Summary
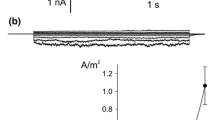
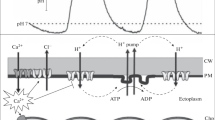
The regulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation was studied using tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis. Since the Ca2+-channel activation has a dominant role in the membrane excitation of tonoplast-free cells (T. Shiina and M. Tazawa,J. Membrane Biol. 96:263–276, 1987), it seems to be reasonable to assume that any change of the membrane excitability reflects a modulation of the Ca2+ channel. When agents that enhance phosphoprotein dephosphorylation (protein kinase, inhibitor, phosphoprotein phosphatase-1, -2A) were introduced to the intracellular surface of the plasmalemma (twice-perfused tonoplast-free cells), the membrane potential depolarized and the membrane resistance decreased under current-clamp experiments. By contrast, when cells were challenged with agents that enhance protein phosphorylation (phosphoprotein phosphatase inhibitor-1, α-naphthylphosphate), the membrane potential hyperpolarized, and the membrane resistance increased. When phosphoprotein phosphatase-1 or -2A was perfused, the current-voltage (I–V) curve which was obtained under ramp voltage-clamp condition exhibited the so-called N-shaped characteristic, indicating an acceleration of the Ca2+-channel activation. This effect was suppressed by the addition of phosphoprotein phosphatase inhibitors. ATP-γ-S, which is assumed to stimulate protein phosphorylation, decreased the inward current in theI–V curve. The dependence of the Ca2+-channel activation on intracellular ATP was different between the once-perfused and twice-perfused cells. In once-perfused cells, the membrane excitability was reduced by low intracellular ATP concentration. By contrast, in twice-perfused cells, excitability was enhanced by ATP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, D., Eckert, R. 1987. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:2518–2522
Beilby, M.J., Coster, H.G.L. 1979. The action potential inCharacorallina. II. Two activation-inactivation transients in voltage clamps of the plasmalemma.Aust. J. Plant. Physiol. 6:323–335
Clint, G.M., MacRobbie, E.A.C. 1987. Sodium efflux from perfused giant algal cells.Planta 171:247–253
Cohen, P. 1982. The role of protein phosphorylation in neutral and hormonal control of cellular activity.Nature (London) 296:613–620
Davies, J.R., Polya, G.M. 1983. Purification and properties of a high specific activity protein kinase from wheat germ.Plant. Physiol. 71:489–495
DeRiemer, D.A., Strong, J.A., Albert, K.A., Greengard, P., Kaczmarek, L.K. 1985. Enhancement of calcium current inAplysia neurons by phorbol ester and protein kinase C.Nature (London) 313:313–316
Doroshenko, P.A., Kostyuk, P.G., Martynyuk, A.E., Kursky, M.D., Vorobetz, Z.D. 1984. Intracellular protein kinase and calcium inward currents in perfused neurons of the snail helix pomatia.Neuroscience 11:263–267
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. 1964. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. IX. Analysis of transient membrane currents.Austr. J. Biol. Sci. 17:400–411
Foulkers, J.G., Cohen, P. 1980. The regulation of glycogen metabolism. Purification and properties of protein phosphatase inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle.Eur. J. Biochem. 105:195–203
Gratecos D., Fischer, E.H. 1974. Adenosine 5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) in the control of phosphorylase activity.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 58:960–967
Hammond, C., Paupardin-Tritsch, D., Nairn, A.C., Greengard, P., Gerschenfeld, M. 1987. Cholecystokinin induces, a decrease in Ca2+ current in snail neurons that appears to be mediated by protein kinase C.Nature (London) 325:809–811
Hayama, T., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1979. Participation of Ca2+ in cessation of cytoplasmic streaming induced by membrane excitation inCharaceae internodal cells.Protoplasma 99:305–321
Hemmings, B.A., Resink, T.J., Cohen, P. 1982. Reconstitution of a Mg-ATP-dependent protein phosphatase and its activation through a phosphorylation mechanism.FEBS Lett. 150:319–324
Kikuyama, M., Oda, K., Shimmen, T., Hayama, T., Tazawa, M. 1984. Potassium and chloride effluxes during excitation of Characeae cells.Plant Cell Physiol.25:965–974
Levitan, I.B. 1985. Phosphorylation of ion channels.J. Membrane Biol. 87:177–190
Li, H.C. 1984. Activation of brain calcineurin phosphatase towards nonprotein phosphoesters by Ca2+, calmodulin, and Mg2+.J. Biol. Chem. 259:8801–8807
Lühring, H., Tazawa, M. 1985. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ has no effect on the excitability ofChara plasmalemma.Plant Cell Physiol. 26:769–774
Lunevsky, V.Z., Zherelova, O.M., Vostrikov, I.Y., Berestovsky, G.N. 1983. Excitation ofCharaceae cell membranes as a result of activation of calcium and chloride channels.J. Membrane Biol. 72:43–58
