Summary
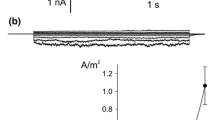
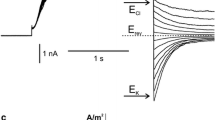
The presence of a Ca2+ channel in the plasmalemma of tonoplast-freeNitellopsis obtusa cells was demonstrated and its characteristics were studied using current- and voltage-clamp techniques. A long-lasting inward membrane current (I m ), recorded using a step voltage clamp, consisted of a single component without time-dependent inactivation. Increasing either [Ca2+] o or [Cl−] o 1) enhanced the maximum amplitude of inwardI m ((I m ) p ) and 2) shifted the peak voltage ((V m ) p ) at(I m ) p to more positive values under ramp-shaped voltage clamping and 3) depolarized the peak value of action potentials. This behavior is consistent with predictions based on the Nernst equation for Ca2+ but not for Cl−. DIDS (4,4′-diisothiocyano-2,2′-disulfonic acid stilbene) did not suppress(I m ) p in tonoplast-free cells, in contrast with its effect on normal cells. La3+ and nifedipine blocked(I m ) p irreversibly. On the other hand, Ca2+ channel agonist, BAY K 8644 irreversibly enhanced(I m ) p . Both Sr2+ influx and K+ efflux increased upon excitation. The charge carried by Sr2+ influx was compensated for by K+ efflux. It is concluded that only the Ca2+ channel is activated during plasmalemma excitation in tonoplast-free cells. In terms of the magnitude of(I m ) p , Sr2+ could replace Ca2+, but Mn2+, Mg2+ and Ba2+ could not. External pH affected(I m ) p and the membrane conductance (g m ) at(I m ) p ((g m ) p ). Increasing the external ionic strength caused increases in both(I m ) p and(g m ) p , and shifted(V m ) p to positive values. At the same time, Sr2+ influx increased. Thus Ca2+ channel activation seems to be enhanced by increasing external ionic strength. The possible involvement of surface potential is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asai, K., Kishimoto, U. 1975. Effects of sodium, potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential ofValonia aegagropila.Plant Cell Physiol. 16:93–100
Beilby, M.J. 1984a. Current-voltage characteristics of the proton pump atChara plasmalemma. I. pH dependence.J. Membrane Biol. 81:113–125
Beilby, M.J. 1984b. Calcium and plant action potentials.Plant Cell Environment 7:415–421
Beilby, M.J., Coster, H.G.L. 1979. The action potential inChara corallina. II. Two activation-inactivation transients in voltage clamps of the plasmalemma.Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 6:323–335
Caldwell, J.H., Brunt, J. van, Harold, F.M. 1986. Calcium-dependent anion channel in the water moldBlastocladiella emersonii.J. Membrane Biol. 89:85–97
Findlay, G.P. 1961. Voltage-clamp experiments withNitella.Nature (London) 191:812–814
Findlay, G.P. 1962. Calcium ions and the action potential inNitella.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 15:69–82
Findlay, G.P. 1964. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. VIII. Membrane currents during a voltage clamp.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 17:388–399
Findlay, G.P. 1970. Membrane electrical behaviour inNitellopsis obtusa.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 23:1033–1045
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. 1964a. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. VII. The separate electrical characteristics of the plasmalemma and tonoplast.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 17:62–77
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. 1964b. Ionic relations ofChara australis. IX. Analysis of transient membrane currents.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 17:400–411
Fujii, S., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1979. Effect of intracellular pH on the light-induced potential change and electrogenic activity in tonoplast-free cells ofChara australis.Plant Cell Physiol. 20:1315–1328
Gaffey, C.T., Mullins, L.J. 1958. Ion fluxes during the action potential inChara.J. Physiol. (London) 144:505–527
Hagiwara, S., Byerly, L. 1981. Calcium channel.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 4:69–125
Hayama, T., Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1979. Participation of Ca2+ in cessation of cytoplasmic streaming induced by membrane excitation inCharaceae internodal cells.Protoplasma 99:305–321
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F. 1952. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon ofLoligo.J. Physiol. (London) 116:449–472
Hodick, D., Sievers, A. 1986. The influence of Ca2+ on the action potential in mesophyll cells ofDionaea muscipulla Ellis.Protoplasma 133:83–84
Hope, A. B. 1961a. The action potential in cells ofChara.Nature (London) 191:811–812
Hope, A.B. 1961b. Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 14:312–321
Hope, A.B., Findlay, G.P. 1964. The action potential inChara.Plant Cell Physiol. 5:377–379
