Abstract
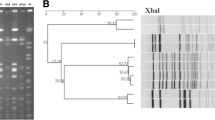
Rahnella aquatilis was isolated from the blood cultures of two patients who were in different units of the same hospital. Both isolates were susceptible to aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, cotrimoxazole, piperacillin, third generation cephalosporins and amoxicillin-clavulanate, but resistant to amoxicillin, ticarcillin, and first generation cephalosporins. The synergistic activity of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid suggested the presence of aΒ-lactamase, confirmed by a positive nitrocefin test and by analytical isoelectric focusing. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and ribotyping with the pKK3535 probe showed that the isolates shared the same banding pattern. The results of an epidemiological study suggested that an in-house total parenteral nutrition solution might be the source of this unusual gram-negative rod.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gavini F, Ferragut C, Lefebvre B, Leclerc H: Etude taxonomique d'Entérobactéries appartenant ou apparentées au genreEnterobacter. Annales de Microbiologie (Institut Pasteur) (1976) 127B:317–335
Izard D, Gavini F, Trinel PA, Leclerc H:Rahnella aquatilis, nouveau membre de la famille desEnterabacteriaceae. Annales de Microbiologie (Institut Pasteur) (1979) 130A:163–177
Christiaens E, Hansen W, Moinet J: Isolement des expectorations d'un patient atteint de leucémie lymphoide chronique et de broncho-emphysème d'uneEnterobacteriaceae nouvellement décrite:Rahnella aquatilis. Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses (1987) 12:732–734
Harrell LJ, Cameron ML, O'Hara CM:Rahnella aquatilis, an unusual gram-negative rod isolated from the bronchial washing of a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Journal of Clinical Microbiology (1989) 27:1671–1672
Alballaa SR, Hussain Qadri SM, Al-Furayh O, Al-Qatary K: Urinary tract infection due toRahnella aquatilis in a renal transplant patient. Journal of Clinical Microbiology (1992) 30:2948–2950
Maraki S, Samonis G, Marnelakis E, Tselentis Y: Surgical wound infection caused byRahnella aquatilis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology (1994) 32:2706–2708
Reina J, Lopez A: Clinical and microbiological characteristics ofRahnella aquatilis strains isolated from children. Journal of Infection (1996) 33:135–137
Goubau P, Van Aelst J, Verhaegen J, Boogaerts M: Septicemia caused byRahnella aquatilis in an immunocompromised patient. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (1988) 7:697–699
Funke G, Rosner H:Rahnella aquatilis bacteremia in an HIV-infected intravenous drug abuser. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (1995) 22:293–296
Oh HML, Tay L: Bacteraemia caused byRahnella aquatilis: report of two cases and review. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases (1995) 27:79–80
Matsukara H, Katayama K, Kitano N, Kobayashi K, Kanegane C, Higuchi A, Kyotani S: Infective endocarditis caused by an unusual gram-negative rod,Rahnella aquatilis. Pediatric Cardiology (1996) 17:108–111
Matthew M, Harris AM, Marshall MJ, Ross GW: The use of isoelectric focusing for detection and identification ofΒ-lactamases. Journal of General Microbiology (1975) 88:169–178
Gouby A, Neuvirth C, Bourg G, Bouziges N, Carles-Nurit M, Despaux E, Ramuz M: Epidemiological study by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of an outbreak of extended-spectrumΒ-lactamase producingKlebsiella pneumonias in a geriatric hospital. Journal of Clinical Microbiology (1994) 32:301–305
Richard P, Le Floch R, Chamoux C, Pannier M, Espaze E, Richet H:Pseudomonas aeruginosa outbreak in a burn unit: role of antimicrobials in the emergence of multiply resistant strains. Journal of Infectious Diseases (1994) 170:377–383
Brosius J, Ullrich A, Raker MA: Construction of fine mapping of recombinant plasmid containing the rrnb ribosomal operon ofE. coli. Plasmid (1981) 6:112–118
Hoppe JE, Herter M, Aleksic S, Klingebiel T, Niethammer D: Catheter-relatedRahnella aquatilis bacteremia in a pediatric bone marrow transplant recipient. Journal of Clinical Microbiology (1993) 31:1911–1912
Freney J, Husson MO, Gavini F, Madier S, Martra A, Izard D, Leclerc H, Fleurette J: Susceptibilities to antibiotics and antiseptics of new species of the familyEnterobacteriaceae. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1988) 32:873–876
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caroff, N., Chamoux, C., Le Gallou, F. et al. Two epidemiologically related cases ofRahnella aquatilis bacteremia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 17, 349–352 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709459
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709459