Summary
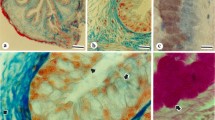
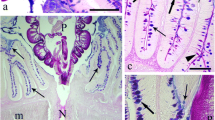
The following five cell types have been recognized and defined on the basis of their fine structure in the gastric epithelium of B. schlosseri: vacuolated and zymogenic cells (described in a previous paper); ciliated mucous, endocrine and plicated cells. The ciliated mucous cells are distributed at the apex and the bottom of the gastric folds and along the dorsal groove. The mucus droplets appear to form from the Golgi complex as secretory granules of variable density and texture, which are released from the cell after fusion of their membranes with the apical plasma membrane. Holocrine or apocrine secretion has not been observed. The endocrine cells are scattered and are characterized by electron dense granules, especially numerous in the basal region of the cell. Finally, the plicated cells, present in the pyloric caecum, show rod-like microvilli, a well developed Golgi complex and abundant, deep infoldings of the basal plasma membrane, which are associated with numerous mitochondria. The possible role of the gastric cell types is discussed taking into account information concerning morphologically similar cells in other animals, as well as previously reported data on the biochemistry and physiology of digestion and excretion in ascidians.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge, M. J., Gupta, B. L.: Fine structural changes in relation to ion and water transport in the rectal papillae of the blowfly, Calliphora. J. Cell Sci. 2, 89–112 (1967)
Berrill, N. J.: The Tunicata with an account of the British species. London: Ray Society 1950
Bulger, R. E.: Fine structure of the rectal (salt-secreting) gland of the spiny Dogfish Squalus acanthias. Anat. Rec. 147, 95–107 (1963)
Burighel, P.: Sviluppo e differenziamento del tubo digerente nel blastozooide dell'ascidia coloniale Botryllus schlosseri (Pallas). Boll. Zool. 37, 177–192 (1970)
Burighel, P.: Osservazioni morfologiche ed istochimiche sull'apparato digerente dell'ascidia coloniale Botrylloides leachi (Savigny). Atti Mem. Accad. Patav. S.S.L.L.A.A. 85, 117–132 (1973)
Burighel, P., Milanesi, C.: The fine structure of the gastric epithelium of the ascidian Botryllus schlosseri. Vacuolated and zymogenic cells. Z. Zellforsch. 145, 541–555 (1973)
Colton, H. J.: The pyloric gland of the ascidian Botryllus an organ of excretion ? Biol. Bull. Woods Hole 19, 35–52 (1910)
Copeland, E.: A mitochondrial pump in the cells of the anal papillae of mosquito larvae. J. Cell Biol. 23, 253–263 (1964)
Degail, L., Levi, C.: Étude au microscope électronique de la glande digestive des Pyuridae (Ascidies). Cah. Biol. Mar. 5, 411–422 (1964)
Doyle, W. L.: The principal cell of the salt gland in marine birds. Exp. Cell Res. 21, 421–427 (1960)
Ericsson, J. L. E., Trump, B. F.: Electron microscopy of the uriniferous tubules. In: The kidney: Morphology, biochemistry, physiology (Rouiller, C., Müller, A. F., eds.), vol. 1, p. 351–447. New York and London: Acad. Press 1969
Erspamer, V.: Presenza di enteramina o di una sostanza enteramino simile negli estratti gastrointestinali e splenici di Pesci e negli estratti gastroenterici delle Ascidie. Experientia (Basel) 2, 369–371 (1946)
Fouque, G.: Contribution à l'étude de la glande pylorique des Ascidiaces. Rec. Trav. Sta. mar. Endôume 6, 45–48 (1953)
Freeman, J. A.: Goblet cell fine structure. Anat. Rec. 154, 121–147 (1966)
Gabe, M.: État actuel des connaissances sur le cellules endocrine gastro-intestinales des Vertébrés. Ann. Biol. 12, 209–291 (1973)
Gaill, F.: Aspect ultrastructural de la glande pylorique et de l'intestin postérieur de Sidnyum argus (Polyclinidae, Tuniciers). Cah. Biol. Mar. 15, 337–341 (1974)
Gerzeli, G.: Le cellule enterocromaffini nei Tunicati. Pubbl. Staz. Zool. Napoli 33, 117–124 (1963)
Gerzeli, G.: The enterochromaffin cells in the oozooids and blastozooids of Tunicates. Folia histochem. cytochem. 2, 225–231 (1964)
Hollmann, K. H.: The fine structure of the goblet cells in the rat intestine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 106, 545–554 (1963)
Kendall, M. D.: The fine structure of the salivary glands of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria Forskål. Z. Zellforsch. 98, 399–420 (1969)
Kühnel, W.: Vergleichende histologische, histochemische und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Tränendrüsen. IV Hund. Z. Zellforsch. 88, 23–38 (1968)
