Summary
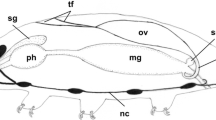
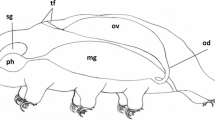
The paired ovaries of Symphyla are sac-shaped. Their interior is filled with synchronously developing oocytes surrounded by a simple follicular epithelium. Previtellogenic oocytes have spherical or oval nuclei, the latter containing a large number of small nucleoli. Part of the nuclear surface is covered by a thick “coat” made up of a granular substance of medium electron density. The “coat” is penetrated by cisternae of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Micropinocytosis is the principal source of yolk in Symphyla; a small amount of yolk material arises within the mitochondrial cristae. Vitellogenic oocytes are characterized by a highly active rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesizing a material, probably lipoprotein in nature, which is incorporated into lipid droplets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beams, H.W., Kessel, R.G.: Electron microscope studies on developing crayfish oocytes with special reference to the origin of yolk. J. Cell Biol. 18, 621–649 (1963)
Beams, H.W., Sekhon, gnS.S.: Fine structure and configuration of the nucleoli in the young oocytes of the centipede. J. Cell Biol. 35, 151A (1967)
Beams, H.W., Sekhon, S.S.: Fine structure of the nucleolus in the young oocyte of a centipede. Z. Zellforsch. 85, 237–242 (1968)
Biliński, S.: Origin of dictyosomes in the oocytes of Tetrodontophora bielanensis (Waga) (Collembola). Acta Biol. Crac. ser. Zool. 18, 125–129 (1975)
Biliński, S.: Ultrastructural studies on the vitellogenesis of Tetrodontophora bielanensis (Waga) (Collembola). Cell Tiss. Res. 168, 399–410 (1976)
Biliński, S.: Oogenesis in Acerentomon gallicum Jonescu (Protura). Previtellogenic and vitellogenic stages. Cell Tiss. Res. 179, 401–412 (1977)
Carasso, N., Favard, P.: Vitellogenèse de la Planorbe. Ultrastructure des plaquettes vitellines. Internat. Cong. Electr. Micr., Berlin 2, 431–435 (1958)
Dumont, J.N., Anderson, E.: Vitellogenesis in the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. J. Microscopie 6, 791–806 (1967)
Fauré-Frémiet, E., Courtines, H., Mugard, H.: Double origine des ribonucléoprotéines dans l'ovocyte de Glomeris marginata. Exp. Cell Res. 4, 253–263 (1950)
Goldblatt, P.J.: The endoplasmic reticulum. In: Frontiers of biology, vol. 15, Handbook of molecular cytology, p. 1101–1129, (Lima de Faria, A., ed.) North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam 1969
Herbaut, C.: Nature et origine des réserves vitellines dans l'ovocyte de Lithobius forficatus L. (Myriapode Chilopode). Z. Zellforsch. 130, 18–27 (1972a)
Herbaut, C.: Etude cytochimique et ultrastructurale de l'ovogenése chez Lithobius forficatus L. (Myriapode Chilopode). Evolution des constituants cellulaires. W. Rou'x Arch. 170, 115–134 (1972b)
Herbaut, C.: Etude cytochimique et origine des enveloppes ovocytaires chez Lithobius forficatus L. (Myriapode Chilopode). Symp. zool. Soc. Lond. No. 32 Myriapoda, 237–247 (1974)
Klag, J.: Oogenesis in Acerentomon gallicum Jonescu (Protura). An ultrastructural analysis of the early previtellogenic stages. Cell Tiss. Res. 189, 365–374 (1978)
Massover, W.H.: Intramitochondrial yolk-crystals of frog oocytes. I Formation of yolk-crystal inclusions by mitochondria during bullfrog oogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 48, 266–279 (1971)
Matsuzaki, M.: Electron microscopic studies on the oogenesis of dragonfly and cricket with special reference to the panoistic ovaries. Dev. Growth Differ. 13, 379–398 (1971)
Osaki, H.: Electron Microscope studies on developing oocytes of the spider, Plexippus paykulli. Annot. Zool. Jap. 45, 187–200 (1972)
Pearse, A.G.E.: Histochemistry, Theoretical and applied. London: Churchill J. A. Ltd 1968
Petit, J.: Etude morphologique et cytochimique de deux types de groupements mitochondriaux dans les jeunes ovocytes de Polydesmus angustus Latz. (Myriapode, Diplopode). J. Microscopie 17, 41–54 (1973)
Reger, J.F.: A study on the origin and fine structure of yolk granules in oocytes of the arachnid, Leiobunum sp. (Phalangid; Harvestman). J. Submicr. Cytol. 2, 1–12 (1970)
Roth, T.F., Porter, K.R.: Yolk protein uptake in the oocyte of the mosquito Aedes aegypti L. J. Cell Biol. 20, 313–332 (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Government Problem Grant II-1.3.13. The author is grateful to Dr. F. Kaczmarski of the Medical Academy, Kraków, for the use of EM facilities in his laboratory and to Dr. W. Hüther, Ruhr-Universität, Bochum, for the identification of the specimens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biliński, S. Ultrastructural studies on oogenesis in Symphyla. Cell Tissue Res. 202, 145–153 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239227
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239227