Abstract
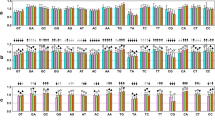
We have studied the behavior of the dinucleotide preferences under G + C content variation in human genes. The doublet preferences for each dinucleotide were compared between two functionally distinct zones in genes, the II-III codon positions, and the introns. The 16 dinucleotides have been tentatively classified in three groups:
-
AA, AC, CC, CT, and GA, doublets showing no difference between introns and II-III codon positions in the full range of G + C variation
-
TG and TA, which differ in the full range of G + C variation
-
AT, AG, GT, TC, TT, GG, GC, CG, and CA, which show differences in regions over 50% G + C
A remarkable pattern observed concerns the behavior of GG, GC, and TC, which showed opposite trends in II-III codon positions and in introns. If codon positions and introns are under the same structural requirements and the same mutational bias, our results indicate that the differences observed could be related to post-transcriptional constraints acting on mRNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aota SI, Ikemura T (1986) Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6345–6355
Bernardi G, Olofsson B, Filipski J, Zerial M, Salinas J, Cuny G, Meunier-Rotival M, Rodier F (1985) The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science 228:953–958
Bernardi G (1989) The isochore organization of the human genome. Annu Rev Genet 23:637–661
Bulmer M (1986) Neighboring base effects on substitution rates in pseudogenes. Mol Biol Evol 3:322–329
Dixon WJ, Brown MB (1979) BMDP-79 biomedical computer programmes P series. University of California Press, Berkeley
Hanai R, Wada A (1988) The effects of guanine and cytosine variation in dinucleotide frequency and amino acid composition in the human genome. J Mol Evol 27:321–325
Hanai R, Wada A (1990) Doublet preference and gene evolution. J Mol Evol 30:109–115
Marín A, Bertraneptit J, Oliver JL, Medina JR (1989) Variation in G + C-content and codon choice: differences among synonymous codon groups in vertebrate genes. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6181–6189
Nussinov R (1980) Some rules in the ordering of nucleotides in the DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 19:4545–4562
Nussinov R (1981a) Eukaryotic dinucleotide preference rules and their implications for degenerate codon usage. J Mol Biol 149:125–131
Nussinov R (1981b) The universal dinucleotide asymmetry rules in DNA and the aminoacid codon choice. J Mol Evol 17:237–244
Nussinov R (1984a) Strong doublet preferences in nucleotide sequence and DNA geometry. J Mol Evol 20:111–119
Nussinov R (1984b) Doublet frequencies in evolutionary distinct groups. Nucleic Acids Res 12:1749–1763
Ohno S (1988) Universal rule for coding sequence construction: TA/CG deficiency-TG/CT excess. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:9630–9634
Stoehr PJ, Cameron GN (1991) The EMBL data library. Nucleic Acids Res 19 Supl:2227–2230
Wada K-N, Watanabe I, Tsuchiya R, Ikemura T (1991) G + C% mosaic structures of the higher vertebrate genome and distribution of dinucleotide frequencies. In: Kimura M, Nakahata T (eds) New aspects of the genetics of molecular evolution. Japan Sci Soc Press, Tokyo/Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 195–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez, G., Oliver, J.L. & Marín, A. Dinucleotides and G + C content in human genes: Opposite behavior of GpG, GpC, and TpC at II-III codon positions and in introns. J Mol Evol 37, 131–136 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407348
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407348