Mimura, T., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1983. Dependence of the membrane potential on intracellular ATP concentration in tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis, obtusa.Planta 157:97–104
Morgan, M., Perry, S.V., Ottaway, J. 1976. Myosin light chain phosphatase.Biochem. J. 157:687–697
Nimmo, G.A., Cohen, P. 1978. The regulation of glycogen metabolism. Purification and characterization of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle.Eur. J. Biochem. 87:341–351
Okazaki, Y., Tazawa, M. 1986. Ca2+ antagonist nifedipine inhibits turgor regulation upon hypotonic treatment in internodal cells ofLamprothamnium.Protoplama 134:65–66
Okazaki, Y., Yoshimoto, Y., Hiramoto, Y., Tazawa, M. 1987. Turgor regulation and cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in the algaLamprothamnium.Protoplasma 140:67–71
Osterreider, W., Brum, G., Hescheler, J., Trautwein, W. 1982. Injection of subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase into cardiac myocytes modulates Ca2+ current.Nature (London) 298:576–578
Pondaven, P., Meijer, L. 1986. Protein phosphorylation and oocyte maturation I. Induction of starfish oocyte maturation by intracellular microinjection of a phosphatase inhibitor, α-naphthylphosphate.Exp. Cell Res. 163:477–488
Rane, S.G., Dunlop, K. 1986. Kinase C activator 1,2-oleoylacetylgycerol attenuates voltage-dependent calcium current in sensory neurons.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:184–188
Reuter, H. 1983. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs.Nature (London) 301:569–574
Shiina, T., Tazawa, M. 1986. Regulation of membrane excitation by protein phosphorylation inNitellopsis obtusa.Protoplasma 134:60–61
Shiina, T., Tazawa, M. 1987a. Demonstration and characterization of Ca2+ channel in tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis obtusa.J. Membrane Biol. 96:263–276
shiina, T., Tazawa, M. 1978b. Ca2+-activated Cl− channel in plasmalemma ofNitellopsis obtusa.J. Membrane Biol..99:137–146
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1977. Control of membrane potential and excitability ofChara cells with ATP and Mg2+ J. Membrane Biol. 37:167–192
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1982. Effects of intracellular vanadare on electrogenesis, excitability and cytoplasmic streaming inNitellopsis obtusa.Plant Cell Physiol. 23:669–677
Strong, J.A., Fox, A.P., Tsien, R.W., Kaczmarek, L.K. 1986. Phorbol ester promotes a large conductance Ca channel inAplysia bag cell neurons.Biophys. J. 49:430a
Szmigielski, A., Guidotti, A., Costa, E. 1977. Endogenous protein kinase inhibitors. Purification, characterization, and distribution in different tissues.J. Biol. Chem. 252:3848–3853
Takeshige, K., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1986. Quantitative analysis of ATP-dependent H+ efflux and pump driven by an electrogenic pump inNitellopsis obtusa.Plant Cell Physiol. 27:337–348
Tazawa, M., Kikuyama, M., Shimmen, T. 1976. Electric characteristics and cytoplasmic streaming of Characeae cells lacking tonoplast.Cell Struct. Func. 1:165–176
Tominaga, Y., Wayne, R., Tung, H.Y.L., Tazawa, M. 1987 Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation is involved in Ca2+-controlled cytoplasmic streaming of Characean cells.Protoplasma 136:161–169
Tsutsui, I., Ohkawa, T., Nagai, R., Kishimoto, U. 1987a. Role of calcium ion in the excitability and electrogenic pump activity of theChara corallina membrane: I. Effects of La3+, verapamil, EGTA, W-7, and TFP on the action potential.J. Membrane Biol. 96:65–74
Tsutsui, I., Ohkawa, T., Nagai, R., Kishimoto, U. 1987b. Role of calcium ion in the excitability and electrogenic pump activity of theChara corallina, membrane: II. Effects of La3+, EGTA, and calmodulin antagonists on the current-voltage relation.J. Membrane Biol. 96:75–84
Tung, H.Y.L., Resink, T.J., Hemmings, B.A., Shenolikar, S., Cohen, P. 1984. The catalytic subunits of protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase-2A are distinct gene products.Eur. J. Biochem. 138:635–641
Zocchi, G. 1985. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of membrane proteins controls the microsomal H+-ATPase activity of corn roots.Plant Sci. 40:153–159
Zocchi, G., Rogers, S.A., Hanson, J.B. 1983. Inhibition of protein pumping in corn roots is associated with increased phosphorylation of membrane proteins.Plant Sci. Lett. 31:215–221
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiina, T., Wayne, R., Lim Tung, H.Y. et al. Possible involvement of protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation in the modulation of Ca2+ channel in tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis . J. Membrain Biol. 102, 255–264 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01925719
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01925719