Summary
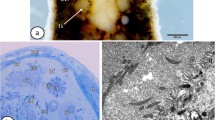
The homologue of mammalian Leydig cells in the testis of fish of the genus Gobius is believed to be a glandular mass lying along the mesorchium and quite distinct from the seminiferous region. This gland was studied in Gobius jozo by light and electron microscopy. Histologically, the gland is composed of cords of polyhedral cells located between the main vessels of the testis and the deferent duct. Dark and light cell varieties were observed both after staining with toluidine blue and with respect to their cytoplasmic electron density. The fine structure of the glandular cells is characterized by a well developed agranular endoplasmic reticulum in the form of random anastomosing tubules and vesicles and by very numerous mitochondria with tubulo-vesicular cristae. In some mitochondria the internal organization is paracrystalline. One or two bodies of unknown nature are Found in the Golgi region. They are partially limited by an unusually thick membrane and contain a material subdivided mostly into small vesicles. Liposomes and lipofuscin pigment granules are also present.
The ultrastructural features of the glandular cells of the testis of Gobius jozo confirm a specialization in steroid hormone production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bara, G.: Histochemical demonstration of 3β-, 3α-, 11β-, and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in the testis of Fundulus heteroclitus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 13, 189–200 (1969)
Bara, G.: Histochemistry of hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in the testis, adrenocortical tissue, and corpuscles of Stannius of Pseudopleuronectes americanus. Acta histochem. Bd. 44, S. 333–347 (1972)
Chieffi, G.: Comparative endocrinology of the vertebrate testis. Am. Zoologist 12, 207–211 (1972)
Chieffi, G., Botte, V.: Osservazioni sul significato funzionale della ghiandola annessa del testicolo dei Blennidii. Boll. Zool. 31, 471–477 (1964)
Christensen, A. K., Gillim, S. W.: The correlation of fine structure and function in steroidsecreting cells, with emphasis on those of the gonads. In: The Gonads (McKerns, K. W., ed.), p. 415–488. Amsterdam: N-Holland Publishing Company (1969)
Colombo, L., Lupo di Prisco, C., Binder, G.: Metabolism of pregnenolone-4-14C by the testis of Gobius paganellus (Teleostei). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 15, 404–419 (1970)
Courrier, R.: Sur l'existence d'une glande interstitielle dans le testicule des Poissons. C. R. Soc. Biol. (Paris) 85, 939–941 (1921)
Delrio, G., Botte, V., Chieffi, G.: Identification of the Leydig-cell homologue in the testis of certain teleost fishes through histoenzymatic reactions. Enzyme Histochemistry. Istituto Lombardo, Fondazione Baselli, p. 3–4 (1967)
Follenius, E.: Cytologie et cytophysiologie des cellules de l'Epinoche: Gasterosteus aculeatus L. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 11, 198–219 (1968)
Follenius, E., Porte, A.: Cytologie fine des cellules interstitielles du testicule du poisson Lebistes reticulatus R. Experientia 16, 190–191 (1960)
Giacomelli, F., Wiener, J., Spiro, D.: Cytological alteration related to stimulation of the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal gland. J. Cell Biol. 26, 499–521 (1965)
Gresik, E. W., Quirk, J. G., Hamilton, J. B.: A fine structural and histochemical study of the Leydig cell in the testis of the teleost, Oryzias latipes (Cyprinidontiformes). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 20, 86–98 (1973)
Kolmer, W., Scheminzky, F.: Finden sich Zwischenzellen nur bei höheren Wirbeltieren ? Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 194, 352–361 (1922)
Lockwood, W. R.: A reliable and easily sectioned epoxy embedding medium. Anat. Rec. 150, 129–140 (1964)
Lofts, B., Bern, H. A.: The functional morphology of steroidogenic tissues. In: Steroids in nonmammalian Vertebrates (Idler, D. R., ed.), p. 37–125. New York and London: Academic Press (1972)
Marshall, A. J., Lofts, B.: The Leydig cell homologue in certain teleost fishes. Nature (London) 177, 704–705 (1956)
O'Halloran, M. J., Idler, D. R.: Identification and distribution of the Leydig cell homolog in the testis of sexually mature Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 15, 361–364 (1970)
Oota, I., Yamamoto, K.: Interstitial cells in the immature testes of the rainbow trout. Annot. Zool. Jap. 39, 142–148 (1966)
Picheral, B.: Les tissus élaborateurs d'hormones stéroïdes chez les amphibiens urodèles. IV. Étude en microscopie électronique et photonique du tissu glandulaire du testicule et de la glande interrénal après hypophysectomie, chez Pleurodeles waltlii Michah. Z. Zellforsch. 107, 68–86 (1970)
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Sabatini, D. D., de Robertis, E. D., Bleichmar, H. B.: Submicroscopic study of the pituitary action on the adreno-cortex of the rat. Endocrinology 70, 390–406 (1962)
Stanley, H., Chieffi, G., Botte, V.: Histological and histochemical observations on the testis of Gobius paganellus. Z. Zellforsch. 65, 350–362 (1965)
Upadhyay, S. N., Guraya, S. S.: Histochemical observations on the interstitial tissue of fish testis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 16, 504–510 (1971)
Weisel, G. F.: A histological study of the testes of the sock-eye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). J. Morph. 73, 207–230 (1943)
Wiebe, J. P.: Steroid dehydrogenases in the gonads of the seaperch Cymatogaster aggregata Gibbons. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 12, 256–266 (1969)
Yaron, Z.: Demonstration of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the testis of Tilapia mossambica (Cichlidae, Teleostei). J. Endocrinol. 34, 127–128 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work aided by grant 72.01033.04 115.4918 from the National Research Council (C.N.R.) of Italy through the sponsorship of the Institute of Marine Biology of Venice and carried out with the facilities of C.N.R. contract 70.01798.04.115.576. We are grateful to Prof. Bruno Battaglia for encouraging this research, to Prof. Giuseppina Mazzocchi for reading the manuscript and to Dr. Elisabetta Leban for technical help.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colombo, L., Burighel, P. Fine structure of the testicular gland of the black goby, Gobius jozo L.. Cell Tissue Res. 154, 39–49 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221070
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221070