Summary
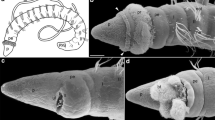
An analysis of the ultrastructure of the tube feet of three species of sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus franciscanus, Arbacia lixula and Echinus esculentus) revealed that the smooth muscle, although known to be cholinoceptive, receives no motor innervation.
The muscle fibers are attached to a double layer of circular and longitudinal connective tissue which surrounds the muscle layer and contains numerous bundles of collagen fibers. On its outside, the connective tissue cylinder is invested by a basal lamina of the outer epithelium to which numerous nerve terminals are attached. These are part of a nerve plexus which surrounds the connective tissue cylinder. The plexus itself is an extension of a longitudinal nerve that extends the whole length of the tube foot. It is composed of axons, but nerve cell bodies and synapses are conspicuously lacking, suggesting that the axons and terminals derive from cells of the radial nerve. Processes of the epithelial cells penetrate the nerve plexus and attach to the basal lamina. There is no evidence that the epithelial cells function as sensory cells.
On the basis of supporting evidence it is suggested that the transmitter released by the nerve terminals diffuses to the muscle cells over a distance of several microns and in doing so affects the mechanical properties of the connective tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenzeller, O.: Electronmicroscopic study of the innervation of the auricular artery in the rat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 98, 87–91 (1964)
Bargmann, W., Behrens, B.: Über den Feinbau des Nervensystems des Seesterns (Asterias rubens L.). II. Mitteilung zur Frage des Baues und der Innervation der Ampullen. Z. Zellforsch. 59, 746–770 (1963)
Bennet-Clark, H.C.: Active control of the mechanical properties of insect endocuticle. J. Insect Physiol. 8, 627–633 (1962)
Bevan, J.A., Verity, M.A.: Postganglionic sympathetic delay in vascular smooth muscle. J. Pharmacol. 152, 221–230 (1966)
Coleman, R.: Ultrastructure of the tube foot wall of a regular echinoid, Diadema antillarum Philippi. Z. Zellforsch. 96, 162–172 (1969)
Engster, M.S., Brown, S.C.: Histology and ultrastructure of the tube foot epithelium in the phanerozonian starfish, Astropecten. Tissue and Cell 4 (3), 503–518 (1972)
Florey, E.: Nervous control of smooth muscle in the absence of synaptic junctions. Abstract XXVI Int. Congr. Physiol. Sci., New Delhi, 1974
Florey, E., Cahill, M.A., Rathmayer, M.: Excitatory actions of GABA and of acetylcholine in sea urchin tube feet. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 51 (C), 5–12 (1975)
Iwayama, T., Furness, J.B., Burnstock, G.: Dual adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the cerebral arteries of the rat. Circulat. Res. 26, 635–646 (1970)
Kawaguti, S.: Electron microscopic structures of the podial wall of an echinoid with special references to the nerve plexus and the muscle. Biol. J. Okayama Univ. 10, 1–12 (1964)
Lever, J.D., Ahmed, M., Irvine, G.: Neuromuscular and intracellular relationships in the coronary arterioles. A morphological and quantitative study. J. Anat. (Lond.) 99, 829–840 (1965)
Lever, J.D., Graham, J.D.P., Irvine, G., Chick, W.J.: The vesiculated axons in relation to arteriolar smooth muscle in the pancreas. A fine structural and quantitative study. J. Anat. (Lond.) 99, 299–313 (1965)
Luft, J.H.: Improvements in epoxy embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 9, 409–414 (1961)
Maddrell, S.H.P.: Nervous control of the mechanical properties of the abdominal wall at feeding in Rhodnius. J. exp. Biol. 44, 59–68 (1966)
Moffat, D.B.: Fine structure of the blood vessels of the renal medulla with special reference to the control of the medullary circulation. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 19, 532–545 (1967)
Neville, A.C.: Biology of the arthropod cuticle. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1975
Nichols, D.: The histology and activities of the tube feet of Echinocyamus pusillus. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 100 (4), 539–555 (1959)
Nichols, D.: A comparative histological study of the tube feet of two regular echinoids. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 102(2), 157–180 (1961)
Pease, D.C., Molinari, S.: Electronmicroscopy of muscular arteries: pial vessels of the cat and monkey. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 3, 447–468 (1960)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Reynolds, S.E.: A post-ecdysial plasticization of the abdominal cuticle in Rhodnius. J. Insect Physiol. 20 (10), 1957–1962 (1974)
Richardson, K.C., Jarret, L., Finke, E.H.: Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 35, 313–323 (1960)
Samarasinghe, D.D.: The innervation of the cerebral arteries in the rat: an electron microscope study. J. Anat. (Lond.) 99, 815–828 (1965)
Sato, S.: An electronmicroscopic study on the innervation of the intracranial artery of the rat. Amer. J. Anat. 118, 873–889 (1966)
Smith, J.E.: The activities of the tube feet of Asterias rubens L. I. The mechanics of movement and of posture. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 88, 1–14 (1947)
Verity, M.A., Bevan, J.E.: Fine structural study of the terminal effector plexus, neuromuscular and intermuscular relationships in the pulmonary artery. J. Anat. (Lond.) 103, 49–63 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Sonderforschungsbereich 138 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Florey, E., Cahill, M.A. Ultrastructure of sea urchin tube feet. Cell Tissue Res. 177, 195–214 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221081
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221081