Latta, H., Mannsbach, A. B., Osvaldo, L.: The fine structure of renal tubules in cortex and medulla. In: Ultrastructure in biological systems, vol.2, Ultrastructure of the kidney (Dalton, A. J., Haguenau, F., eds.), p. 1–56. New York and London: Acad. Press 1967
Lechago, J., Bencosme, S.A.: The endocrine elements of the digestive system. Int. Rev. exp. Path. 12, 119–201 (1973)
Meredith, J., Phillips, J. E.: Rectal ultrastructure in saltand freshwater mosquito larvae in relation to physiological state. Z. Zellforsch. 138, 1–22 (1973)
Millar, R. H.: Ciona. L.M.B.C. Memoirs. Liverpool: Colman 1953
Morton, J. E.: The functions of the gut in ciliary feeders. Biol. Rev. 35, 92–140 (1960)
Munn, E. A.: The structure of mitochondria. London and New York: Acad. Press 1974
Neutra, M., Leblond, C. P.: Synthesis of the carbohydrate of mucus in the Golgi complex as shown by electron microscope radioautography of goblet cells from rats injected with glucose H3. J. Cell Biol. 30, 119–136 (1966)
Olsson, R.: General review of the endocrinology of the Prochordata and Myxinoidea. Gen. comp. Endocr. suppl. 2, 485–499 (1969)
Pease, D. C.: Infolded basal plasma membranes found in epithelia noted for their water transport. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 203–208 (1956)
Peterson, M., Leblond, C.: Synthesis of complex carbohydrates in the Golgi region, as shown by radioautography after injection of labeled glucose. J. Cell Biol. 21, 143–148 (1964)
Potts, W. T. W.: Osmotic and ionic regulation. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 30, 73–104 (1968)
Relini-Orsi, L.: Prime osservazioni morfologiche ed istochimiche sull'apparato digerente di Styela plicata Les. Boll. Musei Ist. Biol. Univ. Genova 36, 157–184 (1968)
Relini-Orsi, L.: L'apparato digerente nei Tunicati: Aspetti istochimici e funzionali in Ciona intestinalis L. Boll. Musei Ist. Biol. Univ. Genova 37, 103–116 (1969)
Robertson, J. D.: The chemical composition of the blood of some aquatic chordates including members of the Tunicata, Cyclostomata and Osteichthyes. J. exp. Biol. 31, 424–442 (1954)
Sabbadin, A.: Ulteriori notizie sull'allevamente e sulla biologia dei Botrilli in condizioni di laboratorio. Arch. Ocean. Limn. 12, 97–107 (1960)
Storch, V., Welsch, U.: The ultrastructure of epidermal mucous cells in marine invertebrates (Nemertini, Polychaeta, Prosobranchia, Opistobranchia). Mar. Biol. 13, 167–175 (1972)
Tandler, B.: Ultrastructure of the human submaxillary gland. II. The base of the striated duct cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 9, 65–75 (1963)
Thomas, N. W.: Mucus-secreting cells from the alimentary canal of Ciona intestinalis L. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 50, 429–438 (1970a)
Thomas, N. W.: Morphology of cell types from the gastric epithelium of Ciona intestinalis L. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 50, 737–746 (1970b)
Vassallo, G., Capella, C., Solcia, E.: Endocrine cells of the human gastric mucosa. Z. Zellforsch. 118, 49–67 (1971)
Vassallo, G., Solcia, E., Capella, C.: Light and electron microscopic identification of several types of endocrine cells in the gastrointestinal mucosa of the cat. Z. Zellforsch. 98, 333–356 (1969)
Weel, P. B. van: Beiträge zur Ernährungsbiologie der Ascidien. Pubbl. Staz. Zool. Napoli 18, 50–79 (1940)
Welsh, J. H., Loveland, R. E.: 5-Hydroxytryptamine in the ascidian, Ciona intestinalis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 27, 719–722 (1968)
Yonge, C. M.: Studies on the comparative physiology of digestion. III. Secretion, digestion and assimilation in the gut of Ciona intestinalis. J. exp. Biol. 2, 373–383 (1925)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are grateful to Mr. G. Tognon for technical help and to the Staff of the Stazione Idrobiologica di Chioggia for their assistance in collecting material. Work supported by a C.N.R. Grant from the Istituto di Biologia del Mare, Venezia, Contract n. 71.00396/04.115.542.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burighel, P., Milanesi, C. Fine structure of the gastric epithelium of the ascidian Botryllus schlosseri. Mucous, endocrine and plicated cells. Cell Tissue Res. 158, 481–496 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220214
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220214