Abstract.
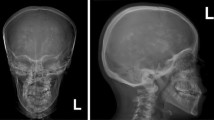
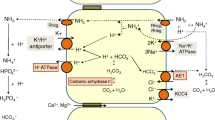
Renal tubular acidosis with osteopetrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder due to deficiency of carbonic anhydrase II (CAII). A 3.5-year-old Egyptian boy with osteopetrosis and cerebral calcification had a persistent normal anion gap type of metabolic acidosis (plasma pH 7.26) and a mild degree of hypokalemia. A baseline urine pH was 7.0; ammonium (NH4 +) excretion was low at 11 μmol/min per 1.73 m2; fractional excretion of bicarbonate HCO3 (FEHCO3) was high at 9%, when plasma HCO3 was 20 mmol/l; citrate excretion rate was high for the degree of acidosis at 0.35 mmol/mmol creatinine. Intravenous administration of sodium bicarbonate led to a urine pH of 7.6, a FEHCO3 of 14%, a urine-blood PCO2 difference of 7 mmHg, NH4 + excretion fell to close to nil, and citrate excretion remained at 0.38 mmol/mmol creatinine. Intravenous administration of arginine hydrochloride caused the urine pH to fall to 5.8, the FEHCO3 to fall to 0, the NH4 + excretion rate to rise to 43 μmol/min per 1.73 m2, and citrate excretion to fall to <0.01 mmol/mmol creatinine. These results show that our patient had a low rate of NH4 + excretion, a low urine minus blood PCO2 difference in alkaline urine, and a low urinary citrate excretion, but only when he was severely acidotic. He failed to achieve a maximally low urine pH. These findings indicate that his renal acidification mechanisms were impaired in both the proximal and distal tubule, the result of his CAII deficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 24, 1996; received in revised form and accepted February 20, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, R., Kooh, S., Balfe, J. et al. Renal tubular acidosis and osteopetrosis with carbonic anhydrase II deficiency: pathogenesis of impaired acidification. Pediatr Nephrol 11, 633–636 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050354
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050354