Abstract
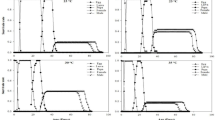
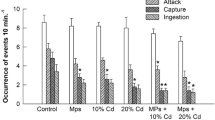
American kestrels (Falco sparverius) were given a single acute dose of the insecticide acephate (50 mg/kg), either alone or superimposed on a moderate background level of DDE (35 ppm wet-weight in carcass homogenates). The combined DDE-acephate treatment was chosen to resemble exposure conditions for wild avian predators whose tissues may contain appreciable sublethal accumulations of organochlorine insecticides. Acephate produced similar cholinesterase (ChE) depression in both groups (39% median depression of serum ChE, 25% median brain ChE depression). Predatory vigilance and attack behavior, measured by frequency and speed of responses to a familiar moving prey model, were not altered by acephate administration in either group. Neither DDE nor acephate at these low dosages has appreciable effects on kestrels' responses to a prey stimulus with which they have had extensive prior contact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard RF (1962) Secondary DDT poisoning in a sparrow hawk. Auk 79:276–277
Bildstein KL, Forsyth DJ (1979) Effects of dietary dieldrin on behavior of white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) towards an avian predator. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 21:93–97
Crowder LA, Lanzaro GC, Whitson RS (1980) Behavioral effects of methyl parathion and toxaphene exposure in rats. J Environ Sci Hlth B15:365–378
Dieter MP, Ludke JL (1975) Studies on combined effects of organophosphates and heavy metals in birds. 1. Plasma and brain cholinesterase in coturnix quail fed methyl mercury and orally dosed with parathion. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 13:257–262
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Fleming WJ (1981) Recovery of brain and plasma cholinesterase activities in ducklings exposed to organophosphorus pesticides. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 10:215–229
Grue CE, Shipley BK (1981) Interpreting population estimates of birds following pesticide applications-behavior of male starlings exposed to an organophosphate pesticide. Studies Avian Biol 6:292–296
Henny CJ (1977) Birds of prey, DDT, and tussock moths in the Pacific Northwest. Trans North Amer Wildlife and Natural Resource Conf 42:397–411
Hill EF, Fleming WJ (1982) Anticholinesterase poisoning of birds: field monitoring and diagnosis of acute poisoning. Environ Toxicol Chem 1:27–38
Hill EF, Mendenhall VM (1980) Secondary poisoning of barn owls with famphur, an organophosphate insecticide. J Wildl Manage 44:676–681
Hollander M, Wolfe DA (1973) Nonparametric statistical methods. Wiley and Sons, New York
Johnston DW (1978) Organochlorine pesticide residues in Florida birds of prey. Pestic Monit J 12:8–15
Kreitzer JF (1980) Effects of toxaphene and endrin at very low dietary concentrations on discrimination acquisition and reversal in bobwhite quail,Colinus virginianus. Environ Pollut (Ser A) 23:217–230
Kreitzer JF, Heinz GH (1974) The effect of sublethal dosages of five pesticides and a polychlorinated biphenyl on the avoidance response of coturnix quail chicks. Environ Pollut 6:21–29
Ludke JL (1977) DDE increases toxicity of parathion to coturnix quail. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 7:28–33
Ludke JL, Hill EF, Dieter MP (1975) Cholinesterase (ChE) response and related mortality among birds fed ChE inhibitors. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 3:1–21
Porter RD, Wiemeyer SN (1972) DDE at low dietary levels kills captive American kestrels. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 8:193–199
Reischl P, VanGelder GA, Karas GG (1975) Auditory detection behavior in parathion-treated squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 34:88–101
Reiter L, Talens G, Woolley D (1973) Acute and subacute parathion treatment: effects on cholinesterase activities and learning in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 25:582–588
Risebrough RW, de Lappe BW, Letterman EF, Lane JL, Firestone-Gillis M, Springer AM, Walker W III (1980) California mussel watch: 1977–78, V 3, Organic pollutants in mussels,Mytilus califomicus andM. edulis, along the California coast. Calif State Water Resources Control Board, Sacramento, Water Qual Monit Rep 79, 22:App 1
Rudolph SG, Anderson DW, Risebrough RW (1983) Kestrel predatory behavior under chronic low-level exposure to DDE. Environ Pollut (Ser A) 32:121–136
Sandier BE, Van Gelder GA, Elsberry DD, Karas GG, Buck WB (1969) Dieldrin exposure and vigilance behavior in sheep. Psychon Sci 15:261–262
Sharma RP, Winn DS, Low JB (1976) Toxic, neurochemical, and behavioral effects of dieldrin exposure in mallard ducks. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 5:43–53
Sparrowe RDeM (1972) Prey-catching behavior in the sparrow hawk. J Wildl Manage 36:297–308
VanGelder GA, Sandier BE, Buck B, Malana JB, Karas GG (1969) Behavioral and electrophysiological effects of dieldrin in sheep. Ind Med 38:111–114
Wiemeyer SN, Porter RD (1970) DDE thins eggshells of captive American kestrels. Nature (Lond) 227:737–738
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudolph, S.G., Zinkl, J.G., Anderson, D.W. et al. Prey-capturing ability of American kestrels fed DDE and acephate or acephate alone. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 13, 367–372 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055288
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055288