Summary
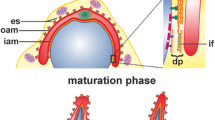
Smooth muscle heavy myosin and actin have been detected in mouse and rat meiotic chromosomes, by indirect immunofluorescence performed on testis cryostat sections and isolated germ cells. Both contractile proteins are detectable in the nuclei of meiotic cells during the first prophase. The appearance and disappearance time of myosin and actin, however, is not synchronous. While actin is visible in small spots from resting to late diplotene spermatocytes, myosin appears as filaments in the primary spermatocytes from the zygotene to the early stage of diplotene. The number of myosin filaments in the pachytene spermatocytes corresponds to the number of bivalent chromosomes, whereas actin spots constantly outnumber the pairing chromosomes by two units. These immunochemical observations suggest that the two contractile proteins are associated with the synaptonemal complex (SC). Myosin seems to be associated with the central region of the SC, while actin is present in its basal knob which is in connection with the nuclear membrane. The difference in number between myosin filaments and actin spots appears to be related to the peculiar behaviour of the pairing sex chromosomes. The presence of contractile proteins in the nuclei of primary spermatocytes seems to suggest that they might play a role in the process of pairing of homologous chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accinni L, Natali PG, Vassallo L, Hsu KC, De Martino C (1975) Immunoelectron microscopic evidence f contractile proteins in the cellular and acellular components of mouse kidney glomeruli. Cell Tissue Res 162:297–312
Avrameas J, Ternynck T (1969) The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for preparations of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry 6:53–66
Behnke O, Forer A, Emmersen J (1971) Actin in sperm tails and meiotic spindles. Nature (Lond) 234:408–409
Bostock CJ, Summer AT (1978) The eukariotic chromosome, North Holland Publishing Comp, Amsterdam New York Oxford, p 306
Cande W, Lazarides E, McIntosh R (1977) A comparison of the distribution of actin and tubulin in the mammalian mitotic spindle as seen by indirect immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol72:552–567
Coleman JR, Moses MJ (1964) DNA and the fine structure of synaptic chromosomes in the domestic rooster (Gallus domesticus). J Cell Biol 23:63–78
Comings DE, Okada TA (1971a) Whole mount electron microscopy of human meiotic chromosomes. Exp Cell Res 65:99–103
Comings DE, Okada TA (1971b) Fine structure of the synaptonemal complex. Exp Cell Res 65:104–116
Martino C de, Stefanini M, Bellocci M, Quintarelli G (1972) Osmium tetroxide-picric acid: a new fixation technique in electron microscopy. J Submicrosc Cytol 4:111–112
Martino C de, Floridi A, Marcante ML, Malorni W, Scorza Barcellona P, Bellocci M, Silvestrini B (1979) Morphological, histochemical and biochemical studies on germ cell mitochondria of normal rats. Cell Tissue Res 196:1–22
Douvas AS, Harrington CA, Bonner J (1975) Major non-histone proteins of rat liver chromatin, preliminary identification of myosin, actin, tubulin and tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 72:3902–3906
Douvas AS, Bakke A, Bonner J (1977) Evidence for the presence of contractile-like, non-histone proteins, in the nuclei and chromatin of eukariotes. In: POP Ts'o (ed.) The molecular biology of the mammalian genetic apparatus. North Holland Publishing Comp, Amsterdam New York Oxford
Engelhardt P, Pusa K (1972) Nuclear pore complexes: “Press Stud” elements of chromosomes in pairing and control. Nature New Biol 240:163–166
Esponda P, Stocker C (1971) Localization of RNA in the synaptinemal complex. J Ultrastruct Res 35:411–417
Fawcett DW (1975) Ultrastructure and function of the Sertoli cell. In: Hamilton DA, Greep RO (eds) Handbook of Physiology, Section 7, Endocrinology. American Physiological Society, Washington DC, Vol V, p 21
