Abstract
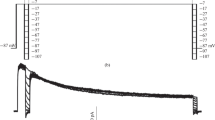
Ion channels present in isolated glial (Müller) cells from the retina of the turtle (Pseudemys scripta elegans) were studied with the patch clamp technique. The predominant conductance in these cells was due to an inward rectifying potassium current. The whole-cell conductance of the inward rectifier was 20.2±1.9 nS (n = 7 cells) in a standard extracellular saline solution (3 mm extracellular potassium). This conductance was dependent on the extracellular potassium concentration, with a 2.88-fold change in conductance per tenfold shift in concentration. The relative permeability sequence to potassium of the inward rectifier was found to be: potassium (1.0) > rubidium (0.7) > ammonium (0.2) > lithium (0.1) = sodium (0.1), which corresponded to the Eisenman sequence IV or V for a strongfield-strength potassium binding site on the channel. The single channel conductance measured in cell-attached patches with potassium chloride (150 mm) in the pipette was 68.5 ± 6.0 pS (n = 3 patches). The inward rectifier current was not blocked by extracellular tetraethylammonium (TEA+, 20 mm), but was blocked by extracellular barium (5 mm) or cesium (5 mm). The TEA+ insensitivity of the inward rectifier potassium channel in Müller cells is unusual, given that this type of channel in most excitable cells is sensitive to micromolar concentrations of this compound, and may be a characteristic of inward rectifier potassium channels that are primarily involved with extracellular potassium regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R.H. 1969. Rectification in muscle membrane. Prog. Biophys.Mol. Biol. 19:340–369
Aldrich, R.W., Yellen, G. 1983. Analysis of nonstationary channel kinetics. In: Single-Channel Recording. B. Sakmann and E. Neher, editors. pp. 287–299. Plenum, New York
Barry, P.H., Lynch, J.W. 1991. Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in patch-clamp analysis. J. Membrane Biol. 121:101–117
Binstock, L., Lecar, H. 1969. Ammonium ion currents in the squid giant axon. J. Gen. Physiol. 52:342–361
Brew, H., Gray, P.T.A., Mobbs, P., Attwell, D. 1986. Endfeet of retinal glial cells have higher densities of ion channels that mediate K+ buffering. Nature 324:466–468
Chao, T.I., Pannicke, T., Reichelt, W., Reichenbach, A. 1993. Na+ channels are expressed by mammalian retinal glial (Müller) cells. Neurorep. 4:575–578
Chen, F., Wetzel, G.T., Friedman, W.F., Klitzner, T.S. 1991. Single channel recording of inwardly rectifying potassium currents in developing myocardium. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 23:259–267
Conner, J.D., Detweiler, P.B., Sarthy, P.V. 1985. Ionic and electro physiological properties of retinal Müller (glial) cells of the turtle. J. Physiol. 362:79–92.
Edwards, R.B., Adler, A.J., Dev, S., Claycomb, R.C. 1992. Synthesis of retinoic acid from retinol by cultured rabbit Müller cells. Exp. Eye Res. 54:481–490
Gallin, E.K., McKinney, L.C. 1988. Patch-clamp studies in human macrophages: Single channel and whole-cell characterization of two K+ conductances. J. Membrane Biol. 103:55–66
Hagiwara, S., Miyazaki, S., Rosenthal, N.P. 1976. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomolous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J. Gen. Physiol. 67:621–638
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Hille, B. 1984. Ionic Channels in Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Ishikawa, T., Cook, D.I., Young, J.A. 1991. An inwardly rectifying K+ channel in sheep parotid cells. Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc. 22: pp138P
Josephson, I.R., Brown, A.M. 1986. Inwardly rectifying single-channel and whole-cell K+ currents in rat ventricular myocytes. J. Membrane Biol. 94:19–35
Karwoski, C.J., Lu, H.-K., Newman, E.A. 1989. Spatial buffering of light-evoked potassium increases by retinal Müller (glial) cells. Science 244:578–580
Katz, B. 1966. Nerve, Muscle and Synapse. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kettenmann, H., Hoppe, D., Gottmann, K., Banati, R., Kreutzberg, G. 1990. Cultured microglial cells have a distinct pattern of membrane channels different from peritoneal macrophages. J. Neurosci.Res. 26:278–287
Koh, D.-S., Jonas, P., Bräu, M.E., Vogel, W. 1992. A TEA-insensitive flickering potassium channel active around the resting potential in myelinated nerve. J. Membrane Biol. 130:149–162