Hope, A.B., Walker, N.A. 1975. The Physiology of Giant Cells. Cambridge University Press, London
Iijima, T., Ciani, S., Hagiwara, S. 1986. Effects of the external pH on Ca channels: Experimental studies and theoretical considerations using a two-ion model.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:654–658
Iijima, T., Sibaoka, T. 1983. Membrane potentials in excitable cells ofAldrovanda vesiculosa trap-lobes.Plant Cell Physiol. 26:1–13
Katsuhara, M., Tazawa, M. 1986. Salt tolerance inNitellopsis obtusa.Protoplasma 135:155–161
Keifer, D.W., Spanswick, R.M. 1978. Activity of the electrogenic pump inChara corallina as infered from measurements of the membrane potential, conductance, and potassium permeability.Plant Physiol. 62:653–661
Kikuyama, M., Oda, K., Shimmen, T., Hayama, T., Tazawa, M. 1984. Potassium and chloride effluxes during excitation of Characeae cells.Plant Cell Physiol. 25:965–974
Kikuyama, M., Tazawa, M. 1983. Transient increase of intracellular Ca2+ during excitation of tonoplast-freeChara cells.Protoplasma 117:62–67
Kishimoto, U. 1964. Current voltage relations inNitella.J. Physiol. (London) 14:515–527
Kishimoto, U., Takeuchi, Y., Ohkawa, T., Kami-ike, N. 1985. A kinetic analysis of the electrogenic pump ofChara corallina: III. Pump activity during action potential.J. Membrane Biol. 86:27–36
Lunevsky, V.Z., Zherelova, O.M., Vostrikov, I.Y., Berestovsky, G.N. 1983. Excitation ofCharaceae cell membranes as a result of activation of calcium and chloride channels.J. Membrane Biol. 72:43–58
Mimura, T., Kirino, Y. 1984. Changes in cytoplasmic pH measured by31P-NMR in cells ofNitellopsis obtusa.Plant Cell Physiol. 25:813–820
Mimura, T., Tazawa, M. 1983. Effects of intracellular Ca2+ on membrane potential and membrane resistance in tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis obtusa.Protoplasma 118:49–55
Oda, K. 1976. Simultaneous recording of potassium and chloride effluxes during an action potential inChara corallina.Plant Cell Physiol. 17:1085–1088
Ohkawa, T., Kishimoto, U. 1977. Breakdown phenomena in theChara membrane.Plant Cell Physiol. 18:67–80
Okazaki, Y., Tazawa, M., 1986a. Involvement of calcium ion in turgor regulation upon hypotonic treatment inLamprothamnium succinctum.Plant Cell Environment 9:185–190
Okazaki, Y., Tazawa, M. 1986b. Effect of calcium ion on cytoplasmic streaming during turgor regulation in a brackish water charophytaLamprothamnium succintum.Plant Cell Environment 9:491–494
Pickard, B.G. 1973. Action potentials in higher plants.Bot. Rev. 39:172–201
Shiina, T., Tazawa, M. 1986. Regulation of membrane excitation by protein phosphorylation inNitellopsis obtusa.Protoplasma 134:60–61
Shimmen, T., Kikuyama, M., Tazawa, M. 1976. Demonstration of two stable potential states of plasmalemma ofChara without tonoplast.J. Membrane Biol. 30:249–270
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1980. Intracellular chloride and potassium ions in relation to excitability ofChara membrane.J. Membrane Biol. 55:223–232
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1982. Effects of intracellular vanadate on electrogenesis, excitability and cytoplasmic streaming inNitellopsis obtusa.Plant Cell Physiol. 23:669–677
Shimmen, T., Tazawa, M. 1983. Activation of K+-channel in membrane excitation ofNitella axilliformis.Plant Cell Physiol. 24:1511–1524
Sibaoka, T. 1969. Physiology of rapid movements in higher plants.Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 20:165–184
Tasaki, I. 1968. Nerve Excitation. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Illinois
Tazawa, M. 1972. Membrane characteristics as revealed by water and ionic relations of algal cells.Protoplasma 75:427–460
Tazawa, M., Kikuyama, M., Shimmen, T. 1976. Electric characteristics and cytoplasmic streaming of Characeae cells lacking tonoplast.Cell Struct. Function 1:165–176
Tsutsui, I., Ohkawa, T., Nagai, R., Kishimoto, U. 1986. Inhibition of Cl− channel activation inChara corallina membrane by lanthanium ion.Plant Cell Physiol. 27:1197–1200
Tyerman, S.D., Findlay, G.P., Paterson, G.J. 1986. Inward membrane current inChara inflata: II. Effects of pH, Cl−-channel blockers and NH 4+ , and significance for the hyperpolarized state.J. Membrane Biol. 89:153–161
Williamson, R.E. 1975. Cytoplasmic streaming inChara: A Cell model activated by ATP and inhibited by cytochalasin B.J. Cell Sci. 17:655–668
Williamson, R.E., Ashley, C.C. 1982. Free Ca2+ and cytoplasmic streaming in the algaChara.Nature (London) 296:647–650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiina, T., Tazawa, M. Demonstration and characterization of Ca2+ channel in tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis obtusa . J. Membrain Biol. 96, 263–276 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869308
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869308