Fay FS, Cooke PH (1973) Reversible disaggregation of myofilaments in vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Biol 56:399–411
Fujiwara K, Pollard TD (1976) Fluorescent antibody localization of myosin in the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow, and meiotic spindle of human cells. J Cell Biol 71:848–875
Fujiwara K, Proter ME, Pollard TD (1978) Alpha-actinin localization in the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 79:268–275
Fukui Y (1978) Intracellular actin bundles induced by dimethyl sulfoxide in interphase nucleus of Dictyoselium. J Cell Biol 76:146–157
Gabbiani R, Ryan GB, Lamelin JP, Vassalli P, Majno G, Bouvier GA, Cruchand A, Luscher EF (1973) Human smooth muscle autoantibody. Its identification as antiactin antibody and a study of its binding to “nonmuscular” cells. Am J Pathol 72:473–489
Gawadi N (1971) Actin in the mitotic spindle. Nature (Lond.) 234:410
Gröschel-Stewart J, Schreiber J, Mahlmeister C, Weber K (1976) Production of specific antibodies to contractile proteins, and their use in immunofluorescence microscopy. I. Antibodies to smooth and striated chicken muscle myosin. Histochemistry 46:229–236
Hartwig JH, Stossel TP (1975) Isolation and properties of actin, myosin and a new actin-binding protein in rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem 250:5699–5705
Hauser M, Beinbrech G, Gröschel-Stewart U, Jockusch BM (1975) Localization by immunological techniques of myosin in nuclei of lower eukariotes. Exp Cell Res 95:127–135
Herman I, Pollard TD (1978) Actin localization in fixed dividing cells stained with fluorescent heavy meromyosin. Exp Cell Res 114:15–25
Hinkey R, Telser A (1974) Heavy meromyosin-binding filaments in the mitotic apparatus of mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res 86:161–164
Huxley HE (1963) Electron microscopic studies on the structure of natural and synthetic protein filaments from striated muscle. J Mol Biol 7:281–302
Jockusch BM (1973) Nuclear proteins in Physarum polycephalum. Ber Deutsch Bot Ges Bol 86:39–54
Jokusch BM, Brown DF, Rusch HP (1970) Synthesis of nuclear proteins in G2phase. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 38:279–283
Jokusch BM, Brown DF, Rusch HP (1971) Synthesis and some properties of an actin-like nuclear protein in the slime mold Physarum polycephalum. J Bacteriol 108:705–714
Jokusch BM, Ryser U, Behnke O (1973) Myosin protein in Physarum nuclei. Exp Cell Res 76:464–466
Jones BM (1966) A unifying hypothesis of cell adhesion. Nature (Lond) 212:362–365
Jones BM, Kemp RB (1970) Aggregation and electrophoretic mobility studies on dissociated cell. II. Effects of ADP and ATP. Exp Cell Res 63:301–308
Jones BM, Kemp RB, Gröschel-Stewart U (1970) Inhibition of cell aggregation by antibodies directed against actomyosin. Nature (Lond) 226:261–262
Jones PTC (1966) A contractile protein model for cell adhesion. Nature (Lond) 212:365–369
Kemp RB, Jones BM, Gröschel-Stewart U (1971) Aggregative behaviour of embryonic chick cells in the presence of antibodies directed against actomyosin. J Cell Sci 9:103–122
Knight VA, Jones BM, Jones PCT (1966) Inhibition of the aggregation of dissociated embryo-chick fibroblast cells by adenosine triphosphate. Nature (Lond) 210:1008–1010
Leblond CP, Clermont Y (1952) Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann NY Acad Sci 55:548–573
LeStourgeon WM, Totten R, Forer A (1974) The nuclear acid proteins in cell proliferation and differentiation. In: Cameron IL, Jeter JR Jr (eds) Acid proteins of the nucleus. Academic Press, New York London, p 159
LeStourgeon WM, Forer Y, Yang YZ, Bertram JS, Rusch HP (1975) Contractile proteins: Major components of nuclear and chromosome non-histone proteins. Biochem Biophys Acta (Amst) 379:529–552
Moses MJ (1968) Synaptinemal complex. Annu Rev Genet 2:363–412
Moses MJ (1969) Structure and function of the synaptonemal complex. Genetic (Princeton) 61, suppl 1:41–51
