Abstract
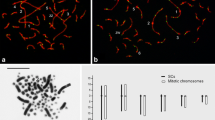
The retinal rod Na-Ca+K exchanger is a unique calcium extrusion protein found only in the outer segments of retinal rod photoreceptors. Rod Na-Ca+K exchanger cDNA (NCKX1) has been cloned from bovine and human retinas. Here, we have used fluorescent in situ hybridization and radiation hybrid mapping to localize the human NCKX1 gene to chromosome 15q22. We have determined the genomic organization of human rod NCKX1 and found one intron in the 5’ untranslated region and eight introns within the coding region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 June 1998 / Accepted: 24 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tucker, J., Winkfein, R., Murthy, S. et al. Chromosomal localization and genomic organization of the human retinal rod Na-Ca+K exchanger. Hum Genet 103, 411–414 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050842
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050842