Abstract
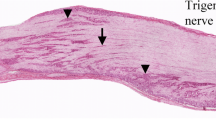
We demonstrate the existence of nerve fibers possessing substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactivity in the mouse cervical ventral roots. The distribution of the SP and CGRP fibers was similar, but CGRP fibers were generally more numerous. Both types entered the ventral pia mater or formed hairpin loops, but they did not enter the spinal cord directly through these roots. SP and CGRP fibers in the ventral roots were thin and had many varicosities. We suggest that these SP and CGRP fibers are involved not only in a sensory mechanism, but also in other functions, via the release of SP and CGRP from varicosities in the ventral roots.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez FJ, Cerrantes C, Blasco I, Villalba R, Martinez-Murillo R, Polak JM, Rodrigo J (1988) Presence of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) immunoreactivity in intraepidermal free nerve endings of cat skin. Brain Res 442:391–395
Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG (1982) Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature 298:240–244
Applebaum ML, Clifton GL, Coggeshall RE, Coulter JD, Vance WH, Willis WD (1976) Unmyelinated fibres in the sacral 3 and caudal 1 ventral roots of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 256:557–572
Azerad J, Hunt CC, Laporte Y, Pollin B, Thiesson D (1986) Afferent fibres in cat ventral roots: electrophysiological and histological evidence. J Physiol (Lond) 379:229–243
Bell C (1811) Idea of a new anatomy of the brain. Reprinted in: Cranefield PF (ed) The Way In and the Way Out. Strahan and Preston, London, 1974
Bjurholm A, Kreicbergs A, Schultzberg M (1989) Fixation and demineralization of bone tissue for immunohistochemical staining of neuropeptides. Calcif Tissue Int 45:227–231
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Clifton GL, Vance WH, Applebaum ML, Coggeshall RE, Willis WD (1974) Responses of unmyelinated afferents in the mammalian ventral root. Brain Res 82:163–167
Coggeshall RE, Ito H (1977) Sensory fibres in ventral roots L7 and S1 in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 267:215–235
Coggeshall RE, Coulter JD, Willis WD (1973) Unmyelinated fibers in the ventral root. Brain Res 57:229–233
Coggeshall RE, Coulter JD, Willis WD (1974) Unmyelinated axons in the ventral roots of the cat lumbosacral enlargement. J Comp Neurol 153:39–58
Coggeshall RE, Emery DG, Ito H, Maynard CW (1977) Unmyelinated and small myelinated axons in rat ventral roots. J Comp Neurol 173:175–184
Cunnane TC, Stjarne L (1984) Transmitter secretion from individual varicosities of guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens: highly intermittent and monoquantal. Neuroscience 13:1–20
Dalsgaard CJ, Risling M, Cuello C (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of substance P in the lumbosacral spinal pia mater and ventral roots of the cat. Brain Res 246:168–171
Edvinsson L, Uddmann R (1982) Immunohistochemical localization and dilatory effect of substance P in human cerebral vessels. Brain Res 232:466–471
Fang XB (1987) The population of the dorsal root ganglion cells which have central processes in ventral root and thier immunoreactivity. Brain Res 402:393–398
Gibson SJ, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Sabatr IM, Mulderry PM, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Morrison JFB, Kelly JS, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and of eight other species. J Neurosci 4:3101–3111
Häbler HJ, Janig W, Koltzenburg M, McMahon SB (1990) A quantitative study of the central projection patterns of unmyelinated ventral root afferents in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 422:265–287
Hsu SM, Reine L (1981) Protein A, avidin and biotin in immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 29:1349–1353
Isida-Yamamoto A, Tohyama M (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the nervous tissue. Prog Neurobiol 33:335–386
Kato M, Tanji J (1971) Physiological properties of sensory fibers in the spinal ventral roots in the cat. Jpn J Physiol 21:71–77
Kim J, Shin HK, Chung JM (1987) Many ventral root afferent fibers in the cat are third branches of dorsal root ganglion cells. Brain Res 417:304–314
Kimura M, Ohtsuki T, Abe T, Yanai T, Kishida R, Goris RC (1992) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive nerve fibers in the mouse ventral root. Regul Pept Abstr 1:S90
Lee Y, Kawai Y, Shiosaka S, Takami K, Kiyama H, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1985) Coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P-like peptide in single cells of the trigeminal ganglion of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res 330:194–196
Light AR, Metz CB (1978) The morphology of the spinal cord efferent and afferent neurons contributing the ventral roots of the cat. J Comp Neurol 179:501–516
Magendie F (1822) Expériences sur les fonctions des racines des nerfs rachidiens. J Physiol Exp Pathol 2:276–279. Reprinted in: Cranefield PF (ed) The Way In and the Way Out. Strahan and Preston, London, 1974
Maynard CW, Leonard RB, Coulter JD, Coggeshall RE (1977) Central connections of ventral root afferents as demonstrated by the HRP method. J Comp Neurol 172:601–608
Oku R, Satoh M, Fujii N, Otaka A, Yajima H, Takagi H (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes mechanical nociception by potentiating release of substance P from the spinal dorsal horn in rats. Brain Res 403:350–354
Risling M, Hildebrand C (1982) Occurrence of unmyelinated axon profiles at distal, middle and proximal levels in the ventral root L7 of cats and kittens. J Neurol Sci 56:219–231
Risling M, Dalsgaard CJ, Cukierman A, Cuello AC (1984) Electron microscopic and immunohistochemical evidence that unmyelinated ventral root axons make U-turn or enter the spinal pia mater. J Comp Neurol 225:53–63
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 304:129–135
White DM, Helme RD (1985) Release of substance P from peripheral nerve terminals following electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve. Brain Res 336:27–31
Zamboni L, De Martino C (1967) Buffered picric acid-formaldehyde: a new, rapid fixative for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 35:148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, M., Kishida, R., Abe, T. et al. Nerve fibers immunoreactive for substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the cervical spinal ventral roots of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res 277, 273–278 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327774