Oakberg EF (1956) Duration of spermatogenesis in the mouse and timing of stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. Am J Anat 99:507–516
Ohnishi T, Kawamura H, Yamamoto T (1963) Extraktion eines dem Aktin ähnlichen Proteins aus dem Zellkern des Kalbsthymus. J Biochem (Tokyo) 54:298–300
Ohnishi T, Kawamura H, Tanaka Y (1964) Die Aktin- und Myosin-ähnlichen Proteine im Kalbsthymuszellkern. J Biochem (Tokyo) 56:6–15
Perdue JF (1973) The distribution, ultrastructure and chemistry in cultured chick embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 58:265–283
Sanger JW (1975) Presence of actin during chromosomal movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 72:2451–2455
Solari AJ (1969) The evolution of the ultrastructure of sex chromosomes (sex vesicle) during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. J Ultrastruct Res 37:289–305
Solari AJ (1972) The ultrastructure and composition of the synaptonemal complex in spread and negatively stained spermatocytes of the golden hamster and albino rat. Chromosoma 39:237–263
Solari AJ (1974) The behaviour of the XY pair in mammals. In: Bourne GH, Danielli JP (eds) International review of cytology. Academic Press, New York London, Vol 38, p 273
Solari AJ, Tres LL (1970) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of the nucleus during male meiotic prophase. In: Rosember E, Paulsen CA (eds) The human testis. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. Plenum Press, New York London, Vol 10, p 127
Solari AJ, Moses MJ (1973) The structure of the central region in the synaptonemal complex of hamster and cricket spermatocytes. J Cell Biol 56:145–152
Stein GS, Stein JS, Kleinsmith LJ (1975) Chromosomal proteins and gene regulation. Sci Am 234:64–79
Stossel TP, Hartwig JH (1975) Interaction between actin, myosin and an actin-binding protein of rabbit alveolar macrophages. Macrophage myosin Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase requires a cofactor for activation by actin. J Biol Chem 250:5706–5712
Stossel TP, Hartwig JH (1976) Interaction of actin, myosin and a new actin-binding protein of rabbit pulmonary macrophages. II. Role in cytoplasmic movement and phagocytosis. J Cell Biol 68:602–219
Tan EM (1967) An immunologic precipitin system between soluble nucleoprotein and serum antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 46:735–745
Tilney LG, Kiehart DP, Sardet C, Tilney M (1978) Polymerization of actin. VI Role of Ca++ and H+ in the assembly of actin and in membrane fusion in the acrosomal reaction of echinoderm sperm. J Cell Biol 77:538–564
Threnchev O, Sneyd P, Holborow EJ (1974) Immunofluorescent tracing of smooth contractile proteins antigens in tissue other than smooth muscle. Clin Exp Immunol 16:125–136
Waldrop FS, Puchtler H, Palmer GR (1976) Light microscopic demonstration of myoid material in nuclei. Histochemistry 46:237–243
Weissmann G (1978) Leukocytes as secretory organs of inflammation. Hosp Practice 13:56–62
Wettstein R, Sótéló JR (1971) The molecular architecture of synaptonemal complex. Adv Cell Mol Biol 1:109–152
Willingham MC, Ostlund RE, Pastan I (1974) Myosin is a component of the cell surface of cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wash) 71:4144–4148
Woollam DHM, Millen JW, Ford EHR (1967) Points of attachment of pachytene chromosomes to the nuclear membrane in mouse spermatocytes. Nature 213:298–299
Wunderlich F, Herlan G (1977) A reversibly contractile nuclear matrix. Its isolation, structure and composition. J Cell Biol 73:271–278
Yanagibashi K, Kusanagi A (1973) Electronmicroscopic ammoniacal silver reaction for the synaptonemal complex of the mouse. Exp Cell Res 78:228–230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Martino, C., Capanna, E., Nicotra, M.R. et al. Immunochemical localization of contractile proteins in mammalian meiotic chromosomes. Cell Tissue Res. 213, 159–178 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236928
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236928