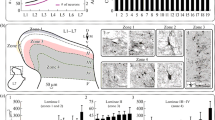
Abstract
Retrograde neuronal tracing in combination with double-labelling immunofluorescence was applied to distinguish the chemical coding of guinea-pig primary sensory neurons projecting to the adrenal medulla and cortex. Seven subpopulations of retrogradely traced neurons were identified in thoracic spinal ganglia T1-L1. Five subpopulations contained immunolabelling either for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) alone (I), or for CGRP, together with substance (P (II), substance P/dynorphin (III), substance P/cholecystokinin (IV), and substance P/nitric oxide synthase (V), respectively. Two additional subpopulations of retrogradely traced neurons were distinct from these groups: neurofilament-immunoreactive neurons (VI), and cell bodies that were nonreactive to either of the antisera applied (VII). Nerve fibres in the adrenal medulla and cortex were equipped with the mediator combinations I, II, IV and VI. An additional meshwork of fibres solely labelled for nitric oxide synthase was visible in the medulla. Medullary as well as cortical fibres along endocrine tissue apparently lacked the chemical code V, while in the external cortex some fibres exhibited code III. Some intramedullary neuronal cell bodies revealed immunostaining for nitric oxide synthase, CGRP or substance P, providing an additional intrinsic adrenal innervation. Perikarya, immunolabelled for nitric oxide synthase, however, were too few to match with the large number of intramedullary nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive fibres. A non-sensory participation is also supposed for the particularly dense intramedullary network of solely neurofilament-immunoreactive nerve fibres. The findings give evidence for a differential sensory innervation of the guineapig adrenal cortex and medulla. Specific sensory neuron subpopulations suggest that nervous control of adrenal functions is more complex than hitherto believed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afework M, Tomlinson A, Belai A, Burnstock G (1992) Colocalization of the nitric oxide synthase and NADPH-diaphorase in rat adrenal gland. Neuroreport 3:893–896
Aimi Y, Fujimura M, Vincent SR, Kimura H (1991) Localization of NADPH-diaphorase-containing neurons in sensory ganglia of the rat. J Comp Neurol 306:382–392
Baude A, Couraud JY, Poizillout JJ (1992) Fine distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve in cats. J Chem Neuroanat 5:263–274
Bloom SR, Edwards AV, Jones CT (1989) Adrenal responses to calcitonin gene-related peptide in conscious hypophysectomized calves. J Physiol 409:29–41
Blottner D, Baumgarten HG (1992) Nitric oxide synthetase (NOS)-containing sympathoadrenal cholinergic neurons of the rat IML-cell column: evidence from histochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and retrograde labeling. J Comp Neurol 316:45–55
Bohn MC, Kessler JA, Adler JE, Markey K, Goldstein M, Black IB (1984) Simultaneous expression of the SP-peptidergic and noradrenergic phenotypes in rat sympathetic neurons. Brain Res 298:378–381
Bornstein SR, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Schertbaum WA, Pfeiffer EF, Holst JJ (1990) Effects of splanchnic nerve stimulation of the adrenal cortex may be mediated by chromaffin cells in a paracrine manner. Endocrinology 127:900–906
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, McIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Bredt DS, Hwang PM, Snyder SH (1990) Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature 347:768–770
Briggs CA (1992) Potentiation of nicotinic transmission in the rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglion: effects of cyclic GMP and nitric oxide generators. Brain Res 573:139–146
Bucsics A, Saria A, Lembeck F (1981) Substance P in the adrenal gland: origin and species distribution. Neuropeptides 1:329–341
Colombo M, Kummer W, Heym C (1987) Immunohistochemistry of opioid peptides in guinea-pig paraganglia. Exp Brain Res Series 16:67–72
Costa M, Cuello AC, Furness JB, Franco R (1980) Distribution of enteric neurons showing immunoreactivity for substance P in the guinea pig ileum. Neuroscience 5:323–331
Coupland RE (1965) The Natural History of the Chromaffin Cell. Longmans, London
