Summary
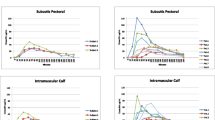
Ciprofloxacin distribution in muscle, subcutaneous fat and perirenal and perivesical fat was studied following a single i.v. bolus injection of 100 mg or oral administration of 500 mg. Levels in muscle were on average 0.75 mg/kg; diffusion into muscle was rapid, whereas elimination from muscle was slow. Similar peak levels were recorded in fatty tissues. However, penetration into subcutaneous fat in particular may be delayed in individual cases. Following an initial lagphase of up to one hour after i.v. injection, ciprofloxacin distribution was as efficient in these patients as in the others. Tissue levels following oral administration were monitored 12 hours after intake. On average, ciprofloxacin concentrations in serum, muscle and perirenal fat were 0.17 mg/l, 0.20 mg/kg and 0.11 mg/kg, respectively. Thus, ciprofloxacin is distributed effectively throughout the extravascular space following i.v. as well as oral administration.
Zusammenfassung
Die Verteilung von Ciprofloxacin in der Muskulatur, dem subkutanen, perirenalen sowie perivesikalen Fett wurde nach intravenöser Bolusinjektion von 100 mg oder einer oralen Verabreichung von 500 mg untersucht. Die Muskelkonzentrationen betrugen im Mittel 0.75 mg/kg; die Diffusion in den Muskel erfolgte schnell, wohingegen die Elimination langsam war. Ähnliche Spitzenspiegel wurden im Fettgewebe gemessen; jedoch war die Diffusion in das subkutane Fett in einigen Fällen verzögert. Nach einer anfänglichen lag-Phase von bis zu einer Stunde nach i.v. Injektion war aber auch in diesen Patienten die Verteilung gleichermaßen effektiv wie in den anderen Patienten. Die Gewebespiegel nach oraler Verabreichung wurden 12 Stunden nach der Einnahme gemessen. Die mittleren Ciprofloxacin-Konzentrationen im Serum, Muskel und perirenalem Fett betrugen 0.17 mg/l, 0.20 mg/kg und 0.11 mg/kg. Somit verteilt sich Ciprofloxacin sowohl nach intravenöser als auch oraler Verabreichung effektiv im Extravasalraum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Zeiler, H. J., Grohe, K. Thein vitro andin vivo activity of ciprofloxacin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 3 (1984) 339–343.
Wingender, W., Graefe, K. H., Gau, W., Förster, D., Beermann, D., Schacht, P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and intravenous administration in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 3 (1984) 355–359.
Boerema, J. B. J., Dalhoff, A., Debruýne, F. M. Y. Ciprofloxacin distribution in prostatic tissue and fluid following oral administration. Chemotherapy 31 (1984) 13–18.
Boerema, J. B. J., Dalhoff, A., Debruyne, F. M. Y. Intraprostatic concentrations of ciprofloxacin following intravenous administration. Lancet II (1984)695–696.
Hoogkamp-Korstanje, J. A. A., van Oort, H. J., Schipper, J. J., van der Wal, T. Intraprostatic concentrations of ciprofloxacin and its activity against urinary pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 14 (1984)641–645.
Dalhoff, A., Weidner, W. Diffusion of ciprofloxacin into prostatic fluid. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 3 (1984) 360–362.
Falser, N., Dalhoff, A., Weuta, H. Ciprofloxacin concentrations in tonsils following a single intravenous administration. Infection 12 (1984) 355–357.
Shah, P. M., Strehl, R., Posselt, H. G., Bender, S. W. Ciprofloxacin bei Mucoviscidose-Cystischer Fibrose, eine pharmakokinetische Untersuchung. Fortschr. Antimikr. Antineoplast. Chemother. 3 (1984) 685–690.
Crump, B., Wise, R., Dent, J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24 (1983) 784–786.
Wise, R., Lockley, R. M., Webberly, M., Dent, J. The pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 26 (1984) 208–210.
Bender, S. W., Posselt, H. G., Wönne, R., Stöver, B., Strehl, R., Shah, P. M.: Oral ciprofloxacin forPseudomonas bronchopneumonia in cystic fibrosis. Proceedings of the 9th International Cystic Fibrosis Congress, Brighton, June 1984, Abstract No. 4.25.
Giamarellou, H., Daphnis, E., Dendrinos, C., Daikos, G. K.: Experience with ciprofloxacin in the treatment of various infections caused mainly byPseudomonas aeruginosa. 6th International Symposium on Future Trends in Chemotherapy, Tirrenia (Pisa), May 1984.
Naber, K., Wick-Bartosik, B. Therapie komplizierter Harnwegsinfektionen mit Norfloxacin versus Ciprofloxacin. Fortschr. Antimikr. Antineopl. Chemother. 3 (1984) 749–758.
Schalkhäuser, K. Ciprofloxacin bei der Behandlung schwerer Harnwegsinfektionen. Vorläufige Mitteilung. Fortschr. Antimikr. Antineopl. Chemother. 3 (1984) 769–772.
Boerema, J. B. J., Bol, B., Muytjens, H. L., Branolte, J. H.: Efficacy and safety of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of patients with complicated urinary tract infections. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodos, October 1984.
Van Poppel, H., Wegge, M., Dammekens, H.: Heavy urinary tract infections in neurogenic bladders treated with ciprofloxacin. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodos, October 1984.
Del Rio, G., Dalet, F.: Clinical evaluation of ciprofloxacin in complicated urinary tract infections. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodos, October 1984.
Peters, H.-J.: First clinical results with ciprofloxacin (BAY o 9867), a new quinolinecarboxylic acid derivative in urinary tract infections. Ist European Congress of Clinical Microbiology, Bologna, October 1983, Abstract No. 353.
Giamarellou, H., Efstratiou, A., Tsagarakis, J., Avlami, A., Daikos, G. K.: Ciprofloxacin:in vitro andin vivo experience in the treatment of urinary tract infections. I. European Congress of Clinical Microbiology, Bologna, October 1983, Abstract No. 354.
Newsom, S. W. B., Murphy, P., Warren, R. E., Matthews, J.: Clinical studies with ciprofloxacin. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodos, October 1984.
Ball, A. P., Fox, C., Brown, I. R. F.: Clinical efficacy and kinetics of ciprofloxacin in UTI. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodos, October 1984.
Follath, F., Borner, M., Hauser, H. P., Wenk, M., Reber, H.: Therapeutic efficacy of ciprofloxacin in patients withPseudomonas infections. 4th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Rhodos, October 1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalhoff, A., Eickenberg, H.U. Tissue distribution of ciprofloxacin following oral and intravenous administration. Infection 13, 78–81 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01660419
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01660419