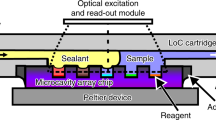
Abstract
Microsystems recently have been introduced as tools for screening in modern chemistry, biochemistry and biology. It has been shown that new microsystems can be implemented in the biomedical laboratory by using the microsystemic approach for the sample carrier – the miniaturized microtiter plate (“the nanotiter plate”) – or the production of nanodroplets with ink jetters and to integrate those systems in macrodevices like xyz tables and detection devices like CCD-cameras. We show in this paper that decisive problems of the approach – the evaporation problem and the problem of chemical/biochemical/biological compatibility of the assays and the used materials can be solved successfully. It is possible to realize chemical synthesis in miniaturized flow systems and to perform isothermal amplification of RNA in silicon wafers. Furthermore real high throughput screening with in vivo systems can be performed and all relevant parameters as evaporation, pipetting and detection can be controlled on reasonable time scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 May 1997/Accepted: 2 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schober, A., Schlingloff, G., Thamm, A. et al. Systemintegration of microsystems/chip elements in miniaturized automata for high-throughput synthesis and screening in biology, biochemistry and chemistry. Microsystem Technologies 4, 35–39 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005420050089
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005420050089