Abstract
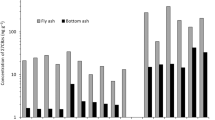
Ashes, obtained from about one-fourth of the operating municipal refuse incinerators in the United States, were analyzed for a range of organic toxicants and mutagens. Thirty percent of the ash samples, which consisted of bottom ash or bottom ash-fly ash mixtures, contained 20–74% organic matter. Thirty percent of the ashes contained direct-acting and/or promutagens which revertedSalmonella typhimurium TA98 or TA100. Sixty percent of the ashes contained more than 5 ng/g of polychlorinated biphenyls. The concentration of tetra- and pentachlorinated biphenyls were higher than the mono-, di-, hepta- and octachlorinated biphenyls. A similar distribution of congeners was seen in polychlorinated dibenzodioxins found in the ashes. The major volatileN-nitroso compounds found in the ashes wereN-nitrosodimethylamine andN-nitrosomorpholine. Other classes of compounds which were found in the ashes included chlorinated benzenes, phthalates, and substituted benzothiophenes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boniforti L, Citti G, Laguzzi G (1981) Identification and quantitative determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in fly ash from municipal incinerators by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Recent Devel Mass Spect Biochem Med Environ Res 7:219–225
Cavallaro A, Bandi G, Invernizzi G, Luciani L, Mongini E, Gorni A (1980) Sampling, occurrence, and evaluation of PCDDs and PCDFs from incinerating solid urban waste. Chemosphere 9:611–621
Clement RE, Viau AC, Karasek FW (1984) Daily variations in composition of extractable organic compounds in fly ash from municipal waste incineration. Int J Environ Anal Chem 17:257–266
Davies IW, Harrison RM, Perry R, Ratnayaka D, Wellings RA (1976) Municipal incinerator as source of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in environment. Environ Sci Technol 10:451–453
Eiceman GA, Clement RE, Karasek FW (1981) Variations in concentrations of organic compounds including polychlorinated di-benzo-p-dioxins and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in fly ash from a municipal incinerator. Anal Chem 53:955–959
Hotchkiss JH, Vecchio AJ (1985) Nitrosamines in fried-out bacon fat and its use as a cooking oil. Food Technol 39:67–73
Hutzinger O, Blumich MJ, Berg Mvd, Olie K (1985) Sources and fate of PCDDs and PCDFs: An overview. Chemosphere 14:581–600
Kamiya A, Ose Y (1987a) Mutagenic activity and PAH analysis in municipal incinerators. Sci Total Environ 61:37–49
— (1987b) Study of the behavior of mutagens in wastewater and emission gas from a municipal incinerator evaluated by means of the Ames assay. Sci Total Environ 65:109–120
Maron DM, Ames BN (1983) Revised methods for theSalmonella mutagenicity test. Mutation Res 113:173–215
Mattson PE, Nygren S (1976) Gas Chromatographic determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and some chlorinated pesticides in sewage sludge using a glass capillary column. J Chromatogr 124:265–275
Murphy TJ, Formanski LJ, Brownawell B, Meyer JA (1985) Poly-chlorinated biphenyl emissions to the atmosphere in the Great Lakes region. Municipal landfills and incinerators. Environ Sci Technol 19:942–946
Oehme M, Manø S, Mikalsen A (1987) Formation and presence of polyhalogenated and polycyclic compounds in the emissions of small and large scale municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere 16:143–153
Owens JL, Kinast OE (1980) An improved procedure for the determination of volatileN-nitrosamines in bacon grease by using the mineral oil distillation-thermal energy analyzer method. J Agric Food Chem 28:1262–1264
Pani B, Laureni U, Babudri N, Collareta A, Venturini S, Ferri R, Carozzi M, Burlini F, Monti-Bragadin C (1983) Mutagenicity test of extracts of airborne dust from the municipal incinerator of Trieste. Environ Mutagen 5:23–32
Sawyer T, Bandiera S, Safe S (1983) Bioanalysis of polychlorinated dibenzofuran and dibenzo-p-dioxin mixtures in fly ash. Chemosphere 12:529–535
Sovocool GW, Mitchum RK, Tondeur Y, Munslow WD, Vonnahme TL, Donnelly JR (1988) Bromo- and bromochloro-polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins and dibenzofurans in municipal incinerator fly ash. Biomed Environ Mass Spect 15:669–676
Steisel N, Morris R, Clarke MJ (1987) The impact of the dioxin issue on resource recovery in the United States. Waste Manag Res 5:381–394
Tong HY, Karasek FW (1986) Comparison of PCDD and PCDF in fly ash collected from municipal incinerators of different countries. Chemosphere 15:1219–1224
US Food & Drug Administration (1971) Dept. of Health, Education and Welfare. Pesticide Analytical Manual, Vol. 1, revised Sec. 211.14a & 211.14d, Washington, DC
Victorin K, Ståhlberg M, Ahlborg UG (1988) Emission of mutagenic substances from waste incineration plants. Waste Manag Res 6:149–161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shane, B.S., Henry, C.B., Hotchkiss, J.H. et al. Organic toxicants and mutagens in ashes from eighteen municipal refuse incinerators. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19, 665–673 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183982
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183982