Summary
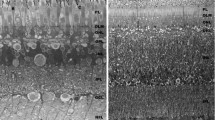
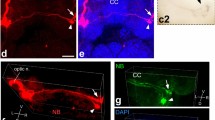
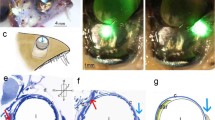
An ocellus of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, has been serially sectioned for light and electron microscopy, its sensory cells have been indexed, and the interconnections of a third of these traced. The ocellus contains 155 retinula cells and 26 arhabdomeric cells, which are secondary sensory neurons. Of these, 55 retinula cells constitute 7 quasi-ommatidial assemblages, each innervated by at least one and a total of 9 arhabdomeric cells. When known electrotonic coupling patterns are compared with gap-junctional connections, retinula cells sensitive to visible or ultraviolet light can be tentatively identified. Retinula cell axons contribute collaterals to a synaptic plexus, in which the arhabdomeric cells apparently do not participate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph, A. R., Tuan, F. J.: Serotonin and inhibition in Limulus lateral eye. J. gen. Physiol. 60, 679–697 (1972)
André, A.: A microscopic description of the eye of Monoculus polyphemus Linnaei. Phil. Trans. B 72, 440–444 (1782)
Carricaburu, P.: Structure optique de l'ocelle de la Limule Xyphosura polyphemus. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) Ser. D 267, 1630–1632 (1968)
Chapman, R. M., Lall, A. B.: Electroretinogram characteristics and the spectral mechanism of the median ocellus and the lateral eye in Limulus polyphemus. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2267–2287 (1967)
Cole, W. H.: Circus movements of Limulus and the tropism theory. J. gen. Physiol. 5, 417–426 (1923)
Demoli, R.: Die Augen von Limulus. Zool. Jb. Abt. Anat. u. Ontog. 38, 443–464 (1914)
Fahrenbach, W. H.: The morphology of the Limulus visual system. V. Protocerebral neurosecretion and ocular innervation. Z. Zellforsch. 144, 153–166 (1973)
Fahrenbach, W. H.: The visual system of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. Int. Rev. Cytol. 41, 285–349 (1975)
Goodman, L. J.: The structure and function of the insect dorsal ocellus. Advanc. Insect Physiol. 7, 97–195 (1970)
Gur, M., Purple, R. L., Whitehead, R.: Ultrastructure within the lateral plexus of the Limulus eye. J. gen. Physiol. 59, 285–304 (1972)
Jones, C., Nolte, J., Brown, J. E.: The anatomy of the median ocellus of Limulus. Z. Zellforsch. 118, 297–309 (1971)
Lall, A. B.: Spectral sensitivity of intracellular responses from visual cells in median ocellus of Limulus polyphemus. Vision Res. 10, 905–909 (1970)
Lall, A. B., Chapman, R. M.: Phototaxis in Limulus under natural conditions: Evidence for reception of near-ultraviolet light in the median dorsal ocellus. J. exp. Biol. 58, 213–224 (1973)
Lankester, E. R., Bourne, A. G.: The minute structure of the lateral and the central eyes of Scorpio and of Limulus. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 23, 177–212 (1883)
Miller, W. H.: The anatomy of the neuropile in the compound eye of Limulus. In: The structure of the eye (ed. J. W. Rohen), p. 159–169. Stuttgart: Schattauer-Verlag 1965
Nolte, J., Brown, J. E.: The spectral sensitivities of single cells in the median ocellus of Limulus. J. gen. Physiol. 54, 636–649 (1969)
Nolte, J., Brown, J. E.: The spectral sensitivities of single receptor cells in the lateral, median, and ventral eyes of normal and white-eyed Limulus. J. gen. Physiol. 55, 787–801 (1970)
Nolte, J., Brown, J. E.: Electrophysiological properties of cells in the median ocellus of Limulus. J. gen. Physiol. 59, 167–185 (1972a)
Nolte, J., Brown, J. E.: Ultraviolet-induced sensitivity to visible light in ultraviolet receptors of Limulus. J. gen. Physiol. 59, 186–200 (1972b)
Nolte, J., Brown, J. E., Smith, T. G., Jr.: A hyperpolarizing component of the receptor potential in the median ocellus of Limulus. Science 162, 647–679 (1968)
Wald, G., Krainin, J. M.: The median eye of Limulus: an ultraviolet receptor. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 50, 1011–1017 (1963)
Wasserman, G. S.: Unconditioned response to light in Limulus: Mediation by lateral, median, and ventral eye loci. Vision Res. 13, 95–105 (1973)
Waterman, T. H.: Action potentials from an arthropod ocellus: the median eye of Limulus. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 39, 687–694 (1953)
Whitehead, R., Purple, R. L.: Synaptic organization in the neuropile of the lateral eye of Limulus. Vision Res. 10, 129–133 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study constitutes Publication No. 776 from the Oregon Regional Primate Research Center, supported by Grants RR00163, RR5694, and EY00392 from the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fahrenbach, W.H., Griffin, A.J. The morphology of the Limulus visual system. Cell Tissue Res. 159, 39–47 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231993
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231993