virology 24:241–253
Thompson CJ, Kieser T, Ward JM, Hopwood DA (1982a) Physical analysis of antibiotic resistance genes fromStreptomyces and their use in vector construction. Gene 20:51–62
Thompson CJ, Ward JM, Hopwood DA (1982b) Cloning of antibiotic resistance and nutritional genes inStreptomyces. J Bacteriol 151:668–677
Yamaguchi K, Tomizawa J (1980) Establishment of anEscherichia coli cell with an integrated high copy number plasmid. Mol Gen Genet 178:525–533
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of M13 mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Goebel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grant, S.R., Lee, S.C., Kendall, K. et al. Identification and characterization of a locus inhibiting extrachromosomal maintenance of theStreptomyces plasmid SLP1. Molec. Gen. Genet. 217, 324–331 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02464900
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02464900