Abstract
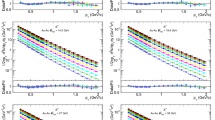
Multiplicity and pseudorapidity distributions have been measured for32S+Al, Cu, Ag and Au at 200A GeV. The widths of the pseudorapidity distributions increase from central to peripheral collisions. The main contribution is assumed to come from the increasing fraction of charged particles stemming from the fragmentation of the target for peripheral collisions as compared to central collisions. On the average 170–180 charged particles per unit of pseudorapidity are attained for the most central32S+Au events at the maximum of the distribution. The target dependence of the yield of charged particles for central collisions is investigated. In the target rapidity region the yield is directly proportional to the target mass. The transverse energy per charged particle has been studied as a function of centrality and pseudorapidity. The experimental results are compared to the results from the Monte-Carlo model VENUS 3.11 which includes rescattering among secondaries. A comparison between different centrality triggers is made.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Proceedings of the Quark Matter '90 conference in Menton, France, Nucl. Phys. A525 (1991)
J.D. Bjorken: Phys. Rev. D27 (1983) 140
E802 Collab., P. Vincent et al.: Nucl. Phys. A498 (1988) 67c
E814 Collab., J. Barette et al.: submitted to Phys. Rev. C
EMU01 Collab., M.I. Adamovich et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 62 (1989) 2801
L.M. Barbier et al.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 60 (1988) 405
HELIOS Collab., T. Åkesson et al.: Nucl. Phys. B333 (1990) 48
NA35 Collab., A. Bamberger et al.: Phys. Lett. 184B (1988) 583
WA80 Collab., R. Albrecht et al.: Phys. Lett. 202B (1988) 596
EMU01 Collab., M.I. Adamovich et al.: Phys. Lett. 227B (1989) 285
HELIOS-Emulsion Collab., T. Åkesson et al.: Nucl. Phys. B342 (1990) 279
P.L. Jain, K. Sengupta, G. Singh, A.Z.M. Ismail: Phys. Lett. 235B (1990) 351
HELIOS Collab., L. Ramello et al.: Nucl. Phys. A498 (1989) 403c
HELIOS Collab., L. Ramello et al.: Nucl. Phys. A525 (1991) 555c
WA80 Collab. R. Albrecht et al.: GSI-report GSI-85-32 (1985)
K. Werner, P. Koch: Phys. Lett. 242B (1990) 251
A. Baden et al.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods A203 (1982) 189
R. Albrecht et al.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods A276 (1989) 131
G.R. Young et al.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods A279 (1989) 503
T.C. Awes et al.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods A279 (1989) 479
E. Albini et al.: Nuovo Cimento 32A (1976) 101
WA80 Collab., R. Albrecht et al.: Z. Phys. C—Particles and Fields 45 (1989) 31
WA80 Collab, R. Albrecht et al.: Phys. Rev. C44 (1991) 2736
B. Nilsson-Almqvist, E. Stenlund: Comput. Phys. Commun. 43 (1987) 387
H. von Gersdorff et al.: Phys. Rev. C39 (1989) 1385
EMU01 Collab., M.I. Adamovich et al.: to be submitted to Phys. Rev. Lett.
J. Stachel: Nucl. Phys. A525 (1991) 23c
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albrecht, R., Awes, T.C., Baktash, C. et al. Multiplicity and pseudorapidity distributions of charged particles from32S induced heavy ion interactions at 200A GeV. Z. Phys. C - Particles and Fields 55, 539–548 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01561291
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01561291