Coupland RE, Selby JE (1976) The blood supply of the mammalian adrenal medulla. J Anat 122:539–551
Coupland RE, Parker TL, Kesse WK, Mohamed AA (1989) The innervation of the adrenal gland. III. Vagal innervation. J Anat 163:173–181
Dawson TM, Bredt DS, Fotuhi M, Hwang PM, Snyder SH (1991) Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal NADPH diaphorase are identical in brain and peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7797–7801
Dogiel AS (1894) Die Nervenendigungen in den Nebennieren der Säugetiere. Archiv für Anatomie und Physiologie 90-104
Dohi T, Morita K, Tsujimoto A (1983) Effect of sodium azide on catecholamine release from isolated adrenal gland and on guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol 94:331–335
Dun NJ, Dun SL, Wu SY, Förstermann U (1993) Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in rat superior cervical ganglia and adrenal glands. Neurosci Lett 158:51–54
Edwards AV (1990) Autonomic control of endocrine pancreas and adrenal function. In: Loewy AD, Spyer KM (eds) Central Regulation of Autonomic Functions. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 286–309
Furchgott RE, Zawadski JV (1980) The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 288:373–376
Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Bornstein JC, Costa M (1988) Chemical neuroanatomy and the analysis of neuronal circuitry in the enteric nervous system. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T, Owman C (eds) Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, vol 6. Elsevier, Amsterdam New York Oxford, pp 161–218
Garcia-Alverez F (1972) Características ultrastructurales y significación de las vesiculas sinápticas adrenérgicas de la corteza suprarenal del cavia cobaya. Anales de Anatomia 21:301–310
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, MacIntyre I, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S (1985) Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptidelike immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett 57:125–130
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M (1987) Pathway-specific patterns of the co-existence of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, cholecystokinin and dynorphin in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res 248:417–437
Haase P, Contestabile A, Flumerfelt BA (1982) Preganglionic innervation of the adrenal gland of the rat using horseradish peroxidase. Exp Neurol 78:217–221
Hardebo JE, Suzuki N, Eklad E, Owman C (1992) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and acetylcholine coexist with neuropeptide Y, dopamine-hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, substance P or calcitonin gene-related peptide in neuronal subpopulations in cranial parasympathetic ganglia of rat. Cell Tissue Res 267:291–300
Heym C, Liu NB, Gleich A, Oberst P, Kummer W (1993) Immunohistochemical evidence for different pathways immunoreactive to substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the guinea pig stellate ganglion. Cell Tissue Res 272:563–574
Heym C, Colombo-Benckmann M, Mayer B (1994) Immunohistochemical demonstration of the synthesis enzyme for nitric oxide and of comediators in neurons and chromaffin cells of the human adrenal medulla. Ann Anat 176:11–16
Hinson JP, Vinson GP (1990) Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates adrenal cortical function in the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland in situ. Neuropeptides 16:129–133
Hökfelt T, Fuxe K, Goldstein M, Joh TH (1973) Immunohistochemical localization of three catecholamine synthesizing enzymes: aspects on methodology. Histochemie 33:231–254
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson O, Luft R, Nilsson G, Arimura A (1976) Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 1:131–136
Holzwarth MA, Cunningham LA, Kleitman N (1987) The role of the adrenal nerves in the regulation of adrenal cortical functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 512:449–464
Hua XY, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Brodin E, Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T (1985) Multiple tachykinins (neurokinin A, neuropeptide K and substance P) in capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in the guinea-pig. Regul Pept 13:1–19
