Abstract.
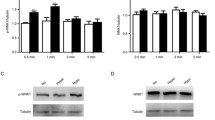
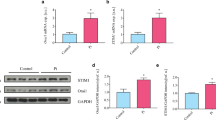
Cultured vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) from rat thoracic aortas were exposed to hyperosmotic media to determine the effects on Na, K-ATPase α1- and β1-mRNA expression. Hyperosmotic media (500 mOsm/kgH2O) supplemented with glucose or mannitol increased α1-mRNA levels threefold at 24 hr and β1-mRNA levels sevenfold at 12 hr. In sharp contrast, hyperosmotic urea medium had no effect at any time. Both the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide and the RNA transcription inhibitor actinomycin D reduced α1- and β1-mRNA upregulation induced by hyperosmotic glucose or mannitol media. Protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors (staurosporine A or calphostin C) or tyrosine kinase (TK) inhibitors (genistein or herbimycin A) had no effect on the α1-mRNA upregulation induced by hyperosmotic glucose or mannitol media. Hyperosmotic glucose or mannitol media (500 mOsm/kgH2O) significantly increased α1- and β1-subunit protein levels and Na, K-ATPase activity, whereas hyperosmotic urea medium had no effect. Transfection experiments with the 5′-flanking sequences of the α1- or β1-subunit genes linked to the luciferase reporter gene revealed that hyperosmolar glucose medium increased luciferase activity 2.9- and 3.7-fold, respectively. Similarly, hyperosmotic mannitol medium increased such activity 2.7- and 3.4-fold, respectively. These results demonstrate that: (i) hyperosmolality induced by the poorly permeating solutes (glucose and mannitol) stimulates α1- and β1-mRNA accumulation, α1- and β1-subunit protein accumulation, and Na, K-ATPase activity, whereas the rapidly permeating solute (urea) has no effect; (ii) the upregulation of α1- and β1-mRNA in response to hyperosmotic glucose or mannitol media requires, at least in part, de novo synthesis of intermediate regulatory proteins; (iii) the hyperosmolality-induced α1-mRNA upregulation occurs through PKC- and TK-independent mechanisms, whereas the hyperosmolality-induced β1-mRNA upregulation occurs through activation of PKC and TK; and (iv) hyperosmolality induced by glucose or mannitol increases promoter activities of the α1- and β1-subunit genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 July 1997/Revised: 5 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muto, S., Ohtaka, A., Nemoto, J. et al. Effects of Hyperosmolality on Na, K-ATPase Gene Expression in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Membrane Biol. 162, 233–245 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900361
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900361