Kuffler, S.W. 1967. Neuroglial cells: Physiological properties and a potassium mediated effect of neuronal activity on the glial membrane potential. Proc. R. Soc. London B. 168:1–21
Martin, D. K., Nakaya, Y., Wyse, K.R., Bursill, J.A., Campbell, T.J. 1993. MS-551 inhibits inwardly rectifying and ATP-sensitive potassium channels in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Proc. Aust.Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc. 25:pp53P
Mayer, M.L., Westbrook, G.L. 1983. A voltage-clamp analysis of in ward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J. Physiol. 340:19–45
Newman, E.A. 1984. Regional specialisation of retinal glial cell membrane. Nature 309:155–157
Newman, E.A. 1985. Voltage-dependent calcium and potassium channels in retinal glial cells. Nature 317:809–811
Newman, E.A. 1993. Inward-rectifying potassium channels in retinal glial (Müller) cells. J. Neurosci. 13:3333–3345
Newman, E.A., Frambach, D.A., Odette, L.L. 1984. Control of extracellular potassium levels by retinal glial cell K+ siphoning. Science 225:1174–1175
Nilius, B., Reichenbach, A. 1988. Efficient K+ buffering by mammalian retinal glial cells is due to cooperation of specialized ion channels. Pfluegers Arch. 411:654–660
Oakley, B., Katz, B.J., Xu, Z., Zheng, J. 1992. Spatial buffering of extracellular potassium by Müller (glial) cells in the toad retina. Exp. Eye Res. 55:539–550
Qian, H., Malchow, R.P., Ripps, H. 1993. The effects of lowered extracellular sodium on γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced currents of Müller (glial) cells of the skate retina. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 13:147–158
Rae, J.L., Dewey, J., Cooper, K. 1989. Properties of single potassium-selective ionic channels from the apical membrane of rabbit corneal endothelium. Exp. Eye Res. 49:591–609
Reichelt, W., Pannicke, T. 1993. Voltage-dependent K+ currents in guinea-pig Müller (glial) cells show different sensitivities to blockade by Ba2+. Neurosci. Lett. 155:15–18
Reichenbach, A. 1989. Glia: neuron index: review and hypothesis to account for different values in various mammals. Glia 2:71–77
Reichenbach, A., Henke, A., Eberhardt, W., Reichelt, W. 1992. K+ ion regulation in retina. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 70:S239-S247
Rudy, B. 1988. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience 25:729–749
Sakmann, B., Trube, G. 1984a. Conductance properties of single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in ventricular cells from guinea-pig heart. J. Physiol. 347:641–657
Sakmann, B., Trube, G. 1984b. Voltage-dependent inactivation of inward-rectifying single-channel currents in the guinea-pig heart cell membrane. J. Physiol. 347:659–683
Schwartz, E.A. 1993. l-glutamate conditionally modulates the K+ current of Müller glial cells. Neuron 10:1141–1149
Standen, N.B., Stanfield, P.R. 1979. Potassium depletion and sodium block of potassium currents under hyperpolarisation in frog sartorius muscle. J. Physiol. 294:497–520
Stanfield, P.R. 1970. The differential effects of tetraethylammonium and zinc ions on the resting conductance of frog skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 209:231–256
Stelling, J.W., Jacob, T.J.C. 1992. The inward rectifier K+ current underlies oscillatory membrane potential behaviour in bovine pigmented ciliary epithelial cells. J. Physiol. 458:439–456
Stolzenberg, J.-U., Haas, J., Härtig, W., Paulke, B.-R., Wolburg, H., Reichelt, W., Chao, T.I., Wolff, J.R., Reichenbach, A. 1992. Phagocytosis of latex beads by rabbit retinal Müller (glial) cells in vitro. J. Hirnforschung 33:557–564
Tachibana, M. 1983. Ionic currents of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J. Physiol. 345:329–351
Trachtenberg, M.C., Pollen, D.A. 1970. Neuroglia: biophysical properties and physiologic function. Science 167:1248–1252
Wen, R., Lui, G.M., Steinberg, R.H. 1993. Whole-cell K+ currents in fresh and cultured cells of the human and monkey retinal pigment epithelium. J. Physiol. 465:121–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Dain, A.C., Anderton, P.J., Martin, D.K. et al. A tetraethylammonium-insensitive inward rectifier K+ channel in müller cells of the turtle (Pseudemys scripta elegans) retina. J. Membarin Biol. 141, 239–245 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235133
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235133