Khalil Z, Marley PD, Livett BG (1988) Effect of substance P on nicotine-induced desensitization of cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: possible receptor subtypes. Brain Res 459:282–288
Klatt P, Heinzel B, John M, Kastner M, Böhme E, Mayer B (1992) Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cytochrome reductase activity of brain nitric oxyde synthase. J Biol Chem 267:11374–11378
Kobayashi S, Miyabayashi T, Uchida T, Yanaihara N (1985) Metenkephalin-arg6-gly7-leu8 in large cored vesicles of splanchnic nerve terminals innervating guinea pig adrenal chromaffin cells. Neurosci Lett 53:247–252
Kondo H (1985) Immunohistochemical analysis of the localization of neuropeptides in the adrenal gland. Arch Histol Jpn 48:453–481
Kong JY, Thureson-Klein A, Klein RL (1989) Differential distribution of neuropeptides and serotonin in pig adrenal glands. Neuroscience 28:765–775
Krukoff TL, Ciriello J, Calaresu FR (1985) Segmental distribution of peptide-like immunoreactivity in cell bodies of the thoracolumbar sympathetic nuclei of the cat. J Comp Neurol 240:90–102
Kummer W (1990) Three types of neurochemically defined autonomic fibres innervate the carotid baroreceptor and chemoreceptor regions in the guinea pig. Anat Embryol 181:477–489
Kummer W, Heym C (1991) Different types of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive neurons in the guinea-pig stellate ganglion as revealed by triple-labelling immunofluorescence. Neurosci Lett 128:187–190
Kuo DG, Krauthammer GM, Yamasaki DG (1981) The organization of visceral sensory neurons in the thoracic dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of the cat studied by horseradish peroxidase (HRP) reaction using the cryostat. Brain Res 208:189–191
Kuramoto H, Kondo H, Fujita T (1985) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in adrenal chromaffin cells and intra-adrenal nerve fibres of rats. Histochemistry 82:507–512
Kuramoto H, Kondo H, Fujita T (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-like immunoreactivity in scattered chromaffin cells and nerve fibers in the adrenal gland of rats. Cell Tissue Res 247:309–315
Le Douarin NM (1982) The Neural Crest. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Linnoila RI, Diaugustine RP, Hervonen A, Miller RJ (1980) Distribution of (Met5)- and (Leu5)-enkephalin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and substance P-like immunoreactivities in human adrenal glands. Neuroscience 5:2247–2259
Livett BG, Kozousek V, Mizobe F, Dean DM (1979) Substance P inhibits nicotinic activation of chromaffin cells. Nature 278:256–257
Livett BG, Marley PD, Wan DCC, Zhou XF (1990) Peptide regulation of adrenal medullary function. J Neural Transm Suppl 29:77–89
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Hemsen A, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Pernow J, Hamberger B, Goldstein M (1986) Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in adrenalin cells of adrenal medulla and in tumors and plasma of pheochromocytoma patients. Regul Pept 13:169–182
Lundberg JM, Martling CR, Hökfelt T (1988) Airways, oral cavity and salivary glands: classical transmitters and peptides in sensory and autonomic motor neurons. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T, Owman C (eds) Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, vol. 6. Elsevier, Amsterdam New York Oxford, pp 391–445
Mohamed AA, Parker TL, Coupland RE (1988) The innervation of the adrenal gland. II. The source of spinal afferent nerve fibres to the guinea-pig adrenal gland. J Anat 160:51–58
Molander C, Ygge J, Dalsgaard CJ (1987) Substance P-, somatostatin-and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity and fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase-activity in relation to retrogradely labelled cutaneous, muscular and visceral primary sensory neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett 74:37–42
Nagy JI, Hunt JP (1982) Fluoride-resistant acid phosphatase neurons in dorsal root ganglia are separate from those containing substance P or somatostatin. Neuroscience 7:89–97
Niijima A, Winter AL (1968) The effect of catecholamines on unit activity in afferent nerves from the adrenal glands. J Physiol 195:647–656
