Abstract
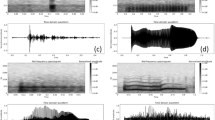
This study is aimed at detecting gastrointestinal sounds (GIS) and correlating their characteristics with gastrointestinal (GI) conditions. The central hypotheses are that GIS generation depends on the motility patterns and the mechanical properties of the gut, and that changes in those result in measurable differences in GIS. An animal model which included both healthy rats and those with small bowel obstruction (SBO) was developed. The acoustic bursts, of GIS were detected by amplitude thresholding the signal envelope. Three methods of envelope estimation were proposed and evaluated. Envelope estimation using a Hilbert transform was found to produce the best results in the current application. The duration and dominant frequency of each detected GIS event was estimated and clear differences between healthy and diseased rats were discovered. In the control state, GIS events were found to consistently be of relatively short duration (3–65ms). Although the majority of events in the SBO state had similar short duration, infrequent longer events were also detected and appeared to be pathognomonic. Long duration events (>100 ms) occurred in each of seven obstructed, but in none of 14 non-obstructed, cases (p<0.001). It is concluded that GIS analysis may prove useful in the non-invasive, rapid, and accurate diagnosis of SBO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon, W. B. (1905): ‘Auscultation of the rhythmic sounds produced by the stomach and intestines’,Am. J. Physiol.,13, pp. 339–353
Chen, C. H. (1986): ‘Seismic and underwater acoustic waveform analysis,’in Young, T. andFu, K-S (Eds): ‘Handbook of pattern recognition and image processing’, (Academic Press, California), pp. 527–543
Choi, H. G., Principe, J. C., Hutchison, A. A. andWozniak, J. A. (1994): ‘Multiresolution segmentation of respiratory electromyographic signals’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,41, pp. 257–266
Claerbout, J. F. (1976): ‘Fundamentals of geophysical data processing,’ (McGraw-Hill, New York), pp. 59–62
Cullen, P. T., Storey, B. E., Cuschieri, A. andCampbell, F. C. (1989): ‘Detection of clustered gastrointestinal contractions in partial intestinal obstruction by surface vibration analysis’,Ann. Surg.,210, pp. 234–238
Dalle, D., Devroede, G., Thibault, R. andPerrault, J. (1975): ‘Computer analysis of bowel sounds’,Comput. Biol. Med.,4, pp. 247–256
Farrar, J. T. andIngelfinger, F. J. (1955): ‘Gastrointestinal motility as revealed by study of abdominal sounds’,Gastroenterology,29, pp. 789–800
Garner, C. G. andEhrenreich, H. (1989): ‘Non-invasive topographic analysis of intestinal activity in man on the basis of acoustic phenomena’,Res. Exp. Med.,189, pp. 129–140.
Heinkelmann, W., Eichmeier, J. andBlumel, G. (1977): ‘Measurement and computerised analysis of sounds and electromyographic wall potential for the investigation of intestinal motility’,Biomed. Tech.,22, pp. 266–272
Inouye, T., Ukai, S., Shinosaki, K., Iyama, A., Matsumoto, Y. andToi, S. (1994): ‘Changes in the fractal dimension of alpha envelope from wakefulness to drowsiness in human electroencephalogram,’Neurosc. Lett.,174, pp. 105–108
Kimura, R. E., Lapine, T. R. andGooch, III, W. M. (1988): ‘Portal venous and aortic glucose and lactate changes in a chronically cathertized rat’,Pediatr. Res.,23, pp. 235–240
Lange, D. H., Pratt, H. andInbar, G. F. (1995): ‘Segmented matched filtering of single event related evoked potentials’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,42, pp. 317–321
Lehner, R. J. andRangayyan, R. M. (1987): ‘A three-channel microcomputer system for segmentation and characterization of the phonocardiogram’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,34, pp. 485–489
Makijarvi, M. (1991): ‘Recording of abnormal late ventricular activity by high-resolution magnetocardiography’,Int. J. Cardiac Imaging.,7 pp. 237–241
Mansy, H. A. andSandler, R. H. (1997): ‘Bowel sound signal enhancement using adaptive filtering’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,16, pp. 105–117
McFadden, D. andZinner, M. (1994): ‘Manifestations of gastrointestinal disease’,in Schwartz, S. I., Shires, G. T. andSpencer, F. C. (Eds.): ‘Principles of Surgery, 6th ed.’ (McGraw-Hill, New York), pp. 1028–1031
Miftakhov, R. N. andWingate, D. L. (1994): ‘Biomechanics of small bowel motility’,Med. Eng. Phys.,16, pp. 406–415
Openheim, A. V. andSchafer, R. W. (1989): ‘Discrete-time signal processing’ (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ), pp. 679–680
Politzer, J. P., Devroede, D., Vasseur, C., Gerard, J. andThibault, R. (1976): ‘The genesis of bowel sounds: influence of viscous and gastrointestinal content,’Gastroenterology,71, pp. 282–285
Rabiner, L. R. andSchafer, R. W. (1978): ‘Digital processing of speech signals’, (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ), pp. 117–133
Ruha, A., Sallinen, S. andNissila, S. (1997): ‘A real-time microprocessor QRS detector system with a 1-ms timing accuracy for the measurement of ambulatory HRV’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,44, pp. 159–167
Sugrue, M. andRedfern, M. (1994): ‘Computerized phonoenterography: the clinical investigation of a new system’,J. Clin. Gastroenterol.,18, pp. 139–144
Tomomasa, T., Morikawa, A., Sandler, R. H., Mansy, H. A., Koneko, H., Masahiko, T., Hyman, P. E. andItoh, Z. (1999): ‘Gastrointestinal sounds and migrating motor complex in fasted humans’,Am. J. Gastroenterology,94, pp. 374–381
Uhing, M. andKimura, R. (1995): ‘The effect of surgical bowel manipulation and anesthesia on intestinal glucose absorption in rats’,J. Clin. Investig.,95, pp. 2790–2798
Witte, H., Eiselt, M., Patakova, I., Petranek, S., Griessbach, G., Krajca, V. andRother, M. (1991): ‘Use of discrete Hilbert transform for automatic spike mapping: a methodological investigation,’Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,29, pp. 242–248
Yoshino, H., Abe, Y., Yoshino, T. andOhsato, K. (1990): ‘Clinical application of spectral analysis of bowel sounds in intestinal obstruction,’Dis. Colon Rectum.,33, pp. 753–757.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mansy, H.A., Sandler, R.H. Detection and analysis of gastrointestinal sounds in normal and small bowel obstructed rats. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 38, 42–48 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344687
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344687