Summary
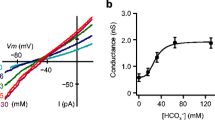
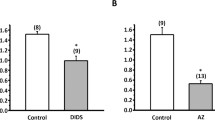
Active HCO t-3 secretion in the anterior rectal salt gland of the mosquito larva,Aedes dorsalis, is mediated by a 1∶1 Cl−/HCO −3 exchanger. The cellular mechanisms of HCO −3 and Cl− transport are examined using ion- and voltage-sensitive microelectrodes in conjunction with a microperfused preparation which allowed rapid saline changes. Addition of DIDS or acetazolamide to, or removal of CO2 and HCO −3 from, the serosal bath caused large (20 to 50 mV) hyperpolarizations of apical membrane potential (V a) and had little effect on basolateral potential (V bl). Changes in luminal Cl− concentration alteredV a in a repid, linear manner with a slope of 42.2 mV/decaloga lCl −. Intracellular Cl− activity was 23.5mm and was approximately 10mm lower than that predicted for a passive distribution across the apical membrane. Changes in serosal Cl− concentration had no effect onV bl, indicating an electrically silent basolateral Cl− exit step. Intracellular pH in anterior rectal cells was 7.67 and the calculated\(a_{HCO_3 }^c \) was 14.4mm. These results show that under control conditions HCO3 enters the anterior rectal cell by an active mechanism against an electrochemical gradient of 77.1 mV and exits the cell at the apical membrane down a favorable electrochemical gradient of 27.6 mV. A tentative cellular model is proposed in which Cl enters the apical membrane of the anterior rectal cells by passive, electrodiffusive movement through a Cl−-selective channel, and HCO −3 exits the cell by an active or passive electrogenic transport mechanism. The electrically silent nature of basolateral Cl− exit and HCO3 entry, and the effects of serosal addition of the Cl−/HCO3 exchange inhibitor, DIDS, on\(J_{net}^{CO_2 } \) and transepithelial potential (V ic) suggest strongly that the basolateral membrane is the site of a direct coupling between Cl− and HCO −3 movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammann, D., Lanter, F., Steiner, R.A., Schulthess, P., Shijo, Y., Simon, W. 1981. Neutral carrier based hydrogen ion selective microelectrode for extra-and intracellular studies.Anal. Chem. 53:2267–2269
Anstee, J.H., Bowler, K. 1979. Ouabain-sensitivity of insect epithelial tissue.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 62A:763–769
Baumgarten, C.M., Fozzard, H.A. 1981. Intracellular chloride activity in mammalian ventricular muscle.Am. J. Physiol. 241:C121-C129
Biagi, B., Kubota, T., Sohtell, M., Giebisch, G. 1981. Intracellular potentials in rabbit proximal tubules perfusedin vitro.Am. J. Physiol. 240:F200-F210
Boron, W.F. 1983. Transport of H− and of ionic weak acids and bases.J. Membrane Biol. 72:1–16
Bradley, T.J., Phillips, J.E. 1975. The secretion of hyperosmotic fluid by the rectum of a saline-water mosquito larva.Aedes taeniorhynchus.J. Exp. Biol. 63:331–342
Brown, H.M., Saunders, J.H. 1977. Cation and anion sequences in dark-adaptedBalanus photoreceptors.J. Gen. Physiol. 70:531–543
Fujimoto, M., Kubota, T. 1976. Physiochemical properties of a liquid ion exchanger microelectrode and its application to biological fluid.Jpn. J. Physiol. 26:631–650
Kielland, J. 1937. Individual activity coefficients of ions in aqueous solutions.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 59:1675–1678
Lewis, S.A. 1971. Charge properties and ion selectivity of the rectal intima of the desert locust. M.Sc. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, B.C.