Nussdorfer GG, Malendowicz LK, Belloni AS, Mazzochi G, Rebuffat P (1988) Effect of substance P on the rat adrenal zona glomerulosa in vivo. Peptides 9:1145–1149
Parker TL, Kesse WK, Mohamed AA, Afework M (1993) The innervation of the mammalian adrenal gland. J Anat 183:265–276
Parker TL, Afework M, Coupland RE (1990a) Sensory innervation of the rat adrenal gland. Neurosci Lett 38:562
Parker TL, Mohamed AA, Coupland RE (1990b) The innervation of the adrenal gland. IV. The source of pre- and postganglionic nerve fibres to the guinea-pig adrenal gland. J Anat 172:17–24
Pelto-Huikko M (1989) Immunocytochemical localization of neuropeptides in the adrenal medulla. J Electr Microsc Tech 12:364–379
Pines L., Narowtschatowa K (1931) Über die Innervation des chromaffinen Gewebes des Sympathicus und über das sympathicochromaffine System in allgemeinen. Archiv für Psychiatrie und Nervenkrankheiten 70:636–647
Price J (1985) An immunohistochemical and quantitative examination of dorsal root ganglion neuronal subpopulations. J Neurosci 8:2051–2059
Role LW, Leeman SE, Perlman RL (1981) Somatostatin and substance P inhibit catecholamine secretion from isolated cells of gunea-pig adrenal medulla. Neuroscience 6:1813–1821
Schramm LP, Adair JR, Stribling JM, Grey LP (1975) Preganglionic innervation of the adrenal gland of the rat: a study using horseradish peroxidase. Exp Neurol 49:540–553
Sternberger LA, Joseph SA (1979) The unlabeled antibody method. J Histochem Cytochem 27:1424–1429
Swinyard CA (1937) The innervation of the suprarenal glands. Anat Rec 68:417–428
Teitlebaum HA (1933) The nature of the thoracic and abdominal distribution of the vagus nerves. Anat Rec 55:297–317
Tuchscherer MM, Seybold VS (1985) Immunohistochemical studies of substance P, cholecystokinin-octapeptide and somatostatin in dorsal root ganglia of the rat. Neuroscience 2:593–605
Unsicker K (1971) On the innervation of the rat and pig adrenal cortex. Z Zellforsch 116:151–156
Unsicker K (1984) Innervation of endocrine tissues. In: Motta PM (ed) Ultrastructure of Endocrine Cells and Tissues. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague, pp 321–332
Vickers JC, Costa M, Vitadello M, Dahl D, Marotta CA (1990) Neurofilament protein-triplet immunoreactivity in distinct subpopulations of peptide-containing neurons in the guinea-pig coeliac ganglion. Neuroscience 39:743–759
Vincent SR, Hope BT (1992) Neurons that say NO. Trends Neuroscience 15:108–113
Weihe E (1990) Neuropeptides in primary afferent neurons. In: Zenker W, Neuhuber WL (eds) The Primary Afferent Neuron. Plenum Press, New York, pp 127–159
Weihe E, McKnight AT, Corbett AD, Kosterlitz HW (1985) Proenkephalin-and prodynorphin-derived opioid peptides in guinea pig heart. Neuropeptides 5:453–456
Wessendorf MW, Elde RP (1986) Characterization of an immunofluorescence technique for the demonstration of co-existing neurotransmitters within nerve fibres and terminals. J Histochem Cytochem 33:984–994
Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (1986) Substance P and somatostatin modulate spinal cord excitability via physiologically different sensory pathways. Brain Res 372:172–175
Yamamoto R, Bredt DS, Snyder SH, Sone RA (1993) The localization of nitric oxide synthase in the rat eye and related cranial ganglia. Neurosci 54:189–200
Zentel HJ, Weihe E (1988) Targets and interactions of nerves coding for substance P, multiple non-tachykinin peptides and/or catecholamines in guinea-pig adrenal gland: Multiple messengers in sensory and sympathetic neuroendocrine interaction. Regul Pept 22:192
Zhou XF, Livett BG (1990) Substance P increases catecholamine secretion from perfused rat adrenal glands evoked by prolonged field stimulation. J Physiol 425:321–334
Zhou XF, Oldfield BJ, Livett BG (1991) Substance P-containing sensory neurons in the rat dorsal root ganglia innervate the adrenal medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst 33:247–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heym, C., Braun, B., Klimaschewski, L. et al. Chemical codes of sensory neurons innervating the guinea-pig adrenal gland. Cell Tissue Res 279, 169–181 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300702
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300702