Abstract:
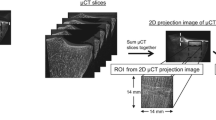
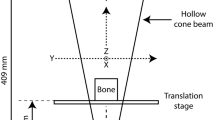
The purpose of this study was to determine the relationship between three-dimensional (3D) trabecular structure and two-dimensional plain radiographic patterns. An in vitro cylinder of human calcaneal trabecular bone was three-dimensionally imaged by micro-CT using synchrotron radiation, at 33.4 μm resolution. The original 3D image was processed using 14 distinct sequences of morphologic operations, i.e., of dilations and erosions, to obtain a total of 15 3D models or images of calcaneal trabecular bone. These 15 models had distinct densities (volume fractions) and architectures. The 3D structure of each calcaneal model was assessed using mean intercept length (fabric), by averaging individual fabric measurements associated with each medial-lateral image slice, and determining the relative anisotropy, R3D, of the structure. A summated pattern or plain radiograph was also computed from the 3D image data for each calcaneal model. Each summated pattern was then locally thresholded, and the resulting two-dimensional (2D) binary image analyzed using the same fabric analysis as used for the 3D data. The anisotropy of the 2D summated pattern was denoted by Rx-ray. The volume fractions of the 15 models ranged from 0.08 to 0.19 with a mean of 0.14. The medial-lateral anisotropies, R3D, ranged from 1.38 to 2.54 with a mean of 1.88. The anisotropy of the 2D summated patterns, Rx-ray, ranged from 1.35 to 2.18 with a mean of 1.71. The linear correlation of the 3D trabecular architecture, R3D, with the radiographic trabecular architecture, Rx-ray, was 0.99 (p<0.0001). This study shows that the plain radiograph contains architectural information directly related to the underlying 3D structure. A well-controlled sequential reproducible plain radiograph may prove useful for monitoring changes in trabecular architecture in vivo and in identifying those individuals at increased risk of osteoporotic fracture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 December 1997 / Accepted: 3 September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, G., Kinney, J., Kaufman, J. et al. Relationship Between Plain Radiographic Patterns and Three- dimensional Trabecular Architecture in The Human Calcaneus . Osteoporos Int 9, 339–345 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980050156
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980050156