Malnic, G., Costasilva, V.L., Campiglia, S.S., Mello Aires, M. de, Giebisch, G. 1980. Tubular permeability to buffer components as a determinant of net H+ ion fluxes.In: “Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. Vol. 13: Cellular Mechanisms of Renal Tubular Ion Transport. pp. 257–264. E.L. Boulpaep, editor. Academic Press, New York
McLaughlin, S.G.A., Dilger, J.P. 1980. Transport of protons across membranes by weak acids.Physiol. Rev. 60:825–863
Meredith, J., Phillips, J.E. 1973. Rectal ultrastructure in salt- and freshwater mosquito larvae in relation to physiological state.Z. Zellforsch. 138:1–22
Ogden, T.E., Citron, M.C., Pierantoni, R. 1978. The jet stream microelectrode beveler: An inexpensive way to bevel ultrafine glass micropipettes.Science 200:469–470
Phillips, J. 1981. Comparative physiology of insect renal function.Am. J. Physiol. 241:R241-R257
Phillips, J.E., Bradley, T.J., Maddrell, S.H.P. 1978. Mechanisms of ionic and osmotic regulation in saline-water mosquito larva.In: Comparative Physiology—Water, Ions and Fluid Mechanics. K. Schmidt-Nielsen, C. Bollis and S.H.P. Maddrell, editors. pp. 151–171. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Phillips, J.E., Dockrill, A.A. 1968. Molecular sieving of hydrophilic molecules by the rectal intima of the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria).J. Exp. Biol. 48:521–532
Phillips, J.E., Maddrell, S.H.P. 1974. Active transport of magnesium by the Malpighian tubules of the larvae of the mosquitoAedes campestris.J. Exp. Biol. 61:761–771
Robinson, R.A., Stokes, R.H. 1965. Electrolyte Solutions. 3rd ed. Buttersworth, London
Schulz, I. 1981. Electrolyte and fluid secretion in the exocrine pancreas.In: Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. L.R. Johnson, editor. Vol. 2, pp. 795–819. Raven, New York
Scudder, G.G.E. 1969. The fauna of saline lakes on the Fraser Plateau in British Columbia.Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 17:430–439
Spring, K.R., Kumura, G. 1978. Chloride reabsorption by renal proximal tubules ofNecturus.J. Membrane Biol. 38:233–254
Steels, P.S., Boulpaep, E.L. 1976. Effect of pH on ionic conductances of the proximal tubule epithelium ofNecturus and the role of buffer permeability.Fed. Proc. 35:465
Strange, K. 1983. Cellular mechanism of bicarbonate regulation and excretion in an insect inhabiting extreme alkalinity. Ph. D. Thesis, University of British Columbia. Vancouver, B.C.
Strange, K., Phillips, J.E. 1984. Mechanisms of total CO2 transport in the microperfused rectal salt gland ofAedes dorsalis. I. Ionic requirements of total CO2 secretion.Am. J. Physiol. 246:R727-R734
Strange, K., Phillips, J.E., Quamme, G.A. 1982. Active HCO −3 secretion in the rectal salt gland of a mosquito larva inhabiting NaHCO3−CO3 lakes.J. Exp. Biol. 101:171–186
Strange, K., Phillips, J.E., Quamme, G.A. 1984. Mechanisms of total CO2 transport in the microperfused rectal salt gland ofAedes dorsalis. II. Site of Cl−/HCO −3 exchange and function of anterior and posterior salt gland segments.Am. J. Physiol. 246:R735-R740
Ullrich, K.J., Radtke, H.W., Rumrich, G. 1971. The role of bicarbonate and other buffers on isotonic fluid absorption in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 330:149–161
Ullrich, K.J., Rumrich, G., Baumann, K. 1975. Renal proximal tubular buffer-(glycodiazine) transport. Inhomogenicity of local transport rate, dependence on sodium, effect of inhibitors and chronic adaptation.Pfluegers Arch. 357:149–163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strange, K., Phillips, J.E. Cellular mechanism of HCO −3 and Cl− transport in insect salt gland. J. Membrain Biol. 83, 25–37 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868735
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868735